Abstract
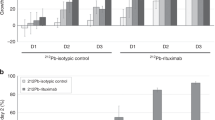
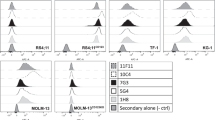
This study demonstrates high-efficiency sterilisation of single cancer cells in a SCID mouse model of leukaemia using rituximab, a monoclonal antibody that targets CD20, labelled with terbium-149, an alpha-emitting radionuclide. Radio-immunotherapy with 5.5 MBq labelled antibody conjugate (1.11 GBq/mg) 2 days after an intravenous graft of 5·106 Daudi cells resulted in tumour-free survival for >120 days in 89% of treated animals. In contrast, all control mice (no treatment or treated with 5 or 300 µg unlabelled rituximab) developed lymphoma disease. At the end of the study period, 28.4%±4% of the long-lived daughter activity remained in the body, of which 91.1% was located in bone tissue and 6.3% in the liver. A relatively high daughter radioactivity concentration was found in the spleen (12%±2%/g), suggesting that the killed cancer cells are mainly eliminated through the spleen. This promising preliminary in vivo study suggests that targeted alpha therapy with 149Tb is worthy of consideration as a new-generation radio-immunotherapeutic approach.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall EJ. Radiobiology for the radiologist. 4th edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1994.
Maecklis RM, Lin JY, Beresford B, Achter RW, Hines JJ, Humm JL. Cellular kinetics, dosimetry, and radiobiology of alpha-particle radioimmunotherapy: inducing of apoptosis. Radiat Res 1992; 130:220–226.
McDevitt MR, Ma D, Simon J, Frank RK, Scheinberg D. Design of225Ac-radiopharmaceuticals. Appl Rad Isot 2002; 57:841–847.
Allen BJ, Blagojevic N. Alpha and beta emitting radiolanthanides in targeted cancer therapy: the potential role for terbium-149. Nucl Med Commun 1996; 17:40–47.
Zalutsky MR, Vaidyanathan G. Astatine-211 labeled radiotherapeuticals: an emerging approach to targeted alpha particle therapy. Current Pharm Design 2000; 6:1433–1455.
Huber R, Seidl C, Schmid E, Seidenschwang S, Becker K-F, Schuhmacher C, Apostolidis C, Nikula T, Kremmer E, Schwaiger M, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke. Locoregional alpha-radioimmunotherapy of intraperitoneal tumor cell dissemination using a tumor-specific monoclonal antibody. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9:3922–3928.
Jurcic JG, Larson SM, Sgouros G, McDevitt MR, Finn RD, Divgi CR, Ballangrud ÅM, Hamacher KA, Ma D, Humm JL, Brechbiel MW, Molinet R, Scheinberg DA. Targeted α-particle immunotherapy for myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002; 100:1233–1239.
McDevitt MR, Sgouros G, Finn RD, Humm JL, Jurcic JG, Larson SM, Scheinberg DA. Radioimmunotherapy with alpha-emitting radionuclides. Eur J Nucl Med 1998; 25:1341–1351.
Allen BJ, Goozee G, Imam S, Sarkar S, Leigh J, Beyer G-J. Targeted cancer therapy: The potential role of terbium-149. 6th International Conference on Radiopharmaceutical Dosimetry, Gatlington, Tenn. (USA), May 7–10, 1996, CERN-PPE/96–127, 1996
Charlton DE, Utteridge TD, Allen BJ. Theoretical treatment of human hemopoietic stem cell survival following irradiation by alpha particles. Int J Radiat Biol 1998; 74:111–118.
Allen BJ. Can alpha immunotherapy succeed where other modalities have failed? Nucl Med Commun 1999; 20:205–207.
Wagner HN Jr, Wiseman GA, Marcus CS, et al. Administration guidelines for radioimmunotherapy of Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with90Y-labeled anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. J Nucl Med 2002; 43:267–272.
Miederer M, Seidl C, Beyer G-J, Charlton DE, Vranješ-Đurić SD, Čomor JJ, Huber R, Nikula T, Apostolidis C, Schuhmacher C, Becker K-F, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R. Comparison of the radiotoxicity of two alpha emitting immunoconjugates, terbium-149 and bismuth-213, directed against a tumor-specific, exon 9 deleted (d9) E-cadherin adhesion protein. Radiat Res 2002; 159:612–620.
