Abstract
Purpose
To determine the metabolic profiles of the translocator protein ligands PBR102 and PBR111 in rat and human microsomes and compare their in vivo binding and metabolite uptake in the brain of non-human primates (Papio hamadryas) using PET-CT.
Methods
In vitro metabolic profiles of PBR102 and PBR111 in rat and human liver microsomes were assessed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. [18F]PBR102 and [18F]PBR111 were prepared by nucleophilic substitution of their corresponding p-toluenesulfonyl precursors with [18F]fluoride. List mode PET-CT brain imaging with arterial blood sampling was performed in non-human primates. Blood plasma measurements and metabolite analysis, using solid-phase extraction, provided the metabolite profile and metabolite-corrected input functions for kinetic model fitting. Blocking and displacement PET-CT scans, using PK11195, were performed.
Results
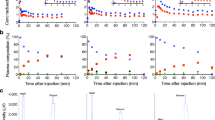
Microsomal analyses identified the O-de-alkylated, hydroxylated and N-de-ethyl derivatives of PBR102 and PBR111 as the main metabolites. The O-de-alkylated compounds were the major metabolites in both species; human liver microsomes were less active than those from rat. Metabolic profiles in vivo in non-human primates and previously published rat experiments were consistent with the microsomal results. PET-CT studies showed that K1 was similar for baseline and blocking studies for both radiotracers; VT was reduced during the blocking study, suggesting low non-specific binding and lack of appreciable metabolite uptake in the brain.
Conclusions
[18F]PBR102 and [18F]PBR111 have distinct metabolic profiles in rat and non-human primates. Radiometabolites contributed to non-specific binding and confounded in vivo brain analysis of [18F]PBR102 in rodents; the impact in primates was less pronounced. Both [18F]PBR102 and [18F]PBR111 are suitable for PET imaging of TSPO in vivo. In vitro metabolite studies can be used to predict in vivo radioligand metabolism and can assist in the design and development of better radioligands.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer J, Sminia T, Wouterlood FG, Dijkstra CD. Phagocytic activity of macrophages and microglial cells during the course of acute and chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res. 1994;38:365–75. doi:10.1002/jnr.490380402.
Venneti S, Lopresti BJ, Wiley CA. The peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (translocator protein 18 kDa) in microglia: from pathology to imaging. Prog Neurobiol. 2006;80:308–22.
Vowinckel E, Reutens D, Becher B, Verge G, Evans A, Owens T, et al. PK11195 binding to the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor as a marker of microglia activation in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res. 1997;50:345–53.
Iannaccone S, Cerami C, Alessio M, Garibotto V, Panzacchi A, Olivieri S, et al. In vivo microglia activation in very early dementia with Lewy bodies, comparison with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013;19:47–52. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.07.002.
Ouchi Y, Yoshikawa E, Sekine Y, Futatsubashi M, Kanno T, Ogusu T, et al. Microglial activation and dopamine terminal loss in early Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:168–75. doi:10.1002/ana.20338.
McGeer EG, Singh EA, McGeer PL. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1988;2:331–6.
Hammoud DA, Endres CJ, Chander AR, Guilarte TR, Wong DF, Sacktor NC, et al. Imaging glial cell activation with [C-11]-R-PK11195 in patients with aids. J Neurovirol. 2005;11:346–55.
Messmer K, Reynolds GP. Increased peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites in the brain of patients with Huntington’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 1998;241:53–6.
Pappata S, Levasseur M, Gunn RN, Myers R, Crouzel C, Syrota A, et al. Thalamic microglial activation in ischemic stroke detected in vivo by PET and [C-11]PK11195. Neurology. 2000;55:1052–4.
Asai H, Ikezu S, Tsunoda S, Medalla M, Luebke J, Haydar T, et al. Depletion of microglia and inhibition of exosome synthesis halt tau propagation. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:1584–93. doi:10.1038/nn.4132.
Rupprecht R, Papadopoulos V, Rammes G, Baghai TC, Fan J, Akula N, et al. Translocator protein (18 kDa) (TSPO) as a therapeutic target for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:971–88. doi:10.1038/nrd3295.
