Abstract
Objective
To provide microdissection and histological confirmation of normal Pacinian corpuscles prospectively identified using MRI in a cadaver model.
Methods
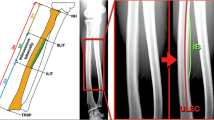
3-T MRI of a cadaveric hand specimen was performed with fiduciary markers on the skin. Based on previous descriptions, subcutaneous nodules representing presumed Pacinian corpuscles were localized with respect to the skin markers, and their sizes and depths were recorded. Focused ultrasound was performed to attempt to visualize the corpuscles. Subsequent microdissection was then performed and the presence and location of Pacinian corpuscles were recorded and compared with the findings on MRI. Histological evaluation for each identified corpuscle was performed.
Results
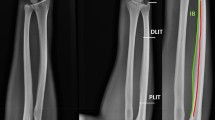
The MRI demonstrated 11 T2-hyperintense palmar subcutaneous nodules around the second through fifth metacarpophalangeal joints. None was visible sonographically. The first eight were dissected and proved to be normal Pacinian corpuscles histologically. In sites devoid of subcutaneous nodules on MRI, subsequent dissection failed to reveal any corpuscles.
Conclusion
On MRI, normal Pacinian corpuscles appear as round or oval, T2-hyperintense subcutaneous nodules in the palms, clustered around the metacarpophalangeal joints, and should not be mistaken for pathological conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gartner L. Textbook of histology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2017.
Rhodes NG, Murthy NS, Lehman JS, Rubin DA. Pacinian corpuscles: an explanation for subcutaneous palmar nodules routinely encountered on MR examinations. Skeletal Radiol. 2018;47(11):1553-1558.
Roset-Llobet J, Domenech-Mateu JM. Uncommon number and distribution of the Pacinian corpuscles in a human hand. J Hand Surg Br. 1991;16(1):89–91.
Stark B, Carlstedt T, Cullheim S, Risling M. Developmental and lesion-induced changes in the distribution of the glucose transporter Glut-1 in the central and peripheral nervous system. Exp Brain Res. 2000;131(1):74–84.
Sakada S, Sasaki T. Blood-nerve barrier in the Vater-Pacini corpuscle of cat mesentery. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1984;169(3):237–47.
Reznik M, Thiry A, Fridman V. Painful hyperplasia and hypertrophy of Pacinian corpuscles in the hand: report of two cases with immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies, and a review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998;20(2):203–7.
Acknowledgements
Terry D Regnier, Stephanie L Jacobson, Joseph P Grande.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
This study was approved by the institutional review board of our institution and by the Biospecimen Subcommittee.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhodes, N.G., Murthy, N.S., Lachman, N. et al. Normal Pacinian corpuscles in the hand: radiology–pathology correlation in a cadaver study. Skeletal Radiol 48, 1591–1597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03223-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03223-y