Abstract
Purpose
Patients with carcinoma in situ (CIS) of the bladder refractory to bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment are usually treated with cystectomy. Therefore, new treatment options with preservation of the urinary bladder are needed. The objective of the study was to investigate the feasibility, safety and efficacy of a novel targeted alpha-emitter immunotherapy for CIS after BCG treatment failure.
Methods
A pilot study was conducted in 12 patients (age range 64–86 years, ten men, two women) with biopsy-proven CIS of the bladder refractory to BCG treatment. The patients were treated intravesically with a single instillation (one patient was treated twice) of the alpha-emitter 213Bi coupled to an anti-EGFR antibody (366–821 MBq). The primary aims of the study were to determine the feasibility of treatment with the 213Bi-immunoconjugate and evaluation of adverse effects. Therapeutic efficacy was monitored by histological mapping of the urinary bladder 8 weeks after treatment and at different time points thereafter.
Results
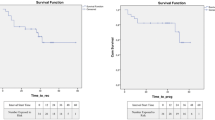
The study proved that intravesical instillation of the 213Bi-immunoconjugate targeting EGFR is feasible. No adverse effects were observed and all blood and urine parameters determined remained in their normal ranges. Therapeutic efficacy was considered satisfactory, in that three of the 12 patients showed no signs of CIS 44, 30 and 3 months after treatment.
Conclusion
Intravesical instillation of 213Bi-anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody was well tolerated and showed therapeutic efficacy. Repeated instillation and/or instillation of higher activities of the 213Bi-immunoconjugate might lead to better therapeutic outcomes. A phase I clinical trial is planned.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30.
Kates M, Date A, Yoshida T, Afzal U, Kanvinde P, Babu T, et al. Preclinical evaluation of intravesical cisplatin nanoparticles for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:6592–601.
Veeratterapillay R, Heer R, Johnson MI, Persad R, Bach C. High-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer-therapy options during intravesical BCG shortage. Curr Urol Rep. 2016;17:68.
Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D, Compérat EM, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016. Eur Urol. 2017;71:447–61.
Gofrit ON, Pode D, Pizov G, Zorn KC, Katz R, Duvdevani M, et al. The natural history of bladder carcinoma in situ after initial response to bacillus Calmette-Gúerin immunotherapy. Urol Oncol. 2009;27:258–62.
Steinberg RL, Thomas LJ, O'Donnell MA. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment failures in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: what truly constitutes unresponsive disease. Bladder Cancer. 2015;1:105–16.
Hassan JM, Cookson MS, Smith JA Jr, Johnson DL, Chang SS. Outcomes in patients with pathological carcinoma in situ only disease at radical cystectomy. J Urol. 2004;172:882–4.
Steinberg RL, Thomas LJ, Nepple KG. Intravesical and alternative bladder-preservation therapies in the management of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer unresponsive to bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Urol Oncol. 2016;34:279–89.
Morales A. BCG: a throwback from the stone age of vaccines opened the path for bladder cancer immunotherapy. Can J Urol. 2017;24:8788–93.
Cardillo MR, Castagna G, Memeo L, De Bernardinis E, Di Silverio F. Epidermal growth factor receptor, MUC-1 and MUC-2 in bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2000;19:225–33.
Rotterud R, Nesland JM, Berner A, Fossa SD. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor family in normal and malignant urothelium. BJU Int. 2005;95:1344–50.
Seidl C. Radioimmunotherapy with α-particle-emitting radionuclides. Immunotherapy. 2014;6:431–58.
Pfost B, Seidl C, Autenrieth M, Saur D, Bruchertseifer F, Morgenstern A, et al. Intravesical alpha-radioimmunotherapy with 213Bi-anti-EGFR-mAb defeats human bladder carcinoma in xenografted nude mice. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:1700–8.
Fazel J, Rötzer S, Seidl C, Feuerecker B, Autenrieth M, Weirich G, et al. Fractionated intravesical radioimmunotherapy with 213Bi-anti-EGFR-MAb is effective without toxic side-effects in a nude mouse model of advanced human bladder carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16:1526–34.
Nikula TK, Curcio MJ, Brechbiel MW, Gansow OA, Finn RD, Scheinberg DA. A rapid, single vessel method for preparation of clinical grade ligand conjugated monoclonal antibodies. Nucl Med Biol. 1995;22:387–90.
Stabin M. Nuclear medicine dosimetry. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51:R187–202.
Chou R, Selph S, Buckley DI, Fu R, Griffin JC, Grusing S, et al. Intravesical therapy for the treatment of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Urol. 2017;197:1189–99.
