Abstract
Purpose
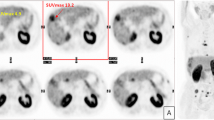
In this prospective study, our goal was to emphasize the diagnostic value of combining 11C-choline and 18F-FDG PET/CT for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with chronic liver disease.
Methods
Thirty-three consecutive patients were enrolled. All patients were suspected to have HCC based on CT and/or MRI imaging. A final diagnosis was obtained by histopathological examination or by imaging alone according to American Association for the Study of Liver Disease criteria. All patients underwent PET/CT with both tracers within a median of 5 days. All lesions showing higher tracer uptake than normal liver were considered positive for HCC. We examined how tracer uptake was related to biological (serum α-fetoprotein levels) and pathological (differentiation status, peritumoral capsule and vascular invasion) prognostic markers of HCC, as well as clinical observations at 6 months (recurrence and death).
Results
Twenty-eight HCC, four cholangiocarcinomas and one adenoma were diagnosed. In the HCC patients, the sensitivity of 11C-choline, 18F-FDG and combined 11C-choline and 18F-FDG PET/CT for the detection of HCC was 75 %, 36 % and 93 %, respectively. Serum α-fetoprotein levels >200 ng/ml were more frequent among patients with 18F-FDG-positive lesions than those with 18F-FDG-negative lesions (p < 0.05). Early recurrence (n=2) or early death (n=5) occurred more frequently in patients with 18F-FDG-positive lesions than in those with 18F-FDG-negative lesions (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
The combined use of 11C-choline and 18F-FDG PET/CT detected HCC with high sensitivity. This approach appears to be of potential prognostic value and may facilitate the selection of patients for surgical resection or liver transplantation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee YJ, Lee JM, Lee JS, Lee HY, Park BH, Kim YH, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnostic performance of multidetector CT and MR imaging – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology. 2015;275:97–109.
Lim JH, Kim CK, Lee WJ, Park CK, Koh KC, Paik SW, et al. Detection of hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic livers: accuracy of helical CT in transplant patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175:693–8.
Bruix J, Sherman M; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011;53:1020–2.
Sharma B, Martin A, Zerizer I. Positron emission tomography-computed tomography in liver imaging. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2013;34:66–80.
Khan MA, Combs CS, Brunt EM, Lowe VJ, Wolverson MK, Solomon H, et al. Positron emission tomography scanning in the evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2000;32:792–7.
Park JW, Kim JH, Kim SK, Kang KW, Park KW, Choi JI, et al. A prospective evaluation of 18F-FDG and 11C-acetate PET/CT for detection of primary and metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:1912–21.
Verhoef C, Valkema R, de Man RA, Krenning EP, Yzermans JN. Fluorine-18 FDG imaging in hepatocellular carcinoma using positron coincidence detection and single photon emission computed tomography. Liver. 2002;22:51–6.
Cascales Campos P, Ramirez P, Gonzalez R, Febrero B, Pons JA, Miras M, et al. Value of 18-FDG-positron emission tomography/computed tomography before and after transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing liver transplantation: initial results. Transplant Proc. 2011;43:2213–5.
Pant V, Sen IB, Soin AS. Role of 18F-FDG PET CT as an independent prognostic indicator in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun. 2013;34:749–57.
Song MJ, Bae SH, Lee SW, Song do S, Kim HY, Yoo IR, et al. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT predicts tumour progression after transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:865–73.
Yamamoto Y, Nishiyama Y, Kameyama R, Okano K, Kashiwagi H, Deguchi A, et al. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma using 11C-choline PET: comparison with 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:1245–8.
Kuang Y, Salem N, Tian H, Kolthammer JA, Corn DJ, Wu C, et al. Imaging lipid synthesis in hepatocellular carcinoma with [methyl-11C]choline: correlation with in vivo metabolic studies. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:98–106.
Bertagna F, Bertoli M, Bosio G, Biasiotto G, Sadeghi R, Giubbini R, et al. Diagnostic role of radiolabelled choline PET or PET/CT in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. 2014;8:493–500.
Wu HB, Wang QS, Li BY, Li HS, Zhou WL, Wang QY. F-18 FDG in conjunction with 11C-choline PET/CT in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2011;36:1092–7.
Talbot JN, Fartoux L, Balogova S, Nataf V, Kerrou K, Gutman F, et al. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma with PET/CT: a prospective comparison of 18F-fluorocholine and 18F-FDG in patients with cirrhosis or chronic liver disease. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1699–706.
Pascali C, Bogni A, Itawa R, Cambiè M, Bombarderi E. [11C]Methylation on a C18 Sep-Pak cartridge: a convenient way to produce [N-methyl-11C]choline. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2000;49:195–203.
Cheung TT, Ho CL, Lo CM, Chen S, Chan SC, Chok KS, et al. 11C-acetate and 18F-FDG PET/CT for clinical staging and selection of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma for liver transplantation on the basis of Milan criteria: surgeon's perspective. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:192–200.
Ho CL, Yu SC, Yeung DW. 11C-acetate PET imaging in hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver masses. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:213–21.
Fartoux L, Balogova S, Nataf V, Kerrou K, Huchet V, Rosmorduc O, et al. A pilot comparison of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and 18F-fluorocholine PET/CT to predict early recurrence of unifocal hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. Nucl Med Commun. 2012;33:757–65.
Lee JW, Paeng JC, Kang KW, Kwon HW, Suh KS, Chung JK, et al. Prediction of tumor recurrence by 18F-FDG PET in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:682–7.
Lee SD, Kim SH, Kim YK, Kim C, Kim SK, Han SS, et al. (18)F-FDG-PET/CT predicts early tumor recurrence in living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Transpl Int. 2013;26:50–60.
Buchenbender C, Heusner TA, Lauenstein TC, Bockisch A, Antoch G. Oncologic PET/MRI, part 1: tumors of the brain, head and neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. J Nucl Med. 2012;6:928–38.
Acknowledgments
We thank Irène Buvat for critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No financial support was received.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the principles of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castilla-Lièvre, MA., Franco, D., Gervais, P. et al. Diagnostic value of combining 11C-choline and 18F-FDG PET/CT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43, 852–859 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3241-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3241-0