Abstract
Purpose
To use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to investigate the knee joint of children following arthroscopic fixation of osteochondral lesions using bioabsorbable nails and to correlate these imaging findings with time from arthroscopic treatment and with risk factors at the time of imaging.
Materials and methods
Our study included postarthroscopic MRI studies from 58 children (mean age at arthroscopy, 13.8 + 2.1 years) who have undergone bioabsorbable nail fixation of unstable osteochondral lesions between February 1, 2011 and September 30, 2017. All studies were retrospectively reviewed for broken nails, intra-articular debris, and internal knee derangement. Demographic information and information pertaining to active symptoms was obtained from both MRI questionnaire that was completed at the time of the study and clinical note that preceded the study. Marginal logistic regression models estimated using generalized estimating equations (GEE) were used to identify factors associated with a broken nail and joint effusion.
Results
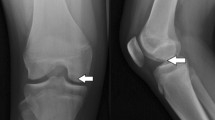
A total of 104 postoperative studies were reviewed, which included 60 with symptoms and 44 without symptoms. Nail breakage was present in 38 (36.6%) studies and associated with presence of symptoms (OR 2.43, p = 0.036) and effusion (OR 2.76, p = 0.025). An effusion was present in 40 (38.5%) studies which decreased with increasing time from treatment (OR 0.89, p = 0.007) and increased with symptoms (OR 10.87, p < 0.001). Meniscal tear was present on 8 (7.7%) and chondral irregularity on 14 (13.5%) studies.
Conclusion
Broken nail, effusion, and less commonly, meniscal tears and chondral irregularity, are all complications that can arise following fixation of osteochondral lesions with bioabsorbable nails. MRI can serve as a valuable tool in assessing these complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 December 2019
Unfortunately in Volume 49, Issue 1 had been published online with an incorrect date (2001 instead of 2020).
References
Matsusue Y, Nakamura T, Suzuki S, Iwasaki R. Biodegradable pin fixation of osteochondral fragments of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;322:166–73.
Gkiokas A, Morassi LG, Kohl S, Zampakides C, Megremis P, Evangelopoulos DS. Bioabsorbable pins for treatment of osteochondral fractures of the knee after acute patella dislocation in children and young adolescents. Adv Orthop. 2012;249687:14.
Dines JS, Fealy S, Potter HG, Warren RF. Outcomes of osteochondral lesions of the knee repaired with a bioabsorbable device. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:62–8.
Makino A, Muscolo DL, Puigdevall M, Costa-Paz M, Ayerza M. Arthroscopic fixation of osteochondritis dissecans of the knee: clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, and arthroscopic follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33:1499–504.
Barrett I, King AH, Riester S, et al. Internal fixation of unstable osteochondritis dissecans in the skeletally mature knee with metal screws. Cartilage. 2016;7:157–62.
Chun KC, Kim KM, Jeong KJ, Lee YC, Kim JW, Chun CH. Arthroscopic bioabsorbable screw fixation of unstable osteochondritis dissecans in adolescents: clinical results, magnetic resonance imaging, and second-look arthroscopic findings. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8:57–64.
Adachi N, Deie M, Nakamae A, Okuhara A, Kamei G, Ochi M. Functional and radiographic outcomes of unstable juvenile osteochondritis dissecans of the knee treated with lesion fixation using bioabsorbable pins. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015;35:82–8.
Kocher MS, Czarnecki JJ, Andersen JS, Micheli LJ. Internal fixation of juvenile osteochondritis dissecans lesions of the knee. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:712–8.
Bostman OM. Absorbable implants for the fixation of fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73:148–53.
Bostman O, Hirvensalo E, Makinen J, Rokkanen P. Foreign-body reactions to fracture fixation implants of biodegradable synthetic polymers. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72:592–6.
Camathias C, Gogus U, Hirschmann MT, et al. Implant failure after biodegradable screw fixation in osteochondritis dissecans of the knee in skeletally immature patients. Arthroscopy. 2015;31:410–5.
