Abstract
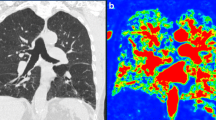
Emphysema is a common and debilitating disease that is the commonest cause of end-stage respiratory failure. Treatment is either by lung transplantation or by lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) that improves the biomechanics of respiration. Patient selection for LVRS hinges on the demonstration of heterogeneous disease, predominantly involving the upper lobes, as a good surgical outcome is most likely in these patients. We used a virtual model of lung scintigraphy to compare planar with tomographic scintigraphy for the detection of diffuse lung disease. Lesions of the magnitude of the lung acinus, as well as larger and smaller lesions, were distributed throughout the lungs in volumes from 2% to 50%. Single-photon emission tomography does not add incremental value to planar images for the detection of diffuse lung disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 29 June and in revised form 10 October 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chicco, P., Magnussen, J.S., Mackey, D.W. et al. SPET of a computerised model of diffuse lung disease. Eur J Nucl Med 28, 150–154 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590000425
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590000425