Abstract
Purpose
Abnormality of the brain norepinephrine transporter (NET) has been reported in several psychiatric and neuronal disorders. Since NET is an important target for the diagnosis of these diseases, the development of radiopharmaceuticals for imaging of brain NET has been eagerly awaited. In this study, we synthesized (S,S)-2-(α-(2-iodophenoxy)benzyl)morpholine [(S,S)-IPBM], a derivative of reboxetine iodinated at position 2 of the phenoxy ring, and evaluated its potential as a radiopharmaceutical for imaging brain NET using SPECT.
Methods
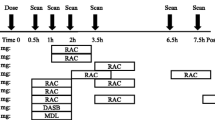
(S,S)-123/125I-IPBM was synthesized in a halogen exchange reaction. The affinity and selectivity of (S,S)-IPBM for NET was measured by assaying the displacement of 3H-nisoxetine and (S,S)-125I-IPBM from the binding site in rat brain membrane, respectively. The biodistribution of (S,S)-125I-IPBM was also determined in rats. Furthermore, SPECT studies with (S,S)-123I-IPBM were carried out in the common marmoset.
Results
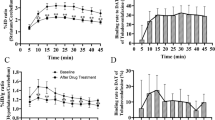
(S,S)-125I-IPBM was prepared with high radiochemical yields (65%) and high radiochemical purity (>98%). (S,S)-IPBM showed high affinity and selectivity for NET in the binding assay experiments. In biodistribution experiments, (S,S)-125I-IPBM showed rapid uptake in the brain, and the regional cerebral distribution was consistent with the density of NET. The administration of nisoxetine, a selective NET-binding agent, decreased the accumulation of (S,S)-125I-IPBM in the brain, but the administration of selective serotonin transporter and dopamine transporter binding agents caused no significant changes in the accumulation. Moreover, (S,S)-123I-IPBM allowed brain NET imaging in the common marmoset with SPECT.
Conclusion
These results suggest that (S,S)-123I-IPBM is a potential SPECT radiopharmaceutical for imaging brain NET.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blakely RD, De Felice LJ, Hartzell HC. Molecular physiology of orepinephrine and serotonin transporters. J Exp Biol 1994;196:263–281
Schomig E, Fischer P, Schonfeld CL, Trendelenburg U. The extent of neuronal re-uptake of 3H-noradrenaline in isolated vasa deferentia and atria of the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 1989;340:502–508
Ryu SH, Lee SH, Lee HJ, Cha JH, Ham BJ, Han CS, et al. Association between norepinephrine transporter gene polymorphism and major depression. Neuropsychobiology 2004;49:174–177
Klimek V, Stockmeier C, Overholser J, Meltzer HY, Kalka S, Dilley G, et al. Reduced levels of norepinephrine transporters in the locus coeruleus in major depression. J Neurosci 1997;17:8451–8458
Brunello N, Mendlewicz J, Kasper S, Leonard B, Montgomery S, Nelson J, et al. The role of noradrenaline and selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibition in depression. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2002;12:461–475
Marien MR, Colpaert FC, Rosenquist AC. Noradrenergic mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases: a theory. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 2004;45:38–78
Tejani-Butt SM, Yang J, Zaffar H. Norepinephrine transporter sites are decreased in the locus coeruleus in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1993;631:147–150
Kiyono Y, Kanegawa N, Kawashima H, Kitamura Y, Iida Y, Saji H. Evaluation of radioiodinated (R)-N-methyl-3-(2-iodophenoxy)-3-phenylpropanamine as a ligand for brain norepinephrine transporter imaging. Nucl Med Biol 2004;31:147–153
Kung MP, Choi SR, Hou C, Zhuang ZP, Foulon C, Kung HF. Selective binding of 2-[125I]iodo-nisoxetine to norepinephrine transporters in the brain. Nucl Med Biol 2004;31:533–541
Chumpradit S, Kung MP, Panyachotipun C, Prapansiri V, Foulon C, Brooks BP, et al. Iodinated tomoxetine derivatives as selective ligands for serotonin and norepinephrine uptake sites. J Med Chem 1992;35:4492–4497
Gehlert DR, Schober DA, Hemrick-Luecke SK, Krushinski J, Howbert JJ, Robertson DW, et al. Novel halogenated analogs of tomoxetine that are potent and selective inhibitors of norepinephrine uptake in brain. Neurochem Int 1995;26:47–52