Bostman OM. Osteolytic changes accompanying degradation of absorbable fracture fixation implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:679–82.
Scioscia TN, Giffin JR, Allen CR, Harner CD. Potential complication of bioabsorbable screw fixation for osteochondritis dissecans of the knee. Arthroscopy 2001;17(2):1–5.
Takizawa T, Akizuki S, Horiuchi H, Yasukawa Y. Foreign body gonitis caused by a broken poly-L-lactic acid screw. Arthroscopy. 1998;14:329–30.
Friederichs MG, Greis PE, Burks RT. Pitfalls associated with fixation of osteochondritis dissecans fragments using bioabsorbable screws. Arthroscopy. 2001;17:542–5.
Camathias C, Festring JD, Gaston MS. Bioabsorbable lag screw fixation of knee osteochondritis dissecans in the skeletally immature. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2011;20:74–80.
Bostman OM, Pihlajamaki HK. Adverse tissue reactions to bioabsorbable fixation devices. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;371:216–27.
Millington KL, Shah JP, Dahm DL, Levy BA, Stuart MJ. Bioabsorbable fixation of unstable osteochondritis dissecans lesions. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38:2065–70.
Tabaddor RR, Banffy MB, Andersen JS, et al. Fixation of juvenile osteochondritis dissecans lesions of the knee using poly 96L/4D-lactide copolymer bioabsorbable implants. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30:14–20.
Weckstrom M, Parviainen M, Kiuru MJ, Mattila VM, Pihlajamaki HK. Comparison of bioabsorbable pins and nails in the fixation of adult osteochondritis dissecans fragments of the knee: an outcome of 30 knees. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:1467–76.
Din R, Annear P, Scaddan J. Internal fixation of undisplaced lesions of osteochondritis dissecans in the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:900–4.
Carey JL, Wall EJ, Grimm NL, et al. Novel arthroscopic classification of osteochondritis dissecans of the knee: a multicenter reliability study. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44:1694–8.
Nguyen JC, Liu F, Blankenbaker DG, Woo KM, Kijowski R. Juvenile osteochondritis Dissecans: cartilage T2 mapping of stable medial femoral condyle lesions. Radiology. 2018;288:536–43.
De Smet AA, Norris MA, Yandow DR, Quintana FA, Graf BK, Keene JS. MR diagnosis of meniscal tears of the knee: importance of high signal in the meniscus that extends to the surface. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993;161:101–7.
De Smet AA, Tuite MJ. Use of the "two-slice-touch" rule for the MRI diagnosis of meniscal tears. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187:911–4.
Brittberg M, Winalski CS. Evaluation of cartilage injuries and repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;2:58–69.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–74.
Pietrzak WS, Sarver DR, Verstynen ML. Bioabsorbable polymer science for the practicing surgeon. J Craniofac Surg. 1997;8:87–91.
Barfod G, Svendsen RN. Synovitis of the knee after intraarticular fracture fixation with biofix. Report of two cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63:680–1.
Friden T, Rydholm U. Severe aseptic synovitis of the knee after biodegradable internal fixation. A case report. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63:94–7.
Matsusue Y, Yamamuro T, Oka M, Shikinami Y, Hyon SH, Ikada Y. In vitro and in vivo studies on bioabsorbable ultra-high-strength poly(L-lactide) rods. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26:1553–67.
Prokop A, Jubel A, Helling HJ, et al. Soft tissue reactions of different biodegradable polylactide implants. Biomaterials. 2004;25:259–67.
Acknowledgements
This study was approved by the institutional review board.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no reverent conflict of interest.
Grant support
None.
Disclosures
None of the authors has any disclosures.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, J.C., Green, D.W., Lin, B.F. et al. Magnetic resonance evaluation of the pediatric knee after arthroscopic fixation of osteochondral lesions with biodegradable nails. Skeletal Radiol 49, 65–73 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03258-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03258-1