Abstract
Objective
To demonstrate the potential of low-dose ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT) images to generate high-quality radiographic images on extremity phantoms and to estimate the radiation dose required for this.
Materials and methods
A hand and knee phantom containing real human bones was imaged on an UHRCT scanner at full-dose, half-dose, and quarter-dose levels using a high-resolution extremity protocol. The raw data was reconstructed using both filtered back projection (FBP) and an iterative reconstruction algorithm (AIDR3D). Using custom designed software, each CT volume data set was converted to attenuation coefficients, and then a synthesized radiograph (synDX) was generated by forward projecting the volume data sets from a point source onto a 2D synthetic detector. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was measured in the synDXs across all dose levels and the root-mean-squared error (RMSE) was computed with the FD synDXs as the reference.
Results
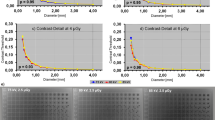
The proposed workflow generates high-quality synDXs at any arbitrary angle. For FBP, the SNR largely tracked with the radiation dose levels for both the knee and hand phantoms. For the knee phantom, iterative reconstruction provided a 6.1% higher SNR when compared to FBP. The RMSE was overall higher for the lowest dose levels and monotonically decreased with increasing dose. No substantial differences were observed qualitatively in the visualization of skeletal detail of the phantoms.
Conclusion
The fine detail provided by UHRCT acquisitions of extremities facilitates the ability to generate quality radiographs, potentially eliminating the need for additional scanning on a conventional digital radiography system.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The algorithm (in MATLAB) used to generate the synthesized radiographs from UHRCT acquisitions is available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Rui P, Kang K, Ashman JJ. National hospital ambulatory medical care survey: 2017 emergency department summary tables. National center for health statistics. 2017. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhamcs/web_tables/2017_ed_web_tables-508.pdf. Accessed 28 Sept 2023.
Ilan DI, Rettig ME. Rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2003;61(3–4):179–85.
Felson DT. The epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis: results from the Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990;20(3 Suppl 1):42–50.
Belsole RJ. Radiography of the wrist. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;202:50–6.
Mino DE, Palmer AK, Levinsohn EM. The role of radiography and computerized tomography in the diagnosis of subluxation and dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1983;8(1):23–31.
Hernandez AM, Wu P, Mahesh M, Siewerdsen JH, Boone JM. Location and direction dependence in the 3D MTF for a high-resolution CT system. Med Phys. 2021;48(6):2760–71.
Tsubamoto M, Hata A, Yanagawa M, Honda O, Miyata T, Yoshida Y, et al. Ultra high-resolution computed tomography with 1024-matrix: comparison with 512-matrix for the evaluation of pulmonary nodules. Eur J Radiol. 2020;128:109033.
Hata A, Yanagawa M, Honda O, Kikuchi N, Miyata T, Tsukagoshi S, et al. Effect of matrix size on the image quality of ultra-high-resolution CT of the lung: comparison of 512 x 512, 1024 x 1024, and 2048 x 2048. Acad Radiol. 2018;25(7):869–76.
Hernandez AM, Boone JM. Tungsten anode spectral model using interpolating cubic splines: unfiltered x-ray spectra from 20 kV to 640 kV. Med Phys. 2014;41(4):042101.
Boone JM, Strauss KJ, Cody DD, McCollough CH, McNitt-Gray MF, Toth TL, et al. Size-specific dose estimates (SSDE) in pediatric and adult body CT examinations: the report of AAPM Task Group 204. American Association of Physicists in Medicine website 2011. https://www.aapm.org/pubs/reports/rpt_204.pdf.
Boone J, Strauss K, Hernandez A, Hardy A, Applegate K, Artz N, et al. Size specific dose estimate (SSDE) for head CT: the report of AAPM Task Group 293. American Association of Physicists in Medicine website 2019. https://www.aapm.org/pubs/reports/RPT_293.pdf.
Saltybaeva N, Jafari ME, Hupfer M, Kalender WA. Estimates of effective dose for CT scans of the lower extremities. Radiology. 2014;273(1):153–9.
Koivisto J, Kiljunen T, Wolff J, Kortesniemi M. Assessment of effective radiation dose of an extremity CBCT, MSCT and conventional X ray for knee area using MOSFET dosemeters. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2013;157(4):515–24.
Koivisto J, van Eijnatten M, Kiljunen T, Shi XQ, Wolff J. Effective radiation dose in the wrist resulting from a radiographic device, two CBCT devices and one MSCT device: a comparative study. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2018;179(1):58–68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors A.M.H. and J.M.B. have research funding from Canon.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hernandez, A.M., Bayne, C.O., Bateni, C. et al. Extremity radiographs derived from low-dose ultra-high-resolution CT: a phantom study. Skeletal Radiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-024-04600-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-024-04600-y