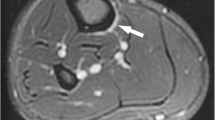
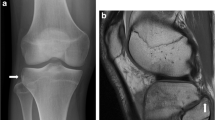
Abstract
Anterior mid-tibial cortex stress fractures (ATCSF) are uncommon and notoriously challenging to treat. They are termed high risk due to their predilection to prolonged recovery, nonunion and complete fracture. Early diagnosis is essential to avoid progression and reduce fracture complications. Imaging plays a key role in confirming the diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is accepted as the gold standard modality due to its high accuracy and nonionizing properties. This report describes three cases of ATCSFs in recreational athletes who had positive radiographic findings with no significant MRI changes. Two athletes had multiple striations within their tibias. Despite the radiographic findings, their severity of symptoms were low with mild or no tenderness on examination. Clinicians should be mindful that the ATCSFs may not present with typical acute stress fracture symptoms. We recommend that plain radiographs should be used as the first line investigation when suspecting ATCSFs. Clinicians should be aware that despite MRI being considered the gold standard imaging modality, we report three cases where the MRI was unremarkable, whilst radiographs and computed tomography confirmed the diagnosis. We urge clinicians to continue to use radiographs as the first line imaging modality for ATCSFs and not to directly rely on MRI. Those who opt directly for MRI may be falsely reassured causing a delay in diagnosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennell KL, Malcolm SA, Thomas SA, Wark JD, Brukner PD. The incidence and distribution of stress fractures in competitive track and field athletes: a twelve-month prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1996;24(2):211–7.
Pegrum J, Crisp T, Padhiar N. Diagnosis and management of bone stress injuries of the lower limb in athletes. BMJ. 2012;344:e2511.
McInnis KC, Ramey LN. High-risk stress fractures: diagnosis and management. PM R. 2016;8(3 Suppl):S113–24.
Matheson GO, Clement DB, McKenzie DC, Taunton JE, Lloyd-Smith DR, MacIntyre JG. Stress fractures in athletes: a study of 320 cases. Am J Sports Med. 1987;15(1):46–58.
Liimatainen E, Sarimo J, Hulkko A, Ranne J, Heikkilä J, Orava S. Anterior mid-tibial stress fractures: results of surgical treatment. Scand J Surg. 2009;98(4):244–9.
Orava S, Hulkko A. Stress fracture of the mid-tibial shaft. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55(1):35–7.
Robertson GA, Wood AM. Return to sports after stress fractures of the tibial diaphysis: a systematic review. Br Med Bull. 2015;114(1):95–111.
Wright AA, Hegedus EJ, Lenchik L, Kuhn KJ, Santiago L, Smoliga JM. Diagnostic accuracy of various imaging modalities for suspected lower extremity stress fractures: a systematic review with evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(1):255–63.
Moran DS, Evans RK, Hadad E. Imaging of lower extremity stress fracture injuries. Sports Med. 2008;38(4):345–56.
Fredericson M, Bergman AG, Hoffman KL, Dillingham MS. Tibial stress reaction in runners: correlation of clinical symptoms and scintigraphy with a new magnetic resonance imaging grading system. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(4):472–81.
Beck BR, Bergman AG, Miner M, Arendt EA, Klevansky AB, Matheson GO, et al. Tibial stress injury: relationship of radiographic, nuclear medicine bone scanning, MR imaging, and CT severity grades to clinical severity and time to healing. Radiology. 2012;263(3):811–8.
Kijowski R, Choi J, Shinki K, Del Rio AM, De Smet A. Validation of MRI classification system for tibial stress injuries. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198(4):878–84.
Mammoto T, Hirano A, Tomaru Y, Kono M, Tsukagoshi Y, Onishi S, et al. High-resolution axial MR imaging of tibial stress injuries. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2012;4(1):16.
BURROWS HJ. Fatigue infraction of the middle of the tibia in ballet dancers. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1956;38-B(1):83–94.
Stanitski CL, McMaster JH, Scranton PE. On the nature of stress fractures. Am J Sports Med. 1978;6(6):391–6.
Boden BP, Osbahr DC. High-risk stress fractures: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000;8(6):344–53.