Vivash LE, O’Brien TJ. Imaging microglial activation with TSPO PET: Lighting up neurological diseases? J Nucl Med. 2015. doi:10.2967/jnumed.114.141713.
Peyronneau MA, Saba W, Goutal S, Damont A, Dolle F, Kassiou M, et al. Metabolism and quantification of [18F]DPA-714, a new TSPO positron emission tomography radioligand. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41:122–31. doi:10.1124/dmd.112.046342.
Katsifis A, Loc’h C, Henderson D, Bourdier T, Pham T, Greguric I, et al. A rapid solid-phase extraction method for measurement of non-metabolised peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands, [18F]PBR102 and [18F]PBR111, in rat and primate plasma. Nucl Med Biol. 2011;38:137–48. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2010.07.008.
Wilson AA, McCormick P, Kapur S, Willeit M, Garcia A, Hussey D, et al. Radiosynthesis and evaluation of [11C]-(+)-4-propyl-3,4,4a,5,6,10b-hexahydro-2H-naphtho[1,2-b][1,4]oxazin-9-ol as a potential radiotracer for in vivo imaging of the dopamine D2 high-affinity state with positron emission tomography. J Med Chem. 2005;48:4153–60. doi:10.1021/jm050155n.
Fookes CJ, Pham TQ, Mattner F, Greguric I, Loc’h C, Liu X, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted [18F]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines and [18F]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines for the study of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor using positron emission tomography. J Med Chem. 2008;51:3700–12.
Van Camp N, Boisgard R, Kuhnast B, Theze B, Viel T, Gregoire MC, et al. In vivo imaging of neuroinflammation: a comparative study between [F-18]PBR111, [C-11]CLINME and [C-11]PK11195 in an acute rodent model. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:962–72.
Owen DR, Yeo AJ, Gunn RN, Song K, Wadsworth G, Lewis A, et al. An 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32:1–5. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2011.147.
Owen DR, Gunn RN, Rabiner EA, Bennacef I, Fujita M, Kreisl WC, et al. Mixed-affinity binding in humans with 18-kDa translocator protein ligands. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:24–32. doi:10.2967/jnumed.110.079459.
Hilton J, Yokoi F, Dannals RF, Ravert HT, Szabo Z, Wong DF. Column-switching HPLC for the analysis of plasma in PET imaging studies. Nucl Med Biol. 2000;27:627–30.
Shetty HU, Zoghbi SS, Simeon FG, Liow JS, Brown AK, Kannan P, et al. Radiodefluorination of 3-fluoro-5-(2-(2-[18F](fluoromethyl)-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl)benzonitrile ([18F]SP203), a radioligand for imaging brain metabotropic glutamate subtype-5 receptors with positron emission tomography, occurs by glutathionylation in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;327:727–35. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.143347.
Yokoi T, Iida H, Itoh H, Kanno I. A new graphic plot analysis for cerebral blood flow and partition coefficient with iodine-123-iodoamphetamine and dynamic SPECT validation studies using oxygen-15-water and PET. J Nucl Med. 1993;34:498–505.
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Ding YS, Alexoff DL. Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:834–40. doi:10.1097/00004647-199609000-00008.
Knust EJ, Kupfernagel C, Stocklin G. Long-chain F-18 fatty acids for the study of regional metabolism in heart and liver; odd-even effects of metabolism in mice. J Nucl Med. 1979;20:1170–5.
Zoghbi SS, Shetty HU, Ichise M, Fujita M, Imaizumi M, Liow JS, et al. PET imaging of the dopamine transporter with 18F-FECNT: a polar radiometabolite confounds brain radioligand measurements. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:520–7.
Fonnum F, Johnsen A, Hassel B. Use of fluorocitrate and fluoroacetate in the study of brain metabolism. Glia. 1997;21:106–13.
Marik J, Ogasawara A, Martin-McNulty B, Ross J, Flores JE, Gill HS, et al. PET of glial metabolism using 2-18F-fluoroacetate. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:982–90. doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.057356.
