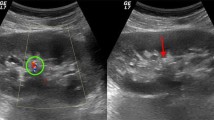
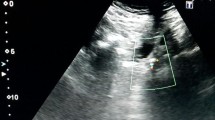
Abstract
Purpose
Our aim was to analyze the value of ultrasound using the twinkling sign in the diagnosis of ureteral stones in patients with renal colic in the emergency setting.
Materials and methods
Prospective study of 100 patients with suspected renal colic who underwent an US examination, including color Doppler mode. We analyzed sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, and accuracy. We evaluated whether the stone was observed before or after the twinkling artifact, and whether the use of the Doppler color increased the examination time.
Results
US including color Doppler detected 76 of the 84 confirmed lithiasis. The sensitivity and specificity were 90 % and 100 %, respectively. The positive predictive value was 100 % and the negative 67 %. The accuracy was 92 %. A total of 59 calculi (78 %) examined by color Doppler sonography showed the twinkling artifact. Seventy percent of the twinkling-positive calculi showed the artifact before the stone itself was detected. Considering the location of the stones the twinkling sign was seen before the stone in 92 % of lithiasis located in the mid lumbar ureter (p = 0.02). The use of the twinkling artifact showed a trend to facilitate the detection of smaller calculi (<10 mm) (p = 0.08). The average examination time was 5.8 min [±4.3] (without differences between the stones detected before or after the twinkling artifact, p = 0.75).
Conclusion
Doppler US examination shows good sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of symptomatic ureteral stones. The twinkling artifact is useful for the early detection of the calculi, especially in the middle tract of the ureter, usually the most difficult place in sonographic diagnosis. It also seems helpful for the detection of smaller stones. The use of color Doppler does not increase the exploration time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith RC, Verga M, McCarthy S, Rosenfield AT (1996) Diagnosis of acute flank pain: value of unenhanced helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 166(1):97–101
Boulay I, Foley WD, White B, Begun FP (1999) Ureteral calculi: diagnostic efficacy of helical CT and implications for treatment of patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:1485–1490
Dalrymple NC, Verga M, Anderson KR, et al. (1998) The value of unenhanced helical computerized tomography in the management of acute flank pain. J Urol 159(3):735–740
Levine JA, Neitlich J, Verga M, Dalrymple N, Smith RC (1997) Ureteral calculi in patients with flank pain: correlation of plain radiography with unenhanced helical CT. Radiology 204:27–31
Catalano O, Nunziata A, Altei F, Siani A (2002) Suspected ureteral colic: primary helical CT versus selective helical CT after unenhanced radiography and sonography. Am J Roentgenol 178:378–387
Ripollés T, Errando J, Agramunt M, Martínez MJ (2004) Ureteral colic: US versus CT. Abdom Imaging 29(2):263–266
Rauhmouni A, Bargoin R, Herment A, Bargoin N, Vasile N (1996) Color Doppler twinkling artifact in hyperechoic region. Radiology 199:269–271
Aytac SK, Ozcan H (1999) Effect of color Doppler system on the twinkling sign associated with urinary tract calculi. J Clin Ultrasound 27(8):433–439
Turrin A, Minola P, Costa F, et al. (2007) Diagnostic value of colour Doppler twinkling artefact in sites negative for stones on B mode renal sonography. Urol Res 35(6):313–317
Mitterberger M, Aigner F, Pallwein L, et al. (2009) Sonographic detection of renal and ureteral stones value of the twinkling sign. Int Braz J Urol 35(5):532–539
Pepe P, Motta L, Pennisi M, Aragona F (2005) Functional evaluation of the urinary tract by color-Doppler ultrasonography (CDU) in 100 patients with renal colic. Eur J Radiol 53:131–135
Ripollés T, Agramunt M, Errando J, et al. (2004) Suspected ureteral colic: plain film and sonography vs unenhanced helical CT. A prospective study in 66 patients. Eur Radiol 14:129–136
Lee JY, Kim SH, Cho JY, Han D (2001) Color and power Doppler twinkling artifacts from urinary stones: clinical observations and phantom studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:1441–1445
Park SJ, Yi BH, Lee HK, et al. (2008) Evaluation of patients with suspected ureteral calculi using sonography as an initial diagnostic tool: how can we improve diagnostic accuracy? J Ultrasound Med 27(10):1441–1450
Mulkens TH, Daineffe S, Wijngaert RD, et al. (2007) Urinary stone disease: comparison of standard-dose and low-dose with 4D MDCT tube current modulation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:553–562
Niemann T, van Straten M, Resinger C, Bayer T, Bongartz G (2011) Detection of urolithiasis using low-dose CT. A noise simulation study. Eur J Radiol 80(2):213–218
Kamaya A, Tuthill T, Rubin JM (2003) Twinkling artifact on color Doppler sonography: dependence of machine parameters and underlying cause. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:215–222
Moesbergen TC, de Ryke RJ, Dunbar S, Wells JE, Anderson NG (2011) Distal ureteral calculi: US follow-up. Radiology 260(2):575–580
Sheafor DH, Hertzberg BS, Freed KS, et al. (2000) Nonenhanced helical CT and US in emergency evaluation of patients with renal colic: prospective comparison. Radiology 217:792–797
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ripollés, T., Martínez-Pérez, M.J., Vizuete, J. et al. Sonographic diagnosis of symptomatic ureteral calculi: usefulness of the twinkling artifact. Abdom Imaging 38, 863–869 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-012-9946-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-012-9946-7