Shore ND, Boorjian SA, Canter DJ, Ogan K, Karsh LI, Downs TM, et al. Intravesical rAd-IFNα/Syn3 for patients with high-grade, bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) refractory or relapsed non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a phase II randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3410–6.
Nedrow JR, Josefsson A, Park S, Bäck T, Hobbs RF, Brayton C, et al. Pharmacokinetics, microscale distribution, and dosimetry of alpha-emitter-labeled anti-PD-L1 antibodies in an immune competent transgenic breast cancer model. EJNMMI Res. 2017;7:57.
Bellmunt J, Powles T, Vogelzang NJ. A review on the evolution of PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for bladder cancer: the future is now. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;54:58–67.
Cordier D, Krolicki L, Morgenstern A, Merlo A. Targeted radiolabeled compounds in glioma therapy. Semin Nucl Med. 2016;46:243–9.
Cederkrantz E, Andersson H, Bernhardt P, Bäck T, Hultborn R, Jacobsson L, et al. Absorbed doses and risk estimates of 211At-MX35 F(ab')2 in intraperitoneal therapy of ovarian cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93:569–76.
Meredith RF, Torgue JJ, Rozgaja TA, Banaga EP, Bunch PW, Alvarez RD, et al. Safety and outcome measures of first-in-human intraperitoneal α-radioimmunotherapy with 212Pb-TCMC-trastuzumab. Am J Clin Oncol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0000000000000353
Kratochwil C, Schmidt K, Afshar-Oromieh A, Bruchertseifer F, Rathke H, Morgenstern A, et al. Targeted alpha therapy of mCRPC: dosimetry estimate of 213Bismuth-PSMA-617. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:31–7.
Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, Bruchertseifer F, Mier W, Apostolidis C, Boll R, et al. 213Bi-DOTATOC receptor-targeted alpha-radionuclide therapy induces remission in neuroendocrine tumours refractory to beta radiation: a first-in-human experience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:2106–19.
Jurcic JG, Rosenblat TL. Targeted alpha-particle immunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2014:e126–31.
Meredith R, Wessels B, Knox S. Risks to normal tissues from radionuclide therapy. Semin Nucl Med. 2008;38:347–57.
Lim S, Koh MJ, Jeong HJ, Cho NH, Choi YD, Cho do Y, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 overexpression is associated with poor survival in patients with resected muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57:831–9.
Tomlinson DC, Baldo O, Harnden P, Knowles MA. FGFR3 protein expression and its relationship to mutation status and prognostic variables in bladder cancer. J Pathol. 2007;213:91–8.
Inoue M, Koga F, Yoshida S, Tamura T, Fujii Y, Ito E, et al. Significance of ERBB2 overexpression in therapeutic resistance and cancer-specific survival in muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients treated with chemoradiation-based selective bladder-sparing approach. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;90:303–11.
Li C, Yang Z, Du Y, Tang H, Chen J, Hu D, et al. BCMab1, a monoclonal antibody against aberrantly glycosylated integrin α3β1, has potent antitumor activity of bladder cancer in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:4001–13.
Inman BA, Longo TA, Ramalingam S, Harrison MR. Atezolizumab: a PD-L1-blocking antibody for bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:1886–90.
Sharabi AB, Lim M, DeWeese TL, Drake CG. Radiation and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy: radiosensitisation and potential mechanisms of synergy. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:e498–509.
Gorin JB, Ménager J, Gouard S, Maurel C, Guilloux Y, Faivre-Chauvet A, et al. Antitumor immunity induced after α irradiation. Neoplasia. 2014;16:319–28.
Ménager J, Gorin JB, Maurel C, Drujont L, Gouard S, Louvet C, et al. Combining α-radioimmunotherapy and adoptive T cell therapy to potentiate tumor destruction. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0130249.
Acknowledgments
We owe special thanks to Reingard Senekowitsch-Schmidtke who introduced treatment of bladder cancer xenografts with 213Bi-anti-EGFR immunoconjugates to the scientific community. The authors are indebted for provision of parts of the 225Ac/213Bi used in this study to the Isotope Development and Production for Research and Applications Program, Office of Nuclear Physics, U.S. Department of Energy.
Funding
This study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the local Ethics Committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Autenrieth, M.E., Seidl, C., Bruchertseifer, F. et al. Treatment of carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder with an alpha-emitter immunoconjugate targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor: a pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45, 1364–1371 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-4003-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-4003-6