Vranješ SD, Miederer M, Čomor JJ, Soloviev D, Beyer G-J and the ISOLDE collaboration. Labeling of monoclonal antibodies with 149-Tb for targeted alpha therapy. J Lab Comp Radiopharm 2001; 44:718–720.
Ghetie MA, Richardson J, Tucker T, Jones D, Uhr JW, Vitetta ES. Disseminated or localized growth of a human B-cell tumor (Daudi) in SCID mice. Int J Cancer 1990; 45:481–485.
McDevitt MR, Ma D, Lai LT, Simon J, Borchardt P, Frank RK, Wu K, Pellegrini V, Curcio MJ, Miederer M, Bander NH, Scheinberg DA. Tumor therapy with targeted atomic nanogenerators. Science 2001; 294:1537–1540.
Firestone RB. Table of isotopes, 8th edn. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1996.
Kugler E. The ISOLDE facility. Hyperfine Interactions 2000; 129:23–42.
Beyer G-J, Čomor JJ, Daković M, Soloviev D, Tamburella C, Hagebø E, Allan B, Dmitriev SN, Zaitseva NG, Starodub GY, Molokanova LG, Vranješ SD, Miederer M, and the ISOLDE Collaboration. Production routes of the alpha emitting 149-Tb for medical application. Radiochim Acta 2002; 90:247–252.
Beyer G-J, Offord RE, Künzi G, Jones RML, Ravn U, Aleksandrova Y, Werlen RC, Mäcke H, Lindroos M, Jahn S, Tengblad O, and the ISOLDE Collaboration. Biokinetics of monoclonal antibodies labeled with radio-lanthanides and 225-Ac in xenografted nude mice. J Label Compd Radiopharm 1995; 37:229–530.
Beyer G-J, Münze R, Fromm WD, Franke WG, Henke E, Khalkin VA, Lebedev NA. Spallation produced 167-Tm for medical application. In: Medical radionuclide imaging 1980, vol 1. Vienna: IAEA; 1981:587 (IAEA-SM-247/60).
Beyer G-J, Offord R, Künzi G, Aleksandrova Y, Ravn U, Jahn S, Backe J, Tengblad O, Lindroos M, and the ISOLDE Collaboration. The influence of EDTMP-concentration on the biodistribution of radio-lanthanides and225Ac in tumor bearing mice. Nucl Med Biol 1997; 24:367–372.
Beyer G-J, Bergmann R, Schomäcker K, Rösch F, Schäfer G, Kulikov EV, Novgorodov AF. Comparison of the biodistribution of225Ac and radiolanthanides as citrate complexes. Isotopenpraxis 1990; 26:111–114.
Beyer G-J, Herrmann E, Khalkin VA. Chemical effects related to different radioactive decay processes of cerium isotopes chelated with different polyaminocarbonic acids. Dubna: JINR P 12–7758, 1974.
Beyer G-J, Herrmann E. Chemical effects of nuclear transformations in lanthanide chelate complexes. In: Proceedings of the COST Chemistry Action D18, Mid Term Evaluation Workshop on Lanthanide Chemistry for Diagnosis and Therapy, Heidelberg (Germany), July 22–25, 2002, p 26.
Stabin MG. MIRDOSE: personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 1996; 37:538–546.
Breeman WAP, DeJong M, Krenning EP. Labeling of DOTA-peptides at high specific activities. ICFE’5, Geneva, Switzerland, August 24–29, 2003, CO4-SL8, abstract book p 197.
Beyer G-J, Ruth TJ. The role of electromagnetic separators in the production of radiotracers for bio-medical research and nuclear medical applications. NIM B 2003; 204:694–700.
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank Prof. S. Larson (MSKCC New York) for his very valuable discussion during the preparation of this manuscript and Prof. D. Scheinberg (MSKCC New York) for providing the rituximab-DTPA bioconjugate used in this study. The support by the Swiss National Science Foundation Project Nr. 31–53672.98 and by the European Commission within the HPRI-Program Nr. HPRI-CT-1999–00018 is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyer, GJ., Miederer, M., Vranješ-Đurić, S. et al. Targeted alpha therapy in vivo: direct evidence for single cancer cell kill using 149Tb-rituximab. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31, 547–554 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-003-1413-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-003-1413-9