Abstract
Purpose
To compare the potential efficiency of [68Ga]Ga-LNC1007 with 2-[18F]FDG/[68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET/CT for detecting renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and to explore parameters derived from [68Ga]Ga-LNC1007 PET/CT for discriminating pathological characteristics in RCC.
Methods
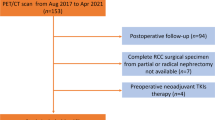
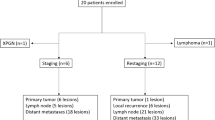
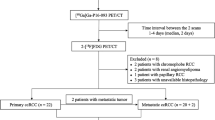
Twenty-five RCC patients confirmed by pathology were enrolled in this prospective study. The maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), mean SUV (SUVmean), gross tumor volume (GTV) and total lesion-tracer (TL-tracer) of lesions were calculated from the corresponding PET/CT images. Pathological characteristics included World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology (WHO/ISUP) grade and adverse pathological features (tumor necrosis or sarcomatoid or rhabdoid feature).
Results
[68Ga]Ga-LNC1007 PET/CT showed a higher detection rate for primary lesions than 2-[18F]FDG and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA (LNC1007 vs. FDG: 13/17 vs. 4/17, P = 0.005; LNC1007 vs. PSMA: 9/11 vs. 6/11, P = 0.361). [68Ga]Ga-LNC1007 PET/CT showed higher SUVmax (6.6 vs. 3.7, P = 0.005), SUVmean (4.1 vs. 2.3, P = 0.001) and TBR (2.6 vs. 1.7, P = 0.011) compared with 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT, and it also showed higher TBR (2.9 vs. 0.5, P = 0.003), TBR-delay (2.8 vs. 0.3, P = 0.003), GTV (84.1 vs. 42.9, P = 0.003) and TL-tracer (442.7 vs. 235.8, P = 0.008) compared with [68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET/CT. SUVmax and TBR derived from [68Ga]Ga-LNC1007 PET/CT could effectively differentiate WHO/ISUP grade (3–4 vs. 1–2) and adverse pathological features (positive vs. negative) (SUVmax: AUC 0.81, P = 0.04; AUC 0.80, P = 0.033; TBR: AUC 0.84, P = 0.026; AUC 0.85, P = 0.014). The SUVmax was positively correlated with the FAP expression, integrin αvβ3 expression and the total expression of FAP and integrin αvβ3 (r = 0.577, P = 0.006, r = 0.701, P < 0.001, and r = 0.702, P < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion
[68Ga]Ga-LNC1007 is a promising tracer for RCC imaging and can effectively identify aggressive pathological characteristics of RCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442.
Joosten SC, Smits KM, Aarts MJ, Melotte V, Koch A, Tjan-Heijnen VC, et al. Epigenetics in renal cell cancer: mechanisms and clinical applications. Nat Rev Urol. 2018;15:430–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-018-0023-z.
Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, Boorjian SA, Bray F, Coleman J, et al. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2019;75:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.036.
Miyakita H, Tokunaga M, Onda H, Usui Y, Kinoshita H, Kawamura N, et al. Significance of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) for detection of renal cell carcinoma and immunohistochemical glucose transporter 1 (GLUT-1) expression in the cancer. Int J Urol. 2002;9:15–8. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1442-2042.2002.00416.x.
Liu Y. The place of FDG PET/CT in renal cell carcinoma: value and limitations. Front Oncol. 2016;6:201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2016.00201.
Aide N, Cappele O, Bottet P, Bensadoun H, Regeasse A, Comoz F, et al. Efficiency of [18F]FDG PET in characterising renal cancer and detecting distant metastases: a comparison with CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:1236–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-003-1211-4.
Hofman MS, Lawrentschuk N, Francis RJ, Tang C, Vela I, Thomas P, et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen PET-CT in patients with high-risk prostate cancer before curative-intent surgery or radiotherapy (proPSMA): a prospective, randomised, multicentre study. The Lancet. 2020;395:1208–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30314-7.
Chang SS, Reuter VE, Heston W, Bander NH, Grauer LS, Gaudin PB. Five different anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) antibodies confirm PSMA expression in tumor-associated neovasculature. Can Res. 1999;59:3192–8.
Golan S, Aviv T, Groshar D, Yakimov M, Zohar Y, Prokocimer Y, et al. Dynamic 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT for the primary evaluation of localized renal mass: a prospective study. J Nucl Med. 2021;62:773–8. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.120.251272.
Gao J, Xu Q, Fu Y, He K, Zhang C, Zhang Q, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT parameters for discriminating pathological characteristics in primary clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48:561–9. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.120.251272.
