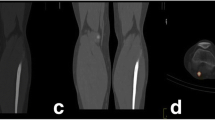
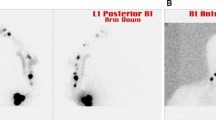
Abstract
Purpose
We compared the outcome of a 1-day and a 2-day sentinel node (SN) biopsy procedure, evaluated in terms of lymphoscintigraphic, surgical and pathological findings.
Methods
We studied 476 patients with melanoma from two melanoma centres using static scintigraphy and blue dye. A proportional odds model was used for statistical analysis.
Results
The number of SNs visualized at scintigraphy increased significantly with time from injection to scintigraphy and activity left in the patient at scintigraphy, and depended on the melanoma location. The number of SNs removed at surgery increased with the number of SNs visualized at scintigraphy and time from injection to surgery. The frequency of nodal metastasis increased with increasing thickness and Clark level of the melanoma, and was highest for two SNs visualized at scintigraphy.
Conclusion
This study showed that early vs. late imaging and surgery do make a difference on the outcome of the SN procedure and confirmed the importance of the scintigraphic visualization of all true SNs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balch CM, Soong S, Ross MI, Urist MM, Karakousis CP, Temple WJ, et al. Long-term results of a multi-institutional randomized trial comparing prognostic factors and surgical results for intermediate thickness melanomas (1.0 to 4.0 mm). Intergroup Melanoma Surgical Trial. Ann Surg Oncol 2000;7:87–97.
Morton DL, Wen DR, Wong JH, Economou JS, Cagle LA, Storm FK, et al. Technical details of intraoperative lymphatic mapping for early stage melanoma. Arch Surg 1992;127:392–9.
Uren RF, Howman-Giles R, Thompson JF, McCarthy WH, Quinn MJ, Roberts JM, et al. Interval nodes. The forgotten sentinel nodes in patients with melanoma. Arch Surg 2000;135:1168–72.
Lock-Andersen J, Horn J, Sjøstrand H, Nürnberg BM, Stokholm KH. Sentinel node biopsy in cutaneous melanoma. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 2006;40:24–31.
Chakera AH, Drzewiecki KT, Eigtved A, Juhl BR. Sentinel node biopsy for melanoma: a study of 241 patients. Melanoma Res 2004;14:521–6.
Stokes ME, Davis CS, Koch GG. Categorical data analysis using the SAS system, 2nd ed. Cary NC: SAS Institute; 2000.
Liang K-Y, Zeger SL. Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika 1986;7:13–22.
Lipsitz SR, Kim K, Zhao L. Analysis of repeated categorical data using generalized estimation equation. Stat Med 1994;13:1149–63.
Uren RF, Howman-Giles R, Thompson JF. Patterns of lymphatic drainage from the skin in patients with melanoma. J Nucl Med 2003;44:570–82.
Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong SJ, Atkins MB, Cascinelli N, Coit DG, et al. New TNM melanoma staging system: linking biology and natural history to clinical outcomes. Semin Surg Oncol 2003;21:43–52.
Cook MG, Green MA, Anderson B, Eggermont AM, Ruiter DJ, Spatz A, et al. The development of optimal pathological assessment of sentinel lymph nodes for melanoma. J Pathol 2003;200:314–9.
Abrahamsen HN, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Larsen J, Steiniche T. Sentinel lymph nodes in malignant melanoma: extended histopathologic evaluation improves diagnostic precision. Cancer 2004;100:1683–91.
Riber-Hansen R, Sjoegren P, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Steiniche T. Extensive pathological analysis of selected melanoma sentinel lymph nodes: high metastasis detection rates at reduced workload. Ann Surg Oncol 2008;15:1492–501.
Uren RF, Howman-Giles R, Thompson JF, Shaw HM, Quinn MJ, O’Brien CJ, et al. Lymphoscintigraphy to identify sentinel lymph nodes in patients with melanoma. Melanoma Res 1994;4:395–9.
Ross MI, Reintgen DI. Role of lymphatic mapping and sentinel node biopsy in the detection of melanoma nodal metastases. Eur J Cancer 1998;34(Suppl 3):S7–11.
McCarter MD, Yeung H, Yeh S, Fey J, Borgen PI, Cody HS 3rd. Localization of the sentinel node in breast cancer: identical results with same-day and day-before isotope injection. Ann Surg Oncol 2001;8:682–6.
Chakera AH, Friis E, Hesse U, Al-Suliman N, Zerahn B, Hesse B. Factors of importance for scintigraphic non-visualization of sentinel nodes in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:286–93.
Babiera GV, Delpassand ES, Breslin TM, Ross MI, Ames FC, Singletary SE, et al. Lymphatic drainage patterns on early versus delayed breast lymphoscintigraphy performed after injection of filtered Tc-99m sulfur colloid in breast cancer patients undergoing sentinel lymph node biopsy. Clin Nucl Med 2005;30:11–5.
Koizumi M, Nomura E, Yamada Y, Takiguchi T, Tanaka K, Yoshimoto M, et al. Sentinel node detection using 99mTc-rhenium sulphide colloid in breast cancer patients: evaluation of 1 day and 2 day protocols, and a dose-finding study. Nucl Med Commun 2003;24:663–70.
Goyal A, Douglas-Jones AG, Newcombe RG, Mansel RE. Effect of lymphatic tumor burden on sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Breast J 2005;11:188–94.
Morton DL, Bostick PJ. Will the true sentinel node please stand? Ann Surg Oncol 1999;6:12–4.
Roaten JB, Pearlman N, Gonzalez R, Gonzalez R, McCarter MD. Identifying risk factors for complications following sentinel lymph node biopsy for melanoma. Arch Surg 2005;140:85–9.
Uren RF, Howman-Giles RB, Thompson JF. Demonstration of second-tier lymph nodes during preoperative lymphoscintigraphy for melanoma: incidence varies with primary tumor site. Ann Surg Oncol 1998;5:517–21.
McMasters KM, Reintgen DS, Ross MI, Wong SL, Gershenwald JE, Krag DN, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for melanoma: how many radioactive nodes should be removed? Ann Surg Oncol 2001;8:192–7.
Klausen TL, Chakera AH, Friis E, Rank F, Heses B, Holm S. Radiation doses to staff involved in sentinel node operations for breast cancer. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2005;25:196–202.
Tanis PJ, van Sandick JW, Nieweg OE, Valdés Olmos RA, Rutgers EJT, Hoefnagel CA, et al. The hidden sentinel node in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:305–11.
Valdés Olmos RA, Tanis PJ, Hoefnagel CA, Nieweg OE, Muller SH, Rutgers EJ, et al. Improved sentinel node visualization in breast cancer by optimizing the colloid particle concentration and tracer dosage. Nucl Med Commun 2001;22:579–86.
Mariani G, Gipponi M, Moresco L, Villa G, Bartolomei M, Mazzarol G, et al. Radioguided sentinel lymph node biopsy in malignant cutaneous melanoma. J Nucl Med 2002;43(6):811–27.
Mariani G, Moresco L, Viale G, Villa G, Bagnasco M, Canavese G, et al. Radioguided sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer surgery. J Nucl Med 2001;42(8):1198–215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakera, A.H., Lock-Andersen, J., Hesse, U. et al. One-day or two-day procedure for sentinel node biopsy in melanoma?. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36, 928–937 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-1036-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-1036-2