Bennell K, Crossley K, Jayarajan J, Walton E, Warden S, Kiss ZS, et al. Ground reaction forces and bone parameters in females with tibial stress fracture. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(3):397–404.
Meardon SA, Willson JD, Gries SR, Kernozek TW, Derrick TR. Bone stress in runners with tibial stress fracture. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(9):895–902.
Milner CE, Ferber R, Pollard CD, Hamill J, Davis IS. Biomechanical factors associated with tibial stress fracture in female runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38(2):323–8.
Brukner P, Fanton G, Bergman AG, Beaulieu C, Matheson GO. Bilateral stress fractures of the anterior part of the tibial cortex: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(2):213–8.
Gigis I, Rallis I, Gigis P, Goulios V. Anterior tibial cortex stress fracture in a high demand professional soccer player. J Med Cases. 2011;2(5):210–5.
Brahms MA, Fumich RM, Ippolito VD. Atypical stress fracture of the tibia in a professional athlete. Am J Sports Med. 1980;8(2):131–2.
Manaster BJ, Dalinka MK, Alazraki N, Berquist TH, Daffner RH, DeSmet AA, et al. Stress/insufficiency fractures (excluding vertebral): ACR appropriateness criteria. Radiology. 2000;215(Suppl):265–72.
Dixon S, Newton J, Teh J. Stress fractures in the young athlete: a pictorial review. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2011;40(1):29–44.
Gaeta M, Minutoli F, Scribano E, Ascenti G, Vinci S, Bruschetta D, et al. CT and MR imaging findings in athletes with early tibial stress injuries: comparison with bone scintigraphy findings and emphasis on cortical abnormalities. Radiology. 2005;235(2):553–61.
Kijowski R, Choi J, Mukharjee R, de Smet A. Significance of radiographic abnormalities in patients with tibial stress injuries: correlation with magnetic resonance imaging. Skelet Radiol. 2007;36(7):633–40.
Nattiv A, Kennedy G, Barrack MT, Abdelkerim A, Goolsby MA, Arends JC, et al. Correlation of MRI grading of bone stress injuries with clinical risk factors and return to play: a 5-year prospective study in collegiate track and field athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(8):1930–41.
Seki N, Okuyama K, Kamo K, Chiba M, Shimada Y. Negative magnetic resonance imaging in femoral neck stress fracture with joint effusion: a case report. Skelet Radiol. 2016;45(6):843–6.
Sato RYS, Mihashi M, et al. A case of femoral neck stress fracture without early diagnosis by magnetic resonance imaging. Chubuseisaishi. 2007;50:1095–6. (in Japanese)
Matesan M, Behnia F, Bermo M, Vesselle H. SPECT/CT bone scintigraphy to evaluate low back pain in young athletes: common and uncommon etiologies. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):76.
Rolf C, Ekenman I, Törnqvist H, Gad A. The anterior stress fracture of the tibia: an atrophic pseudoarthosis? Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1997;7(4):249–52.
Orava S, Karpakka J, Hulkko A, Väänänen K, Takala T, Kallinen M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of stress fractures located at the mid-tibial shaft in athletes. Int J Sports Med. 1991;12(4):419–22.
Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Magid D, Scott WW, Brooker AF, Siegelman SS. Fracture nonunion: CT assessment with multiplanar reconstruction. Radiology. 1988;167(2):483–8.
Miller EH, Schneider HJ, Bronson JL, McLain D. A new consideration in athletic injuries: the classical ballet dancer. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975;111:181–91.
Schneider HJ, King AY, Bronson JL, Miller EH. Stress injuries and developmental change of lower extremities in ballet dancers. Radiology. 1974;113(3):627–32.
Daffner RH. Anterior tibial striations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984;143(3):651–3.
Burke R, Chiang AL, Lomasney LM, Demos TC, Wu K. Multiple anterior tibial stress fractures complicated by acute complete fracture of the distal tibia. Orthopedics. 2014;37(4):217, 274–218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Presentation
The authors directly declare that the results of the study are presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, R., Moghal, M., Newton, J.L. et al. Negative magnetic resonance imaging in three cases of anterior tibial cortex stress fractures. Skeletal Radiol 46, 1775–1782 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2773-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2773-8