Abstract
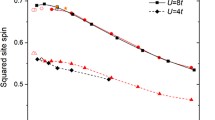
The Projector Quantum Monte Carlo method is used to study the two-dimensional Hubbard model with generalized boundary conditions at half-filling. The convergence of the algorithm depends strongly on the initial trial state. Spin-density waves provide an excellent trial state for the case of weak and of strong correlations. This choice of a trial state with broken symmetry allows us to calculate directly the staggered (or sublattice) magnetization m 0 as a function of the on-site repulsion U. The use of general boundary conditions strongly reduces finite size effects in m 0.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hetzel, R., Topalis, P. & Becker, K. Magnetization in the two-dimensional Hubbard model: a numerical study. Zeitschrift für Physik B Condensed Matter 104, 347–352 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002570050460
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002570050460