Abstract
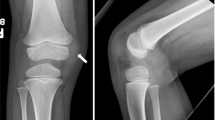
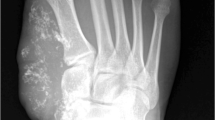
Fibroma-like perivascular epithelioid cell (PEComa) tumor is an extremely rare family of mesenchymal tumors composed of cells co-expressing melanocytic and myogenic markers. To date, 13 cases of primary bone PEComa have been reported in the literature and five reported fibroma-like PEComas were found in the soft tissues of patients with tuberous sclerosis (TSC). However, no fibroma-like PEComa has been reported in bone, either sporadic or TSC-associated. Here we report the case of a 22-year-old man with known TSC, who presented for evaluation of an asymptomatic mass in his left fibula diaphysis that had been present for 5 years. He had no activity-related pain, numbness, weakness, or limitations in range of motion. Both 3-T MRI and CT demonstrated a tumor originating from the midshaft middiaphyseal fibula. Axial T1-weighted and fat-saturated T2-weighted fast spin echo images showed a well-defined lesion in the fibula with extension into the surrounding soft tissues. Whole body bone scan was negative for metastasis using technetium-99m. Renal ultrasound was unremarkable with no evidence of angiomyolipoma. Histopathology demonstrated isolated spindle cells in a dense collagenous matrix. By immunohistochemical staining, tumor cells were positive for HMB-45 and MiTF and partially positive for alpha-smooth muscle actin supporting a diagnosis of fibroma-like PEComa of the midshaft fibula. Although fibroma-like PEComa of bone is very rare, a bone tumor in the setting of TSC should raise suspicion for the diagnosis, in particular if histology demonstrates rare epithelioid cells in a densely fibrotic stroma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thway K, Fisher C. PEComa: morphology and genetics of a complex tumor family. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015;19(5):359–68.
Folpe AL, Mentzel T, Lehr HA, Fisher C, Balzer BL, Weiss SW. Perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms of soft tissue and gynecologic origin: a clinicopathologic study of 26 cases and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29(12):1558–75.
Sukov WR, Cheville JC, Amin MB, Gupta R, Folpe AL. Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) of the urinary bladder: report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33(2):304–8.
Doyle LA, Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. PEComa of the gastrointestinal tract: clinicopathologic study of 35 cases with evaluation of prognostic parameters. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37(12):1769–82.
Yamashita K, Fletcher CD. PEComa presenting in bone: clinicopathologic analysis of 6 cases and literature review. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(11):1622–9.
Liegl B, Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Primary cutaneous PEComa: distinctive clear cell lesions of skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32(4):608–14.
Desy NM, Bernstein M, Nahal A, Aziz M, Kenan S, Turcotte RE, et al. Primary perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm (PEComa) of bone: report of two cases and review of the literature. Skelet Radiol. 2012;41(11):1469–74.
Lian DW, Chuah KL, Cheng MH, Yap WM. Malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumour of the fibula: a report and a short review of bone perivascular epithelioid cell tumour. J Clin Pathol. 2008;61(10):1127–9.
Folpe AL, Kwiatkowski DJ. Perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms: pathology and pathogenesis. Hum Pathol. 2010;41(1):1–15.
Crino PB, Nathanson KL, Henske EP. The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(13):1345–56.
Henske EP, Jozwiak S, Kingswood JC, Sampson JR, Thiele EA. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16035.
Pan CC, Chung MY, Ng KF, Liu CY, Wang JS, Chai CY, et al. Constant allelic alteration on chromosome 16p (TSC2 gene) in perivascular epithelioid cell tumour (PEComa): genetic evidence for the relationship of PEComa with angiomyolipoma. J Pathol. 2008;214(3):387–93.
Argani P, Aulmann S, Illei PB, Netto GJ, Ro J, Cho HY, et al. A distinctive subset of PEComas harbors TFE3 gene fusions. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(10):1395–406.
Odono EIG, Tan KB, Tay SY, Lee VKM. Cutaneous ‘fibroma-like’ perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: a case report and review of literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2020.
Larque AB, Kradin RL, Chebib I, Nielsen GP, Selig MK, Thiele EA, et al. Fibroma-like PEComa: a tuberous sclerosis complex-related lesion. Am J Surg Pathol. 2018;42(4):500–5.
Harvey JP, Suster DI, Raskin KA, Nielsen GP, Bredella MA. Intra-articular fibroma-like perivascular epithelioid tumor (PEComa) mimicking tenosynovial giant cell tumor, diffuse type. Skelet Radiol. 2019;48(6):965–9.
Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Sclerosing PEComa: clinicopathologic analysis of a distinctive variant with a predilection for the retroperitoneum. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32(4):493–501.
Insabato L, De Rosa G, Terracciano LM, Fazioli F, Di Santo F, Rosai J. Primary monotypic epithelioid angiomyolipoma of bone. Histopathology. 2002;40(3):286–90.
Torii I, Kondo N, Takuwa T, Matsumoto S, Okumura Y, Sato A, et al. Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the rib. Virchows Arch. 2008;452(6):697–702.
Righi A, Dimosthenous K, Rosai J. PEComa: another member of the MiT tumor family? Int J Surg Pathol. 2008;16:16–20.
Kazzaz D, Khalifa M, Alorjan M, Shaw M, Rezajooi K, Saifuddin A. Malignant PEComa of the lumbar vertebra: a rare bone tumour. Skelet Radiol. 2012;41(11):1465–8.
Lao IW, Yu L, Wang J. Malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) of the femur: a case report and literature review. Diagn Pathol. 2015;10:54.
Yu H, Zhu X, Sheng H, Gao H, Xiao W, Wang C. Primary perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm of thigh bone: a case report and literature review. 2016;9:2487–91.
Sadigh S, Shah P, Weber K, Sebro R, Zhang PJ. Primary malignant perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm (PEComa) of the bone mimicking granular cell tumor in core biopsy: a case report and literature review. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(3):2946–52.
Yang J, Tian W, Zhu X, Wang J. Chondroblastoma in the long bone diaphysis: a report of two cases with literature review. Chin J Cancer. 2012;31(5):257–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the mother of the patient due to mild cognitive delay of the patient.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramezanpour, S., Horvai, A.E., Zimel, M. et al. Fibroma-like perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: a rare case in a long bone. Skeletal Radiol 50, 821–825 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03610-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03610-w