Abstract
Purpose
Affibody molecules represent a novel class of high-affinity agents for radionuclide tumour targeting. Fusion of the Affibody molecules with an albumin-binding domain (ABD) enables modification of the blood kinetics of the Affibody molecules and reduction of the renal dose. 177Lu-CHX-A″-DTPA-ABD-(ZHER2:342)2, an anti-HER2 Affibody molecule-ABD fusion protein has earlier demonstrated promising results in treatment of HER2-expressing micro-xenografts in mice. The use of the in vivo generator 114mIn/114In as a label for ABD-fused Affibody molecules would create preconditions for efficient treatment of both micrometastases (due to conversion and Auger electrons of 114mIn) and bulky tumours (due to high-energy beta particles from the daughter nuclide 114In). The goal of this study was to investigate if different chelators influence the biodistribution of ABD-(ZHER2:342)2 and to find an optimal chelator for attachment of 114mIn to the Affibody molecule-ABD fusion protein.
Methods
Isothiocyanate derivatives of Bz-DOTA and CHX-A″-DTPA were coupled to ABD-(ZHER2:342)2. The cellular processing of both conjugates was studied in vitro. The influence of chelators on the biodistribution was investigated in mice using double isotope (114mIn and 111In) labelling.
Results
The apparent affinity of CHX-A″-DTPA-ABD-(ZHER2:342)2 and Bz-DOTA-ABD-(ZHER2:342)2 to the extracellular domain of HER2 was similar, 13.5 and 15.0 pM, respectively. It was found that both conjugates were internalized by SKOV-3 cells. The use of CHX-A″-DTPA provided better cellular retention of the radioactivity, better tumour accumulation of radioactivity and better tumour to organ dose ratios than Bz-DOTA-ABD-(ZHER2:342)2.
Conclusion
CHX-A″-DTPA is more suitable for 114mIn labelling of Affibody molecule-ABD fusion proteins for radionuclide therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldenberg DM. Advancing role of radiolabeled antibodies in the therapy of cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2003;52:281–96.
Jain M, Venkatraman G, Batra SK. Optimization of radioimmunotherapy of solid tumors: biological impediments and their modulation. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:1374–82.
Tolmachev V, Orlova A, Nilsson FY, Feldwisch J, Wennborg A, Abrahmsén L. Affibody molecules: potential for in vivo imaging of molecular targets for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2007;7:555–68.
Nilsson FY, Tolmachev V. Affibody molecules: new protein domains for molecular imaging and targeted tumor therapy. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel 2007;10:167–75.
Orlova A, Feldwisch J, Abrahmsén L, Tolmachev V. Update: affibody molecules for molecular imaging and therapy for cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2007;22:573–84.
Fortin MA, Orlova A, Malmström PU, Tolmachev V. Labelling chemistry and characterization of [90Y/177Lu]-DOTA-ZHER2:342-3 Affibody molecule, a candidate agent for locoregional treatment of urinary bladder carcinoma. Int J Mol Med 2007;19:285–91.
Tolmachev V, Orlova A, Pehrson R, Galli J, Baastrup B, Andersson K, et al. Radionuclide therapy of HER2-positive microxenografts using a 177Lu-labeled HER2-specific Affibody molecule. Cancer Res 2007;67:2773–82.
Wheldon TE, O’Donoghue JA, Barrett A, Michalowski AS. The curability of tumours of differing size by targeted radiotherapy using 131I or 90Y. Radiother Oncol 1991;21:91–9.
Kassis AI. The amazing world of auger electrons. Int J Radiat Biol 2004;80:789–803.
de Jong M, Breeman WAP, Valkema R, Bernard BE, Krenning EP. Combination radionuclide therapy using 177Lu- and 90Y-labeled somatostatin analogs. J Nucl Med 2005;46:13S–7S.
Aas M, Mardirossian G, Griffin TW, Salimi AR, Ito T, Bushe HS, et al. Long-term biodistribution in tumored mice of murine and chimeric B72.3-IgG antibody radiolabeled with 114mIn via both DTPA and a macrocyclic chelator. J Nucl Biol Med 1992;36:33–40.
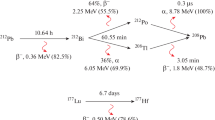
Tolmachev V, Bernhardt P, Forssell-Aronsson E, Lundqvist H. 114mIn, a candidate for radionuclide therapy: low-energy cyclotron production and labeling of DTPA-D-phe-octreotide. Nucl Med Biol 2000;27:183–8.
Sabbah EN, Kadouche J, Ellison D, Finucane C, Decaudin D, Mather SJ. In vitro and in vivo comparison of DTPA- and DOTA-conjugated antiferritin monoclonal antibody for imaging and therapy of pancreatic cancer. Nucl Med Biol 2007;34:293–304.
Froidevaux S, Heppeler A, Eberle AN, Meier AM, Häusler M, Beglinger C, et al. Preclinical comparison in AR4–2J tumor-bearing mice of four radiolabeled 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-somatostatin analogs for tumor diagnosis and internal radiotherapy. Endocrinology 2000;141:3304–12.
Brechbiel MW. Bifunctional chelates for metal nuclides. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;52:166–73.
Boswell CA, Brechbiel MW. Development of radioimmunotherapeutic and diagnostic antibodies: an inside-out view. Nucl Med Biol 2007;34:757–78.
