Abstract
Background
Our study was aimed to evaluate the functional status of pancreatic transplants using dynamic MR pancreatography after secretin stimulation.
Methods
Thirteen asymptomatic patients previously submitted to isolated pancreas (n = 6) or combined kidney–pancreas (n = 7) transplantation, with enteric-portal pancreatic drainage, underwent MR examination at 1.5 T using a phased-array coil. After the acquisition of axial and coronal T1- and T2-weighted sequences, dynamic MR pancreatography was performed using a coronal breath-hold, thick-slab (40–60 mm), single-shot T2-weighted fast spin-echo sequence. After the intravenous administration of secretin (Secrelux®, Sanochemia; 1 cU/kg body/weight), a single-slice image acquisition was repeated every 30 s up to 15 min. We estimated the calibre changes of the pancreatic ductal system and the filling of the donor’s duodenum on the basis of pancreatic secretion after secretin stimulation, also evaluated by using a mean signal intensity/time histogram in a chosen region of interest including the transplanted pancreas and the connected small bowel.
Results
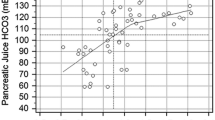
All patients well tolerated the examination, and no side effects were reported after secretin administration. In 12/13 cases, a significant increase (more than 1 mm) in the diameter of the mean pancreatic duct was observed after secretin stimulation; in all patients, a noticeable filling of the duodenal graft was demonstrated during dynamic MR pancreatography on both qualitative and quantitative analyses.
Conclusions
Dynamic MR imaging after secretin administration allows non-invasive evaluation of exocrine function of the pancreatic transplants and could be used to differentiate patients with graft rejection from those with normal graft function.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stratta RJ, Taylor RJ, Bynon JS, et al. (1994) Patterns of rejection after combined pancreas-kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc 26:524–525
Cappelliez O, Delhaye M, Deviere J, et al. (2000) Chronic pancreatitis: evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function with MR pancreatography after secretin stimulation. Radiology 215:358–364
Monill J, Pernas J, Clavero J, et al. (2004) Pancreatic duct after pancreatoduodenectomy: morphologic and functional evaluation with secretin-stimulated MR pancreatography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:1267–1274
Heverhagen JT, Wagner HJ, Ebel H, et al. (2004) Pancreatic transplants: noninvasive evaluation with secretin-augmented MR pancreatography and MR perfusion measurements: preliminary results. Radiology 233:273–280
Neri E, Cappelli C, Boggi U, et al. (2004) Multirow CT in the follow-up of pancreas transplantation. Transplant Proc 36:597–600
Robertson RP, Davis C, Larsen J, et al. (2003) Pancreas transplantation for patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabete Care 26(suppl 1):S120
Boggi U, Vistoli F, Del Chiaro M, et al. (2004) Retroperitoneal pancreastransplantation with portal-enteric drainage. Transplant Proc 36:571–574
Boggi U, Vistoli F, Signori S, et al. (2005) A technique for retroperitoneal pancreas transplantation with portal-enteric drainage. Transplantation 79:1137–1142
Sollinger HW, Messing EM, Eckhoff DE, et al. (1993) Urological complications in 210 consecutive simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants with bladder drainage. Ann Surg 218:561–570
Matte J, Fery F, Lankoande C, et al. (1995) Insulin secretion and glucose tolerance evolution in kidney–pancreas graft. Transplant Proc 27:3073–3074
Boggi U, Mosca F, Vistoli F, et al. (2005) Ninety-five percent insulin independence rate 3 years after pancreas transplantation alone with portal-enteric drainage. Transplant Proc 37:1274–1277
Kuo PC, Johnson LB, Schweitzer EJ, et al. (1997) Simultaneous pancreas/kidney transplantation: a comparison of enteric and bladder drainage of exocrine pancreatic secretions. Transplantation 63:238–243
Philosophe B, Farney AC, Schweitzer EJ, et al. (2001) Superiority of portal venous drainage over systemic venous drainage in pancreas transplantation: a retrospective study. Ann Surg 234:689–696
Papadimitriou JC, Drachenberg CB, Wiland A, et al. (1998) Histologic grading of acute allograft rejection in pancreas needle biopsy: correlation to serum enzymes, glycemia, and response to immunosuppressive treatment. Transplantation 66:1741–1745
Sugitani A, Egidi MF, Gritsch HA, et al. (1998) Serum lipase as a marker for pancreatic allograft rejection. Clin Transplant 12:224–227
Gruessner RW, Kendall DM, Drangstveit MB, et al. (1997) Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation from live donors. Ann Surg 226: 471–480
Nikolaidis P, Amin RS, Hwang CM, et al. (2003) Role of sonography in pancreatic transplantation. RadioGraphics 23:939–949
Wong JJ, Krebs TL, Klassen DK, et al. (1996) Sonographic evaluation of acute pancreatic transplant rejection: morphology-Doppler analysis versus guided percutaneous biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 166:803–807
Atwell TD, German B, Larson TS, et al. (2004) Pancreas transplants: experience wih 232 percutaneous US-guided biopsy procedures in 88 patients. Radiology 231:845–849
Lee BC, McGahan JP, Perez RV, et al. (2000) The role of percutaneous biopsy in detection of pancreatic transplant rejection. Clin Transplant 14:493–498
Kelcz F, Sollinger HW, Pirsch JD (1991) MRI of the pancreas transplant: lack of correlation between imaging and clinical status. Magn Reson Med 21:30–38
Vahey TN, Glazer GM, Francis IR, et al. (1988) MR diagnosis of pancreatic transplant rejection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 150:557–560
Fernandez MP, Bernardino ME, Neylan JF, et al. (1991) Diagnosis of pancreatic transplant dysfunction: value of gadopentetate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 156:1171–1176
Krebs TL, Daly B, Wong-You-Cheong JJ, et al. (1999) Acute pancreatic transplant rejection: evaluation with dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging compared with histopathologic analysis. Radiology 210:437–442
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Angelo Ferrara and Claudio Moriani for their important contribution in performing the procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boraschi, P., Donati, F., Gigoni, R. et al. Pancreatic transplants: secretin-stimulated MR pancreatography. Abdom Imaging 32, 207–214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-007-9178-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-007-9178-4