Abstract
Purpose
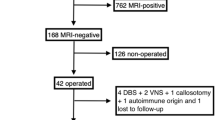
To evaluate morphometric analysis program (MAP) and quantitative positron emission tomography (QPET) in epileptogenic zone (EZ) identification using a simultaneous positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (PET/MRI) system in MRI-negative epilepsies.
Methods
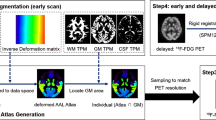
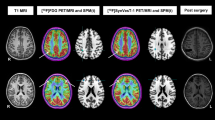
Seventy-one localization-related MRI-negative epilepsies who underwent preoperative simultaneous PET/MRI examination and surgical resection were enrolled retrospectively. MAP was performed on a T1-weighted volumetric sequence, and QPET was analyzed using statistical parametric mapping (SPM) with comparison to age- and gender-matched normal controls. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of MAP, QPET, MAP + QPET, and MAP/QPET in EZ localization were assessed. The correlations between surgical outcome and modalities concordant with cortical resection were analyzed.
Results
Forty-five (63.4%) patients had Engel I seizure outcomes. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of MAP were 64.4%, 69.2%, 78.3%, and 52.9%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV of QPET were 73.3%, 65.4%, 78.6%, and 58.6%, respectively. MAP + QPET, defined as two tests concordant with cortical resection, had reduced sensitivity (53.3%) but increased specificity (88.5%) relative to individual tests. MAP/QPET, defined as one or both tests concordant with cortical resection, had increased sensitivity (86.7%) but reduced specificity (46.2%) relative to individual tests. The regions determined by MAP, QPET, MAP + QPET, or MAP/QPET concordant with cortical resection were significantly associated with the seizure-free outcome.
Conclusion
QPET has a superior sensitivity than MAP, while the combined MAP + QPET obtained from a simultaneous PET/MRI scanner may improve the specificity of the diagnostic tests in EZ localization coupled with the preferable surgical outcome in MRI-negative epilepsies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials are available from Jie Lu.
References
Malmgren K, Krýsl D. Epilepsy: long-term outcomes in MRI-negative patients with epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13:132–3.
Pellinen J, Kuzniecky R, Doyle W, Devinsky O, Dugan P. MRI-negative PET-negative epilepsy long-term surgical outcomes: a single-institution retrospective review. Epilepsy Res. 2020;67:106481.
Wang ZI, Jones SE, Jaisani Z, Najm IM, Prayson RA, Burgess RC, et al. Voxel-based morphometric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) postprocessing in MRI-negative epilepsies. Ann Neurol. 2015;77:1060–75.
Sun K, Ren Z, Yang D, Wang X, Yu T, Ni D, et al. Voxel-based morphometric MRI post-processing and PET/MRI co-registration reveal subtle abnormalities in cingulate epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2021;171:106568.
Wagner J, Weber B, Urbach H, Elger CE, Huppertz HJ. Morphometric MRI analysis improves detection of focal cortical dysplasia type II. Brain. 2011;134:2844–54.
Kim YK, Lee DS, Lee SK, Kim SK, Chung CK, Chang KH, et al. Differential features of metabolic abnormalities between medial and lateral temporal lobe epilepsy: quantitative analysis of (18)F-FDG PET using SPM. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:1006–12.
Liu F, Ruan W, Deng X, Song Y, Song W, Hu F, et al. Efficacy of delayed 18F-FDG hybrid PET/MRI for epileptic focus identification: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48:293–301.
Zhu Y, Feng J, Wu S, Hou H, Ji J, Zhang K, et al. Glucose metabolic profile by visual assessment combined with statistical parametric mapping analysis in pediatric patients with epilepsy. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1293–9.
von Oertzen TJ. PET and ictal SPECT can be helpful for localizing epileptic foci. Curr Opin Neurol. 2018;31:184–91.
Ponisio MR, Zempel JM, Day BK, Eisenman LN, Miller-Thomas MM, Smyth MD, et al. The role of SPECT and PET in epilepsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216:759–68.
