Abstract.
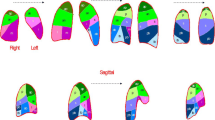
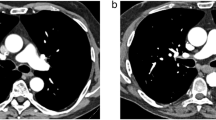
The objective of this study was to quantify the changes in pulmonary perfusion due to therapy for pulmonary embolism (PE). To this end, seven consecutive patients (five men, two women; mean age 64±10 years) were studied. After basal pulmonary arteriography had demonstrated the presence of massive PE, patients were injected intravenously with 4 mCi of technetium-99m-labelled human albumin microspheres and were treated soon thereafter with a 2-h infusion of either alteplase 100 mg (five patients) or heparin 1,750 IU/h (two patients). Then, a second pulmonary arteriography study was obtained, and soon afterwards a single-photon emission tomographic (SPET) perfusion scan was performed. Immediately thereafter, a second intravenous injection of 4 mCi of 99mTc-labelled microspheres was administered, followed by a second SPET scan. At the end of the study, the perfusion changes due to therapy were quantified by subtraction of the images of the two SPET studies; the reperfused areas could be visualised and the volumes of reperfusion quantified. This study demonstrates the validity of a newly devised, relatively rapid and non-invasive method for quantification of the early effects of therapy on pulmonary perfusion in patients presenting with acute PE.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 26 March and in revised form 7 July 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palla, A., Riccardo Bellina, C., Marini, C. et al. A non-invasive, quantitative method to demonstrate the early effects of therapy in acute pulmonary embolism. Eur J Nucl Med 28, 1605–1609 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590100613
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590100613