Abstract
Objective
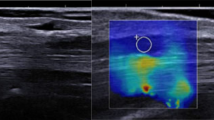
To quantify the shear velocity and stiffness of the median nerve (MN) with shear wave elastography (SWE) at the carpal tunnel entrance and determine whether SWE is useful for diagnosing and staging carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
Materials and methods
The study included 58 patients (79 wrists) with clinical and electroneuromyographic diagnoses of CTS and 55 healthy controls (63 wrists). MN shear velocity and stiffness were measured by SWE on the axial plane in both groups. The differences between CTS patients and controls and between different grades of CTS based on electrodiagnostic tests were studied using Student’s t test and ANOVA with ROC analysis.
Results
The mean MN shear velocity and stiffness were significantly greater in CTS patients (2.5 ± 0.37 m/s and 19.4 ± 5.8 kPa) than in controls (1.91 ± 0.24 m/s and 11.1 ± 3.0 kPa) (p < 0.001) and greater in the severe CTS group (2.69 ± 0.39 m/s and 22.4 ± 7.1 kPa) than in the mild CTS group (2.37 ± 0.35 m/s and 17.3 ± 4,8 kPa). The cutoff value for the shear velocity was 2.13 m/s, with 86% and 82% sensitivity and specificity, respectively, and the cutoff value for stiffness was 13.6 kPa, with 87% and 82% sensitivity and specificity.
Conclusion
MN shear velocity and stiffness are significantly higher in CTS patients. SWE can be used to diagnose CTS and distinguish between patients with mild and severe disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xin H, Hu HY, Liu B, Liu X, Li X, Li J. Ultrasound elastographic evaluation of the median nerve in hemodialysis with carpal tunnel syndrome. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2017;44(1):123–31.
Kantarci F, Ustabasioglu FE, Delil S, Olgun DC, Korkmazer B, Dikici AS, et al. Median nerve stiffness measurement by shear wave elastography: a potential sonographic method in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(2):434–40.
Koyuncuoglu HR, Kutluhan S, Yesildag A, Oyar O, Guler K, Ozden A. The value of ultrasonographic measurement in carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with negative electrodiagnostic tests. Eur J Radiol. 2005;56(3):365–9.
Yu G, Chen Q, Wang D, Wang X, Li Z, Zhao J, et al. Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome assessed using high-frequency ultrasonography: cross-section areas of 8-site median nerve. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35(10):2557–64.
El Habashy HR, El Hadidy RA, Ahmed SM, El Sayed BB, Ahmed AS. Carpal tunnel syndrome grading using high-resolution ultrasonography. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;34(4):353–8.
Moschovos C, Tsivgoulis G, Kyrozis A, Ghika A, Karachalia P, Voumvourakis K, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of high-resolution ultrasound in screening for carpal tunnel syndrome and grading its severity is moderated by age. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;130(3):321–30.
Schrier VJMM, Lin J, Gregory A, Thoreson AR, Alizad A, Amadio PC, et al. Shear wave elastography of the median nerve: a mechanical study. Muscle Nerve. 2020;61(6):826–33.
Zakrzewski J, Zakrzewska K, Pluta K, Nowak O, Miłoszewska-Paluch A. Ultrasound elastography in the evaluation of peripheral neuropathies: a systematic review of the literature. Pol J Radiol. 2019;84:e581-591.
Taljanovic MS, Gimber LH, Becker GW, Latt LD, Klauser AS, Melville DM, et al. Shear-wave elastography: basic physics and musculoskeletal applications. Radiographics. 2017;37(3):855–70.
Moran L, Royuela A, De Vargas AP, Lopez A, Cepeda Y, Martinelli G. Carpal tunnel syndrome: diagnostic usefulness of ultrasound measurement of the median nerve area and quantitative elastographic measurement of the median nerve stiffness. J Ultrasound Med. 2020;39(2):331–9.
Lin CP, Chen IJ, Chang KV, Wu WT, Özçakar L. Utility of ultrasound elastography in evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019;45(11):2855–65.
Miyamoto H, Morizaki Y, Kashiyama T, Tanaka S. Grey-scale sonography and sonoelastography for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome. World J Radiol. 2016;8(3):281–7.
Nam K, Peterson SM, Wessner CE, Machado P, Forsberg F. Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome using shear wave elastography and high-frequency ultrasound imaging. Acad Radiol. 2021;28(9):e278-287.
Wee TC, Simon NG. Ultrasound elastography for the evaluation of peripheral nerves: a systematic review. Muscle Nerve. 2019;60(5):501–12.
Cingoz M, Kandemirli SG, Alis DC, Samanci C, Kandemirli GC, Adatepe NU. Evaluation of median nerve by shear wave elastography and diffusion tensor imaging in carpal tunnel syndrome. Eur J Radiol. 2018;101:59–64.
American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine AeAoN, and American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome: summary statement. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 25(6):918–922.
Padua L, LoMonaco M, Gregori B, Valente EM, Padua R, Tonali P. Neurophysiological classification and sensitivity in 500 carpal tunnel syndrome hands. Acta Neurol Scand. 1997;96(4):211–7.
Wee TC, Simon NG. Shearwave elastography in the differentiation of carpal tunnel syndrome severity. PM R. 2020;12(11):1134–9.
Paluch Ł, Pietruski P, Walecki J, Noszczyk BH. Wrist to forearm ratio as a median nerve shear wave elastography test in carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018;71(8):1146–52.
Zhang C, Li M, Jiang J, Zhou Q, Xiang L, Huang Y, et al. Diagnostic value of virtual touch tissue imaging quantification for evaluating median nerve stiffness in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36(9):1783–91.
He Y, Xiang X, Zhu BH, Qiu L. Shear wave elastography evaluation of the median and tibial nerve in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019;9(2):273–82.
Aslan M, Aslan A, Emeksiz HC, Candan F, Erdemli S, Tombul T, et al. Assessment of peripheral nerves with shear wave elastography in type 1 diabetic adolescents without diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Ultrasound Med. 2019;38(6):1583–96.
Tang X, Zhu B, Tian M, Guo R, Huang S, Tang Y, et al. Preliminary study on the influencing factors of shear wave elastography for peripheral nerves in healthy population. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):5582.
Arslan H, Yavuz A, İlgen F, Aycan A, Ozgokce M, Akdeniz H, et al. The efficiency of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography in the diagnosis and staging of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2018;45(3):453–9.
Mohammadi A, Afshar A, Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari M, Mokhtari SAS. Application of shear wave elastography and median nerve cross-section area in the diagnosis and staging of carpal tunnel syndrome: a case-control study. Pol J Radiol. 2021;86:e638–43.
Abrishamchi F, Zaki B, Basiri K, Ghasemi M, Mohaghegh M. A comparison of the ultrasonographic median nerve cross-sectional area at the wrist and the wrist-to-forearm ratio in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Res Med Sci. 2014;19(12):1113–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sernik, R.A., Pereira, R.F.B., Cerri, G.G. et al. Shear wave elastography is a valuable tool for diagnosing and grading carpal tunnel syndrome. Skeletal Radiol 52, 67–72 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04143-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04143-0