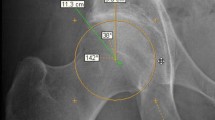
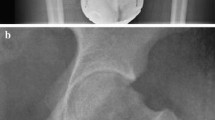
Abstract
Objective
To assess diagnostic accuracy and agreement among radiologists in detecting femoroplasty on pre- and post-arthroscopic comparison frog lateral and anteroposterior (AP) pelvic radiographs after treatment of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) syndrome.
Materials and methods
In this retrospective, cross-sectional study, 86 patients underwent hip arthroscopy (52 with and 34 without femoroplasty) for treatment of FAI syndrome. Three radiologists blinded to clinical data and chronological order of the pre- and post-arthroscopic comparison radiographs independently examined AP pelvis and frog lateral radiographs to detect femoroplasty changes. Statistical analysis outputs included diagnostic accuracy parameters and inter- and intra-observer agreement.
Results
Identification of femoroplasty in the frog lateral projection has mean sensitivity 70%, specificity 82%, inter-observer agreement κ 0.74–0.76 and intra-observer agreement κ 0.72–0.85. Using the AP pelvis projection to detect femoroplasty has mean sensitivity 32%, specificity 71%, inter-observer agreement κ 0.47–0.65, and intra-observer agreement κ, 0.56–0.84.
Conclusions
Radiologists are only moderately sensitive, though more specific, in femoroplasty detection in the frog lateral projection. The AP pelvis projection yields lower sensitivity and specificity. Both projections have moderate inter- and intra-observer agreement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffin DR, Dickenson EJ, O’Donnell J, Agricola R, Awan T, Beck M, et al. The Warwick Agreement on femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI syndrome): an international consensus statement. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50:1169–76.
Ito K, Minka MA, Leunig M, Werlen S, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect: a MRI-based quantitative anatomical study of the femoral head-neck offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:171–6.
Reiman MP, Thorborg K, Hölmich P. Femoroacetabular impingement surgery is on the rise: but what is the next step? J Orthop Sport Phys Ther. 2016;46:406–8.
Steppacher SD, Anwander H, Zurmühle CA, Tannast M, Siebenrock KA. Eighty percent of patients with surgical hip dislocation for femoroacetabular impingement have a good clinical result without osteoarthritis progression at 10??Years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473:1333–41.
de Sa D, Urquhart N, Philippon M, Ye J-E, Simunovic N, Ayeni OR. Alpha angle correction in femoroacetabular impingement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22:812–21.
Sardana V, Philippon MJ, de Sa D, Bedi A, Ye L, Simunovic N, et al. Revision hip arthroscopy indications and outcomes: a systematic review. Arthroscopy. 2015;31:2047–55.
Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:556–60.
Hetaimish BM, Khan M, Crouch S, Simunovic N, Bedi A, Mohtadi N, et al. Consistency of reported outcomes after arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:780–7.
Dzaja I, Martin K, Kay J, Memon M, Duong A, Simunovic N, et al. Radiographic outcomes reporting after arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: a systematic review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016;9:411–7.
Kottner J, Audig L, Brorson S, Donner A, Gajewski BJ. Guidelines for reporting reliability and agreement studies (GRRAS) were proposed. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:96–106.
Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Paul P, Irwig L, et al. STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for. Res Methods Reporting. 2015;5527:1–9.
Ilizaliturri VM. Complications of arthroscopic femoroacetabular impingement treatment: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:760–8.
Ross JR, Larson CM, Adeoyo O, Kelly BT, Bedi A. Residual deformity is the most common reason for revision hip arthroscopy: a three-dimensional CT study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014;1388–1395.
Gupta A, Redmond JM, Stake CE, Finch NA, Dunne KF, Domb BG. Does the femoral cam lesion regrow after osteoplasty for femoroacetabular impingement? Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:2149–55.
Ross JR, Bedi A, Stone RM, Sibilsky Enselman E, Leunig M, Kelly BT, et al. Intraoperative fluoroscopic imaging to treat cam deformities: correlation with 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:1370–6.
Bedi A, Zaltz I, De La Torre K, Kelly BT. Radiographic comparison of surgical hip dislocation and hip arthroscopy for treatment of cam deformity in femoroacetabular impingement. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(Suppl):20S–8S.
Jackson TJ, Stake CE, Trenga AP, Morgan J, Domb BG. Arthroscopic technique for treatment of femoroacetabular impingement. Arthrosc Tech. 2013;2:e55–9.
Landis JR, Koch GG. Agreement measures for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–74.
Rakhra KS, Sheikh AM, Allen D, Beaulé PE. Comparison of MRI alpha angle measurement planes in femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:660–5.
Nepple JJ, Martel JM, Kim YJ, Zaltz I, Clohisy JC. Do plain radiographs correlate with CT for imaging of cam-type femoroacetabular impingement? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470:3313–20.
Pfirrmann CW. A, Mengiardi B, Dora C, Kalberer F, Zanetti M, Hodler J. Cam and pincer femoroacetabular impingement: characteristic MR arthrographic findings in 50 patients. Radiology. 2006;240:778–85.
Audenaert EA, Baelde N, Huysse W, Vigneron L, Pattyn C. Development of a three-dimensional detection method of cam deformities in femoroacetabular impingement. Skelet Radiol. 2011;40:921–7.
Mardones R, Lara J, Donndorff A, Barnes S, Stuart MJ, Glick J, et al. Surgical correction of “cam-type” femoroacetabular impingement: a cadaveric comparison of open versus arthroscopic debridement. Arthroscopy. 2009;25:175–82.
Hellman MD, Mascarenhas R, Gupta A, Fillingham Y, Haughom BD, Salata MJ, et al. The false-profile view may be used to identify cam morphology. Arthroscopy. 2015:1–5.
Domayer SE, Ziebarth K, Chan J, Bixby S, Mamisch TC, Kim YJ. Femoroacetabular cam-type impingement: diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of radiographic views compared to radial MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80:805–10.
Meyer DC, Beck M, Ellis T, Ganz R, Leunig M. Comparison of six radiographic projections to assess femoral head/neck asphericity. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006;PAP:181–5.
Hanauer DA, Preib R, Zheng K, Choi SW. Patient-initiated electronic health record amendment requests. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2014;21:992–1000.
Stähelin L, Stähelin T, Jolles BM, Herzog RF. Arthroscopic offset restoration in femoroacetabular cam impingement: accuracy and early clinical outcome. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:51–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
This study was partially funded by Dartmouth Clinical and Translational Science Institute (NIH award number UL1TR001086 to Steffen Haider).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haider, S.J., Siegel, A.H., Spratt, K.F. et al. Detection of femoroplasty on pre- and post-arthroscopic comparison radiographs following treatment of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome: multi-reader accuracy and agreement study. Skeletal Radiol 47, 233–242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2789-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2789-0