Abstract
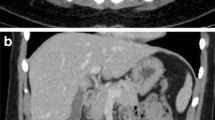
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the presence of the hyperdense appendix in acute appendicitis. The CT scans of 183 patients with pathologically proven acute appendicitis were reviewed to determine the prevalence of a hyperdense appendix, defined as a high-attenuated appendix when compared with the adjacent cecal wall on precontrast CT. A control group consisted of 100 patients with CT examinations performed in the emergency department were also randomly allocated to search for any hyperdense appendix in other disease conditions. The images were reviewed by two radiologists who reached a decision by consensus. A hyperdense appendix sign was found in 61 of 183 (33%) patients, including 92 men and 91 women ranging in age from 17 to 85 years (mean 37 years). On the other hand, the sign was seen in only two (2%) of the 88 patients in whom appendicitis was not diagnosed. The hyperdense appendix sign on unenhanced CT is seen in about 33% of patients with acute appendicitis. The false-positive rate is very low, rendering it a very useful sign for diagnosis of acute appendicitis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro MP, Gale ME, Gerzof SG (1989) CT of appendicitis: diagnosis and treatment. Radiol Clin North Am 27:753–762
Ernst O, Bulois P, Saint-Drenant S, et al. (2003) Helical CT in acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Eur J Radiol 13:114–117
Cobelli R, Zompatori M, De Luca G, et al. (2005) Clinical usefulness of computed tomography study without contrast injection in the evaluation of acute pulmonary embolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29:6–12
Cheng SM, Ng SP, Shih SL (2004) Hyperdense gallbladder wall sign: an overlooked sign of acute cholecystitis on unenhanced CT examination. Clin Imaging 28:128–131
Wiesner W, Khurana B, Ji H, et al. (2003) CT of acute bowel ischemia. Radiology 226:635–650
Lane MJ, Mindelzun RE (1999) Appendicitis and its mimickers. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 20:77–85
Macari M, Balthazar EJ (2003) The acute right lower quadrant: CT evaluation. Radiol Clin North Am 41:1117–1136
Rao PM, Rhea JT, Novelline RA (1997) Sensitivity and specificity of the individual CT signs of appendicitis: experience with 200 helical appendiceal CT examinations. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21:686–692
Balthazar EJ, Megibow AJ, Gordon RB, et al. (1988) Computer tomography of the abnormal appendix. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12:595–601
Cakirer S, Basak M, Colakoglu B, et al. (1993) Diagnosis of acute appendicitis: value of unenhanced CT. Am J Roentgenol 160:763–766
Chou CK, Mak CW, Tzeng WS, et al. (2004) CT of small bowel ischemia. Abdom Imaging 29:18–22
Frager DH, Baer JW (1995) Role of CT in evaluating patients with small-bowel obstruction. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 16:127–140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, SP., Cheng, SM., Yang, FS. et al. Hyperdense appendix on unenhanced CT: a sign of acute appendicitis. Abdom Imaging 32, 701–704 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-007-9176-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-007-9176-6