Millan MJ, Gobert A, Lejeune F, Newman-Tancredi A, Rivet JM, Auclair A, et al. S33005, a novel ligand at both serotonin and norepinephrine transporters: I. Receptor binding, electrophysiological, and neurochemical profile in comparison with venlafaxine, reboxetine, citalopram, and clomipramine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001;298:565–580
Wilson AA, Johnson DP, Mozley D, Hussey D, Ginovart N, Nobrega J, et al. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of novel radiotracers for the in vivo imaging of the norepinephrine transporter. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:85–92
Ding YS, Lin KS, Garza V, Carter P, Alexoff D, Logan J, et al. Evaluation of a new norepinephrine transporter PET ligand in baboons, both in brain and peripheral organs. Synapse 2003;50:345–352
Schou M, Halldin C, Sovago J, Pike VW, Gulyas B, Mozley PD, et al. Specific in vivo binding to the norepinephrine transporter demonstrated with the PET radioligand, (S,S)-[11C]MeNER. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:707–714
Schou M, Halldin C, Sovago J, Pike VW, Hall H, Gulyas B, et al. PET evaluation of novel radiofluorinated reboxetine analogs as norepinephrine transporter probes in the monkey brain. Synapse 2004;53:57–67
Melloni P, Della Torre A, Lazzari E, Mazzini G, Meroni M. Configurational studies on 2-[α-(2-ethoxyphenoxy)benzyl] morpholine FCE 20124. Tetrahedron 1985;41:1393–1399
Cheetham SC, Viggers JA, Butler SA, Prow MR, Heal DJ. [3H]nisoxetine—a radioligand for noradrenaline reuptake sites: correlation with inhibition of [3H]noradrenaline uptake and effect of DSP-4 lesioning and antidepressant treatments. Neuropharmacology 1996;35:63–70
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951;193:265–275
Choi SR, Hou C, Oya S, Mu M, Kung MP, Siciliano M, et al. Selective in vitro and in vivo binding of [125I]ADAM to serotonin transporters in rat brain. Synapse 2000;38:403–412
Cheng Y, Prusoff WH. Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (IC50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 1973;22:3099–3108
Tejani-Butt SM. [3H]nisoxetine: a radioligand for quantitation of norepinephrine uptake sites by autoradiography or by homogenate binding. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1992;260:427–436
Tseng YT, Padbury JF. Expression of a pulmonary endothelial norepinephrine transporter. J Neural Transm 1998;105:1187–1191
Kiyono Y, Kanegawa N, Kawashima H, Fujiwara H, Iida Y, Nishimura H, et al. A new norepinephrine transporter imaging agent for cardiac sympathetic nervous function imaging: radioiodinated (R)-N-methyl-3-(2-iodophenoxy)-3-phenylpropanamine. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:697–706
Toyohira Y, Yanagihara N, Minami K, Ueno S, Uezono Y, Tachikawa E, et al. Down-regulation of the noradrenaline transporter by interferon-alpha in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells. J Neurochem 1998;70:1441–1447
Ding YS, Lin KS, Logan J, Benveniste H, Carter P. Comparative evaluation of positron emission tomography radiotracers for imaging the norepinephrine transporter: (S,S) and (R,R) enantiomers of reboxetine analogs ([11C]methylreboxetine, 3-Cl-[11C]methyl-reboxetine and [18F]fluororeboxetine), (R)-[11C]nisoxetine, [11C]oxaprotiline and [11C]lortalamine. J Neurochem 2005;94:337–351
Logan J, Ding YS, Lin KS, Pareto D, Fowler J, Biegon A. Modeling and analysis of PET studies with norepinephrine transporter ligands: the search for a reference region. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32:531–542
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Daiichi Radioisotope Laboratories Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, for providing Na123I. This study was supported in part by Grants-in-aid for General Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and the 21st Century COE Program “Knowledge Information Infrastructure for Genome Science”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanegawa, N., Kiyono, Y., Kimura, H. et al. Synthesis and evaluation of radioiodinated (S,S)-2-(α-(2-iodophenoxy)benzyl)morpholine for imaging brain norepinephrine transporter. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33, 639–647 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-0017-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-0017-y