Abstract.
Objective:
Twisting injuries occur as a result of differential motion of different tissue types in injuries with some rotational force. These injuries are well described in brain injuries but, to our knowledge, have not been described in the musculoskeletal literature. We correlated the clinical examination and MR findings of 20 patients with twisting injuries of the soft tissues around the knee.
Design and patients:
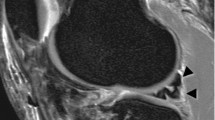
We prospectively followed the clinical courses of 20 patients with knee injuries who had clinical histories and MR findings to suggest twisting injuries of the subcutaneous tissues. Patients with associated internal derangement of the knee (i.e., meniscal tears, ligamentous or bone injuries) were excluded from this study. MR findings to suggest twisting injuries included linear areas of abnormal dark signal on T1-weighted sequences and abnormal bright signal on T2-weighted or short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences and/or signal to suggest hemorrhage within the subcutaneous tissues. These MR criteria were adapted from those established for indirect musculotendinous junction injuries.
Results:
All 20 patients presented with considerable pain that suggested internal derangement on physical examination by the referring orthopedic surgeons. All presented with injuries associated with rotational force. The patients were placed on a course of protected weight-bearing of the affected extremity for 4 weeks. All patients had pain relief by clinical examination after this period of protected weight-bearing.
Conclusions:
Twisting injuries of the soft tissues can result in considerable pain that can be confused with internal derangement of the knee on physical examination. Soft tissue twisting injuries need to be recognized on MR examinations as they may be the cause of the patient’s pain despite no MR evidence of internal derangement of the knee. The demonstration of soft tissue twisting injuries in a patient with severe knee pain but no documented internal derangement on MR examination may allow the orthopedic surgeon to elect for a trial of conservative nonsurgical management.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 December 2000 Revision requested: 8 February 2001 Revision received: 27 February 2001 Accepted: 27 February 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magee, T., Shapiro, M. Soft tissue twisting injuries of the knee. Skeletal Radiol 30, 460–463 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002560100365
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002560100365