Orlova A, Rosik D, Sandström M, Lundqvist H, Einarsson L, Tolmachev V. Evaluation of [111/114mIn]-CHX-A"-DTPA-ZHER2:342, an affibody ligand conjugate for targeting of HER2-expressing malignant tumors. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;51:314–23.
Lundberg E, Höidén-Guthenberg I, Larsson B, Uhlén M, Gräslund T. Site-specifically conjugated anti-HER2 Affibody molecules as one-step reagents for target expression analyses on cells and xenograft samples. J Immunol Methods 2007;319:53–63.
Orlova A, Tran T, Widström C, Engfeldt T, Eriksson Karlström A, Tolmachev V. Pre-clinical evaluation of [111In]-benzyl-DOTA-Z(HER2:342), a potential agent for imaging of HER2 expression in malignant tumors. Int J Mol Med 2007;20:397–404.
Schubiger PA, Alberto R, Smith A. Vehicles, chelators, and radionuclides: choosing the “building blocks” of an effective therapeutic radioimmunoconjugate. Bioconjug Chem 1996;7:165–79.
Knapp FF Jr, Mirzadeh S. The continuing important role of radionuclide generator systems for nuclear medicine. Eur J Nucl Med 1994;21:1151–65.
Horak E, Hartmann F, Garmestani K, Wu C, Brechbiel M, Gansow OA, et al. Radioimmunotherapy targeting of HER2/neu oncoprotein on ovarian tumor using lead-212-DOTA-AE1. J Nucl Med 1997;38:1944–50.
Su FM, Beaumier P, Axworthy D, Atcher R, Fritzberg A. Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy in tumored mice using an in vivo 212Pb/212Bi generator. Nucl Med Biol 2005; 32:741–7.
Milenic DE, Garmestani K, Brady ED, Albert PS, Ma D, Abdulla A, et al. Alpha-particle radioimmunotherapy of disseminated peritoneal disease using a 212Pb-labeled radioimmunoconjugate targeting HER2. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2005;20:557–68.
McDevitt MR, Ma D, Simon J, Frank RK, Scheinberg DA. Design and synthesis of 225Ac radioimmunopharmaceuticals. Appl Radiat Isot 2002;57:841–7.
Miederer M, McDevitt MR, Sgouros G, Kramer K, Cheung NK, Scheinberg DA. Pharmacokinetics, dosimetry, and toxicity of the targetable atomic generator, 225Ac-HuM195, in nonhuman primates. J Nucl Med 2004;45:129–37.
Dahle J, Borrebaek J, Melhus KB, Bruland OS, Salberg G, Olsen DR, et al. Initial evaluation of 227Th-p-benzyl-DOTA-rituximab for low-dose rate alpha-particle radioimmunotherapy. Nucl Med Biol 2006;33:271–9.
Melhus KB, Larsen RH, Stokke T, Kaalhus O, Selbo PK, Dahle J. Evaluation of the binding of radiolabeled rituximab to CD20-positive lymphoma cells: an in vitro feasibility study concerning low-dose-rate radioimmunotherapy with the alpha-emitter 227Th. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2007;22:469–79.
Rösch F, Brockmann J, Lebedev NA, Qaim SM. Production and radiochemical separation of the Auger electron emitter 140Nd. Acta Oncol 2000;39:727–30.
Yakushev EA, Kovalík A, Filosofov DV, Korolev NA, Lebedev NA, Lubashevski AV, et al. An experimental comparison of the K- and L-Auger electron spectra generated in the decays of 140Nd and 111In. Appl Radiat Isot 2005;62:451–6.
Lubberink M, Lundqvist H, Tolmachev V. Production, PET performance and dosimetric considerations of 134Ce/134La, an Auger electron and positron-emitting generator for radionuclide therapy. Phys Med Biol 2002;47:615–29.
Jaggi JS, Kappel BJ, McDevitt MR, Sgouros G, Flombaum CD, Cabassa C, et al. Efforts to control the errant products of a targeted in vivo generator. Cancer Res 2005;65:4888–95.
Jaggi JS, Seshan SV, McDevitt MR, Sgouros G, Hyjek E, Scheinberg DA. Mitigation of radiation nephropathy after internal alpha-particle irradiation of kidneys. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;64:1503–12.
Orlova A, Bruskin A, Sjöström A, Lundqvist H, Gedda L, Tolmachev V. Cellular processing of 125I- and 111In-labeled epidermal growth factor (EGF) bound to cultured A431 tumor cells. Nucl Med Biol 2000;27:827–35.
Acknowledgement
This study was financially supported by a grant from the Swedish Cancer Society. The authors thank Dr. Fredrik Y Frejd (Affibody AB) for stimulating discussions. We thank also Veronika Eriksson and the staff of the animal facility of Rudbeck Laboratory for technical assistance. The authors also wish to thank the personnel of the Svedberg Laboratory, Uppsala, Sweden, especially Lars Einarsson, for technical support in the production of 114mIn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolmachev, V., Wållberg, H., Andersson, K. et al. The influence of Bz-DOTA and CHX-A″-DTPA on the biodistribution of ABD-fused anti-HER2 Affibody molecules: implications for 114mIn-mediated targeting therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36, 1460–1468 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1134-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1134-9