Mori T, Sun LQ, Kobayashi M, Kiyono Y, Okazawa H, Furukawa T, et al. Preparation and evaluation of ethyl [18F]fluoroacetate as a proradiotracer of [18F]fluoroacetate for the measurement of glial metabolism by PET. Nucl Med Biol. 2009;36:155–62. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2008.11.006.
Peyronneau MA, Saba W, Dolle F, Goutal S, Coulon C, Bottlaender M, et al. Difficulties in dopamine transporter radioligand PET analysis: the example of LBT-999 using [18F] and [11C] labelling: part II: metabolism studies. Nucl Med Biol. 2012;39:347–59. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2011.09.006.
Zhang MR, Maeda J, Ogawa M, Noguchi J, Ito T, Yoshida Y, et al. Development of a new radioligand, N-(5-fluoro-2-phenoxyphenyl)-N-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl-5-methoxybenzyl)acetamide, for PET imaging of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in primate brain. J Med Chem. 2004;47:2228–35.
Wilson AA, Garcia A, Parkes J, McCormick P, Stephenson KA, Houle S, et al. Radiosynthesis and initial evaluation of [18F]-FEPPA for PET imaging of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Nucl Med Biol. 2008;35:305–14. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.12.009.
Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Simeon FG, Imaizumi M, Gourley JP, Shetty HU, et al. Single-step high-yield radiosynthesis and evaluation of a sensitive, F-18-labeled ligand for imaging brain peripheral benzodiazepine receptors with PET. J Med Chem. 2009;52:688–99.
Katsifis A, Mattner F, Dikic B, Papazian V. Synthesis of substituted [123I]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines as potential probes for the study of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptors using SPECT. Radiochim Acta. 2000;88:229–32.
Trapani G, Franco M, Latrofa A, Ricciardi L, Carotti A, Serra M, et al. Novel 2-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives as potent and selective ligands for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors: synthesis, binding affinity, and in vivo studies. J Med Chem. 1999;42:3934–41.
Yui J, Maeda J, Kumata K, Kawamura K, Yanamoto K, Hatori A, et al. 18F-FEAC and 18F-FEDAC: PET of the monkey brain and imaging of translocator protein (18 kDa) in the infarcted rat brain. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1301–9. doi:10.2967/jnumed.109.072223.
Saba W, Goutal S, Kuhnast B, Dolle F, Auvity S, Fontyn Y, et al. Differential influence of propofol and isoflurane anesthesia in a non-human primate on the brain kinetics and binding of [18F]DPA-714, a positron emission tomography imaging marker of glial activation. Eur J Neurosci. 2015;42:1738–45. doi:10.1111/ejn.12946.
Imaizumi M, Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Gourley JP, Hong J, Musachio JL, et al. Kinetic evaluation in nonhuman primates of two new PET ligands for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in brain. Synapse. 2007;61:595–605. doi:10.1002/syn.20394.
Colasanti A, Guo Q, Muhlert N, Giannetti P, Onega M, Newbould RD, et al. In vivo assessment of brain white matter inflammation in multiple sclerosis with 18F-PBR111 PET. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:1112–8. doi:10.2967/jnumed.113.135129.
Guo Q, Colasanti A, Owen DR, Onega M, Kamalakaran A, Bennacef I, et al. Quantification of the specific translocator protein signal of 18F-PBR111 in healthy humans: a genetic polymorphism effect on in vivo binding. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:1915–23. doi:10.2967/jnumed.113.121020.
Bourdier T, Henderson D, Fookes CJ, Lam P, Mattner F, Fulham M, et al. Synthesis of [11C]PBR170, a novel imidazopyridine, for imaging the translocator protein with PET. Appl Radiat Isot. 2014;90:46–52. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2014.03.009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eberl, S., Katsifis, A., Peyronneau, M.A. et al. Preclinical in vivo and in vitro comparison of the translocator protein PET ligands [18F]PBR102 and [18F]PBR111. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44, 296–307 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3517-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3517-z