Raveenthiran S, Esler R, Yaxley J, Kyle S. The use of 68Ga-PET/CT PSMA in the staging of primary and suspected recurrent renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:2280–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04432-2.
Hamson EJ, Keane FM, Tholen S, Schilling O, Gorrell MD. Understanding fibroblast activation protein (FAP): substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy. Proteomics-Clin Appl. 2014;8:454–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.201300095.
Li M, Younis MH, Zhang Y, Cai W, Lan X. Clinical summary of fibroblast activation protein inhibitor-based radiopharmaceuticals: cancer and beyond. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49:2844–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-05706-y.
Pang Y, Zhao L, Luo Z, Hao B, Wu H, Lin Q, et al. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG uptake in gastric, duodenal, and colorectal cancers. Radiology. 2021;298:393–402. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020203275.
Chen X, Hou Y, Tohme M, Park R, Khankaldyyan V, Gonzales-Gomez I, et al. Pegylated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide: 64Cu labeling and PET imaging of brain tumor αvβ3-integrin expression. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1776–83.
Chen X, Park R, Tohme M, Shahinian AH, Bading JR, Conti PS. MicroPET and autoradiographic imaging of breast cancer αv-integrin expression using 18F-and 64Cu-labeled RGD peptide. Bioconjug Chem. 2004;15:41–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc0300403.
Zang J, Wen X, Lin R, Zeng X, Wang C, Shi M, et al. Synthesis, preclinical evaluation and radiation dosimetry of a dual targeting PET tracer [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-RGD. Theranostics. 2022;12:7180. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.79144.
Delahunt B, Eble JN, Egevad L, Samaratunga H. Grading of renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2019;74:4–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.13735.
Moch H, Amin MB, Berney DM, Compérat EM, Gill AJ, Hartmann A, et al. The 2022 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs—part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2022.06.016.
Dagher J, Delahunt B, Rioux-Leclercq N, Egevad L, Srigley JR, Coughlin G, et al. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: validation of World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology grading. Histopathology. 2017;71:918–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.13311.
Delahunt B, McKenney JK, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Thompson RH, Boorjian SA, et al. A novel grading system for clear cell renal cell carcinoma incorporating tumor necrosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37:311–22. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e318270f71c.
Khor L-Y, Dhakal HP, Jia X, Reynolds JP, McKenney JK, Rini BI, et al. Tumor necrosis adds prognostically significant information to grade in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40:1224–31. https://doi.org/10.1097/pas.0000000000000690.
Katz MD, Serrano MF, Grubb RL III, Skolarus TA, Gao F, Humphrey PA, et al. Percent microscopic tumor necrosis and survival after curative surgery for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2010;183:909–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.11.010.
Sengupta S, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Frank I, Thompson RH, Webster WS, et al. Histologic coagulative tumor necrosis as a prognostic indicator of renal cell carcinoma aggressiveness. Cancer. 2005;104:511–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.21206.
de Peralta-Venturina M, Moch H, Amin M, Tamboli P, Hailemariam S, Mihatsch M, et al. Sarcomatoid differentiation in renal cell carcinoma: a study of 101 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25:275–84. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-200103000-00001.
Pichler R, Compérat E, Klatte T, Pichler M, Loidl W, Lusuardi L, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid features: finally new therapeutic hope? Cancers. 2019;11:422. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030422.
Zhang BY, Cheville JC, Thompson RH, Lohse CM, Boorjian SA, Leibovich BC, et al. Impact of rhabdoid differentiation on prognosis for patients with grade 4 renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2015;68:5–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.01.002.
Przybycin CG, McKenney JK, Reynolds JP, Campbell S, Zhou M, Karafa MT, et al. Rhabdoid differentiation is associated with aggressive behavior in renal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of 76 cases with clinical follow-up. T Am J Surg Pathol. 2014;38:1260–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/pas.0000000000000251.
Verhoeff SR, van Es SC, Boon E, van Helden E, Angus L, Elias SG, et al. Lesion detection by [89Zr] Zr-DFO-girentuximab and [18F] FDG-PET/CT in patients with newly diagnosed metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:1931–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04358-9.
Fendler WP, Eiber M, Beheshti M, Bomanji J, Calais J, Ceci F, et al. PSMA PET/CT: joint EANM procedure guideline/SNMMI procedure standard for prostate cancer imaging 2.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023;50:1466–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-06089-w.
Zhao L, Wen X, Xu W, Pang Y, Sun L, Wu X, et al. Clinical Evaluation of 68Ga-FAPI-RGD for Imaging of Fibroblast Activation Protein and Integrin αvβ3 in Various Cancer Types. J Nucl Med. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.122.265383.