Mayoral M, Marti-Fuster B, Carreño M, Carrasco JL, Bargalló N, Donaire A, et al. Seizure-onset zone localization by statistical parametric mapping in visually normal (18) F-FDG PET studies. Epilepsia. 2016;57:1236–44.
Peter J, Houshmand S, Werner TJ, Rubello D, Alavi A. Applications of global quantitative 18F-FDG-PET analysis in temporal lobe epilepsy. Nucl Med Commun. 2016;37:223–30.
Kumar A, Juhász C, Asano E, Sood S, Muzik O, Chugani HT. Objective detection of epileptic foci by 18F-FDG PET in children undergoing epilepsy surgery. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1901–7.
Lin Y, Fang YD, Wu G, Jones SE, Prayson RA, Moosa ANV, et al. Quantitative positron emission tomography-guided magnetic resonance imaging postprocessing in magnetic resonance imaging-negative epilepsies. Epilepsia. 2018;59:1583–94.
Blümcke I, Thom M, Aronica E, Armstrong DD, Vinters HV, Palmini A, et al. The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission. Epilepsia. 2011;52:158–74.
Engel JJ, Van Ness NP, Rasmussen TB, Ojemann LM. Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures. In: Engel JJ, editor. Surgical treatment of the epilepsies. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press; 1993. p. 609–21.
Ryvlin P, Rheims S. Predicting epilepsy surgery outcome. Curr Opin Neurol. 2016;29:182–8.
Krucoff MO, Chan AY, Harward SC, Rahimpour S, Rolston JD, Muh C, et al. Rates and predictors of success and failure in repeat epilepsy surgery: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Epilepsia. 2017;58:2133–42.
Juhász C, John F. Utility of MRI, PET, and ictal SPECT in presurgical evaluation of non-lesional pediatric epilepsy. Seizure. 2020;77:15–28.
Tomás J, Pittau F, Hammers A, Bouvard S, Picard F, Vargas MI, et al. The predictive value of hypometabolism in focal epilepsy: a prospective study in surgical candidates. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:1806–16.
Widjaja E, Shammas A, Vali R, Otsubo H, Ochi A, Snead OC, et al. FDG-PET and magnetoencephalography in presurgical workup of children with localization-related non-lesional epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2013;54:691–9.
Ding Y, Zhu Y, Jiang B, Zhou Y, Jin B, Hou H, et al. 18F-FDG PET and high-resolution MRI co-registration for pre-surgical evaluation of patients with conventional MRI-negative refractory extra-temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:1567–72.
Desarnaud S, Mellerio C, Semah F, Laurent A, Landre E, Devaux B, et al. 18F-FDG PET in drug-resistant epilepsy due to focal cortical dysplasia type 2: additional value of electroclinical data and co-registration with MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:1449–60.
Mendes Coelho VC, Morita ME, Amorim BJ, Ramos CD, Yasuda CL, Tedeschi H, et al. Automated online quantification method for 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/CT improves detection of the epileptogenic zone in patients with pharmaco-resistant epilepsy. Front Neurol. 2017;8:453.
Tan YL, Kim H, Lee S, Tihan T, Ver Hoef L, Mueller SG, et al. Quantitative surface analysis of combined MRI and PET enhances detection of focal cortical dysplasia. Neuroimage. 2018;166:10–8.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yuchao Xu, Ph.D. and Yan Guo, MD from GE Healthcare for editing drafts and statistical suggestions for this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Ascent Plan [grant number DFL20180802].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The research involved human participants. This retrospective study was permitted by the Research Ethics Committee of the Capital Medical University of Xuanwu hospital.
Consent to participate
All patients gave written informed consent prior to enrollment in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Neurology
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, K., Wang, J., Wang, Z. et al. Morphometric analysis program and quantitative positron emission tomography in presurgical localization in MRI-negative epilepsies: a simultaneous PET/MRI study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 49, 1930–1938 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05657-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05657-w