Abstract
Objective
The purpose of the study was to investigate if the TKA design (cruciate retaining (CR), posterior stabilized (PS), revision prostheses) had an influence on the bone tracer uptake (BTU) pattern at the origin of the popliteus muscle.
Materials and methods
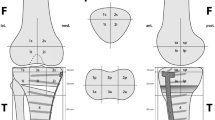
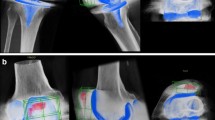
A total of 92 knees (male:female = 46:46) which had undergone prior TKA were included in this retrospective study, comprising the following 3 groups: (i) CR primary TKA (n = 45); (ii) PS primary TKA (n = 24); (iii) revision TKA (n = 23). All patients received a SPECT/CT after TKA surgery. SPECT/CT images were reviewed for the presence of BTU in the lateral femoral condyle (origin of the popliteus muscle) by two observers using Syngo.via software (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). The observers recorded the BTU pattern qualitatively in the lateral femoral condyle as either (i) absent; (ii) present and diffuse; and (iii) present and focal in the region of the popliteus muscle origin.
Results
In patients with a CR and PS design, focal increased BTU at the origin of the popliteus muscle was found in 80.0% and 83.3% respectively. Diffuse BTU was the predominant finding in patients with revision TKA (60.9%). The patterns of BTU did not show significant differences between the CR and the PS design. However, patterns of BTU differed significantly between primary TKA designs and revision TKA (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Differences in patterns of BTU at the popliteus muscle origin between primary TKA and revision prosthesis may be the result of decreased insertional tensile forces of the popliteus muscle after revision surgery due to increased stability provided by the revision design.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadie P, Galaud B, Michaut M, Fallet L, Boisrenoult P, Beaufils P. Distal femur rotational alignment and patellar subluxation: a CT scan in vivo assessment. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009;95:267–71.
Awengen R, Rasch H, Amsler F, Hirschmann MT. Symptomatic versus asymptomatic knees after bilateral total knee arthroplasty: what is the difference in SPECT/CT? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:762–72.
Forrer F, Hirschmann MT, Rasch HF. SPECT/CT for the assessment of painful knee prosthesis. Nucl Med Commun. 2014;35:782.
Hirschmann MT, Iranpour F, Konala P, Kerner A, Rasch H, Cobb JP, et al. A novel standardized algorithm for evaluating patients with painful total knee arthroplasty using combined single photon emission tomography and conventional computerized tomography. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:939–44.
Hirschmann MT, Konala P, Iranpour F, Kerner A, Rasch H, Friederich NF. Clinical value of SPECT/CT for evaluation of patients with painful knees after total knee arthroplasty--a new dimension of diagnostics? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:36.
Slevin O, Schmid FA, Schiapparelli F, Rasch H, Hirschmann MT. Increased in vivo patellofemoral loading after total knee arthroplasty in resurfaced patellae. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26:1805–10.
Slevin O, Schmid FA, Schiapparelli F-F, Rasch H, Amsler F, Hirschmann MT. Coronal femoral TKA position significantly influences in vivo patellar loading in unresurfaced patellae after primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25:3605–10.
Hirschmann MT, Iranpour F, Davda K, Rasch H, Hügli R, Friederich NF. Combined single-photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computerized tomography (SPECT/CT): clinical value for the knee surgeons? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:341–5.
Hirschmann MT, Schön S, Afifi FK, Amsler F, Rasch H, Friederich NF, et al. Assessment of loading history of compartments in the knee using bone SPECT/CT: a study combining alignment and 99mTc-HDP tracer uptake/distribution patterns. J Orthop Res. 2013;31:268–74.
Mathis DT, Hirschmann A, Falkowski AL, Kiekara T, Amsler F, Rasch H, et al. Increased bone tracer uptake in symptomatic patients with ACL graft insufficiency: a correlation of MRI and SPECT/CT findings. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26:563–73.