Lan L, Zhang S, Xu T, Liu H, Wang W, Feng Y, et al. Prospective comparison of 68Ga-FAPI versus 18F-FDG PET/CT for tumor staging in biliary tract cancers. Radiology. 2022;304:648–57. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.213118.
Lin R, Lin Z, Chen Z, Zheng S, Zhang J, Zang J, et al. [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the evaluation of gastric cancer: comparison with [18F]FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49:2960–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-05799-5.
Xie F, Fu L, Zhou W. Superiority of 68Ga-FAPI-04 in Delineation of Soft Tissue and Liver Metastases in Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma for Restaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2022;47:e758–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000004374.
Dong A, Yang B, Bai Y, Zuo C. 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT in a Small Sarcomatoid Renal Cell Carcinoma With Widespread Metastases. Clin Nucl Med. 2023;48:457–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000004607.
Civan C, Isik EG, Karadogan S, Sanli Y, Kuyumcu S. 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Papillary Renal Cell Cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2022:10.1097. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000004587.
Dong A, Yang Q, Hua M, Cheng C, Zuo C. Lipid-poor renal angiomyolipoma mimicking renal cell carcinoma on 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2022;47:991–3. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000004297.
Toriihara A, Duan H, Thompson HM, Park S, Hatami N, Baratto L, et al. 18F-FPPRGD2 PET/CT in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:1518–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04295-7.
Withofs N, Signolle N, Somja J, Lovinfosse P, Nzaramba EM, Mievis F, et al. 18F-FPRGD2 PET/CT imaging of integrin αvβ3 in renal carcinomas: correlation with histopathology. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:361–4. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.114.149021.
Wang G, Li L, Wang J, Zang J, Chen J, Xiao Y, et al. Head-to-head comparison of [68Ga]Ga-P16-093 and 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023;50:1499–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-06101-3.
Sasikumar A, Joy A, Nanabala R, Unni M, Padmanabhan T. Complimentary pattern of uptake in 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga–prostate-specific membrane antigen PET/CT in a case of metastatic clear cell renal carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2016;41:e517–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000001394.
Siva S, Callahan J, Pryor D, Martin J, Lawrentschuk N, Hofman MS. Utility of 68Ga prostate specific membrane antigen–positron emission tomography in diagnosis and response assessment of recurrent renal cell carcinoma. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2017;61:372–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.12590.
Sandgren K, Johansson L, Axelsson J, Jonsson J, Ögren M, Ögren M, et al. Radiation dosimetry of [68Ga]PSMA-11 in low-risk prostate cancer patients. EJNMMI physics. 2019;6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40658-018-0239-2.
Quinn B, Dauer Z, Pandit-Taskar N, Schoder H, Dauer LT. Radiation dosimetry of 18F-FDG PET/CT: incorporating exam-specific parameters in dose estimates. BMC Med Imaging. 2016;16:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-016-0143-y.
Judmann B, Braun D, Wängler B, Schirrmacher R, Fricker G, Wängler C. Current state of radiolabeled heterobivalent peptidic ligands in tumor imaging and therapy. Pharmaceuticals. 2020;13:173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080173.
Summer D, Rangger C, Klingler M, Laverman P, Franssen GM, Lechner BE, et al. Exploiting the concept of multivalency with 68Ga-and 89Zr-labelled fusarinine C-minigastrin bioconjugates for targeting CCK2R expression. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018;2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3171794.
Liu S, Liu Z, Chen K, Yan Y, Watzlowik P, Wester H-J, et al. 18F-Labeled Galacto and PEGylated RGD Dimers for PET Imaging of αvβ3 Integrin Expression. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010;12:530–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0284-2.
Dijkgraaf I, Yim C-B, Franssen GM, Schuit RC, Luurtsema G, Liu S, et al. PET imaging of αvβ3 integrin expression in tumours with 68Ga-labelled mono-, di- and tetrameric RGD peptides. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:128–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1615-x.
Funding
This study was funded in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No.2023J01568, No.2022J01694), Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (No. 2021Y9134, No.2021Y9094), Fujian Provincial Health Technology Project (No.2021QNA031) and Startup Fund for Scientific Research of Fujian Medical University (No.2020QH1044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures involving human participants were carried out in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any experiments with animals.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, R., Wang, C., Chen, S. et al. [68Ga]Ga‑LNC1007 PET/CT in the evaluation of renal cell carcinoma: comparison with 2-[18F]FDG/[68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 51, 535–547 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-023-06436-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-023-06436-5