Abstract
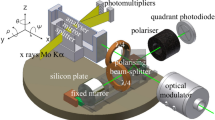
By using the formalism developed in Part I, we investigated errors in the measurement of the silicon lattice parameter by scanning LLL x-ray interferometry. We show that lattice spacing does not determine uniquely the period of travelling fringes unless crystal motion and form are free from geometrical aberrations. Owing to limited accuracy in manufacturing and operation, crystal movement may change interferometer geometry which, in turn, causes period deviations from the spacing of diffracting planes. We review the special cases of the so-called weak and strong absorptions and, additionally, consider the case of medium absorption, which is of great experimental interest. Finally, we examine how the phase of travelling fringes depends on interferometer design and point out non-linear effects and resonances, so far overlooked, which are related to the oscillatory structure of x-ray diffraction.