Rechsteiner J, Hirschmann MT, Dordevic M, Falkowski AL, Testa EA, Amsler F, et al. Meniscal pathologies on MRI correlate with increased bone tracer uptake in SPECT/CT. Eur Radiol. 2018;28:4696–704.
Horger M, Bares R. The role of single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography in benign and malignant bone disease. Semin Nucl Med. 2006;36:286–94.
Hirschmann MT, Amsler F, Rasch H. Clinical value of SPECT/CT in the painful total knee arthroplasty (TKA): a prospective study in a consecutive series of 100 TKA. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:1869–82.
Kesman TJ, Kaufman KR, Trousdale RT. Popliteus tendon resection during total knee arthroplasty: an observational report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:76–81.
Takeda S, Tajima G, Fujino K, Yan J, Kamei Y, Maruyama M, et al. Morphology of the femoral insertion of the lateral collateral ligament and popliteus tendon. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:3049–54.
Bonnin MP, de Kok A, Verstraete M, Van Hoof T, Van Der Straten C, Saffarini M, et al. Popliteus impingement after TKA may occur with well-sized prostheses. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25:1720–30.
Rosner B. The intraclass correlation coefficient. In: Rosner B, editor. Fundamentals of biostatistics. 7th ed. Boston: Brooks/Cole. Cengage Learning; 2011. p. 568–71.
Mucha A, Dordevic M, Hirschmann A, Rasch H, Amsler F, Arnold MP, et al. Effect of high tibial osteotomy on joint loading in symptomatic patients with varus aligned knees: a study using SPECT/CT. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:2315–23.
Cottino U, Bruzzone M, Rosso F, Dettoni F, Bonasia DE, Rossi R. The role of the popliteus tendon in total knee arthroplasty: a cadaveric study: SIGASCOT Best Paper Award Finalist 2014. Joints. 2015;3:15–9.
Simsek ME, Akkaya M, Gursoy S, Isik C, Zahar A, Tarabichi S, et al. Posterolateral overhang affects patient quality of life after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138:409–18.
Ghosh KM, Hunt N, Blain A, Athwal KK, Longstaff L, Amis AA, et al. Isolated popliteus tendon injury does not lead to abnormal laxity in posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:1763–9.
Barnes CL, Scott RD. Popliteus tendon dysfunction following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast. 1995;10:543–5.
Allardyce TJ, Scuderi GR, Insall JN. Arthroscopic treatment of popliteus tendon dysfunction following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast. 1997;12:353–5.
Rasch H, Falkowski AL, Forrer F, Henckel J, Hirschmann MT. 4D-SPECT/CT in orthopaedics: a new method of combined quantitative volumetric 3D analysis of SPECT/CT tracer uptake and component position measurements in patients after total knee arthroplasty. Skelet Radiol. 2013;42:1215–23.
van der Bruggen W, Hirschmann MT, Strobel K, Kampen WU, Kuwert T, Gnanasegaran G, et al. SPECT/CT in the postoperative painful knee. Semin Nucl Med. 2018;48:439–53.
Soininvaara T, Nikola T, Vanninen E, Miettinen H, Kröger H. Bone mineral density and single photon emission computed tomography changes after total knee arthroplasty: a 2-year follow-up study. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2008;28:101–6.
Barthassat E, Afifi F, Konala P, Rasch H, Hirschmann MT. Evaluation of patients with painful total hip arthroplasty using combined single photon emission tomography and conventional computerized tomography (SPECT/CT)—a comparison of semi-quantitative versus 3D volumetric quantitative measurements. BMC Med Imaging. 2017;17:31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Level of clinical evidence: III
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moser, L.B., Mandegaran, R., Hess, S. et al. Increased focal bone tracer uptake at the popliteus muscle origin in primary TKA compared with revision TKA. Skeletal Radiol 49, 1127–1133 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03387-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03387-y