Abstract
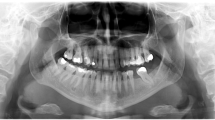
Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia (FCOD) is a rare, benign, multifocal fibro-osseous dysplastic process affecting tooth-bearing areas of the jaw, characterized by replacement of normal trabecular bone with osseous tissue and dense acellular cementum in a fibrous stroma. It is one clinicopathologic variant in a spectrum of related non-neoplastic fibro-osseous lesions known as cemento-osseous dysplasias (CODs), thought to arise from elements of the periodontal ligament. Diagnosis primarily relies upon radiographic and clinical findings; unnecessary biopsy should be avoided, as inoculation with oral pathogens may precipitate chronic infection in these hypovascular lesions. Appropriate management of uncomplicated FCOD consists of periodic radiographic follow-up. Accordingly, it is important that both radiologists and clinicians performing endodontic interventions possess familiarity with this entity in order to prevent misdiagnosis and inappropriate intervention, which may result in a protracted clinical course. Lesions are usually asymptomatic in the absence of infection, typically discovered on routine dental radiographs or imaging performed for unrelated indications. Radiographically, the condition typically manifests as widespread non-expansile intraosseous masses of varying internal lucency and sclerosis that surround the root apices of vital teeth or edentulous areas in the posterior jaw. While all CODs share similar microscopic features, FCOD is distinguished by its multifocal distribution, involving two or more quadrants of the maxilla and mandible, often in a bilateral symmetric fashion. The vast majority of cases are sporadic, though few exhibit an autosomal dominant familial inheritance pattern. In this pictorial review, we discuss the radiologic characteristics of this entity, pertinent clinical and histologic features, differential diagnoses, and management options.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coleman H, Altini M, Kieser J, Nissenbaum M. Familial florid cemento-osseous dysplasia—a case report and review of the literature. J Dent Assoc S Afr. 1996;51(12):766–70.
Slootweg PJ. Maxillofacial fibro-osseous lesions: classification and differential diagnosis. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1996;13:104–12.
Waldron CA. Fibro-osseous lesions of jaws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993;51:828–35.
Kramer IRH, Pindborg JJ, Shear M. Neoplasm and other lesions related to bone. In: WHO, editor. Histologic typing of odontogenic tumours. Berlin: Springer; 1992.
Summerlin DJ, Tomich CE. Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia: a clinicopathologic study of 221 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994;78:611–20.
Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Cemento-osseous dysplasia. 3rd ed. Saunders; 2009. p. 635–648.
Miyauchi M, Ogawa I, Takata T, Ito H, Nikai H, Ijuhin N, et al. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia with concomitant simple bone cysts: a case in a Japanese woman. J Oral Pathol Med. 1995;24(6):285–7.
Ong ST, Siar CH. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia in a young Chinese man. Case report. Aust Dent J. 1997;42(6):404–8.
Ariji Y, Ariji E, Higuchi Y, Kubo S, Nakayama E, Kanda S. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia. Radiographic study with special emphasis on computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994;78(3):391–6.
Singer SR, Mupparapu M, Rinaggio J. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia and chronic diffuse osteomyelitis. Report of a simultaneous presentation and review of the literature. J Am Dent Assoc. 2005;136:927–31.
Jerjes W, Banu B, Swinson B, Hopper C. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia in a young Indian woman. A case report. Br Dent J. 2005;198:477–8.
MacDonald-Jankowski DS. Fibro-osseous lesions of the face and jaws. Clin Radiol. 2004;59(1):11–25.
Higuchi Y, Nakamura N, Tashiro H. Clinicopathologic study of cemento-osseous dysplasia producing cysts of the mandible. Report of four cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988;65:339–42.
Mahomed F, Altini M, Meer S, Coleman H. Cemento-osseous dysplasia with associated simple bone cysts. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;63:1549–54.
Gonçalves M, Píspico R, Alves Fde A, Lugão CE, Gonçalves A. Clinical, radiographic, biochemical and histological findings of florid cemento-osseous dysplasia and report of a case. Braz Dent J. 2005;16:247–50.
Young SK, Markowitz NR, Sullivan S, Seale TW, Hirschi R. Familial gigantiform cementoma: classification and presentation of a large pedigree. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989;68:740–7.
Melrose RJ, Abrams AM, Mills BG. Florid osseous dysplasia. A clinical-pathologic study of thirty-four cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1976;41:62–82.
Waldron CA. Bone pathology. In: Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE, editors. Oral & maxillofacial pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2002. p. 533–87.
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D. World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Lyon: IARC press; 2005.
Beylouni I, Farge P, Mazoyer JF, Coudert JL. Florid cementoosseous dysplasia: report of a case documented with computed tomography and 3D imaging. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;85:707–11.
Eversole R, Su L, ElMofty S. Benign fibro-osseous lesions of the craniofacial complex. A review. Head Neck Pathol. 2008;2(3):177–202.
Damm DD, Fantasia JE. Multifocal mixed radiolucencies. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia. Gen Dent. 2001;49:461–538.
Resnick CM, Novelline RA. Cemento-osseous dysplasia, a radiological mimic of periapical dental abscess. Emerg Radiol. 2008;15(6):367–74.
Alawi F. Benign fibro-osseous diseases of the maxillofacial bones. A review and differential diagnosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;118(Suppl):S50–70.
MacDonald-Jankowski DS. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: a systematic review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2003;32:141–9.
White SC, Pharoah MJ. Disease of bone manifested in the jaws. In: White SC, Pharoah MJ, editors. Oral radiology. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 2000. p. 444–71.
Kim JH, Song BC, Kim SH, Park YS. Clinical, radiographic and histological findings of florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: a case report. Imaging Sci Dent. 2011;41:139–42.
Potochny EM, Huber AR. Focal osseous dysplasia. Head Neck Pathol. 2011;5(3):265–7.
Scholl JR, Kellet HM, et al. Cysts and cystic lesions of the mandible: clinical and radiologic-histopathologic review. Radiographics. 1999;19(5):1107–24.
Su L, Weathers DR, Waldron CA. Distinguishing features of focal cemento-osseous dysplasia and cemento-ossifying fibromas. II. A clinical and radiologic spectrum of 316 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1997;84:540–9.
Miyake M, Nagahata S. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia report of a case. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;28(1):56–7.
Neville BW, Albenesius RJ. The prevalence of benign fibro-osseous lesions of periodontal ligament origin in black women: a radiographic survey. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1986;62:340–4.
Toffanin A, Benetti R, Manconi R. Familial florid cementoosseous dysplasia: a case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58:1440–6.
Ogunsalu C, Miles D. Cemento-osseous dysplasia in Jamaica: review of six cases. West Indian Med J. 2005;54(4):264–7.
Philipsen HP, Reichart PA, Slootweg PJ, Slater LJ. Odontogenic tumours. In: Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D, editors. Pathology and genetics: head and neck tumours. Lyon: IARC Press; 2005. p. 323.
Abdelsayed RA, Eversole LR, Singh BS, Scarbrough FE. Gigantiform cementoma: clinicopathologic presentation of 3 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;91(4):438–44.
Sedano HO, Kuba R, Gorlin RJ. Autosomal dominant cemental dysplasia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982;54(6):642–6.
Cannon JS, Keller EE, Dahlin DC. Gigantiform cementoma: report of two cases (mother and son). J Oral Surg. 1980;38:65–70.
Oikarinen K, Altonen M, Happonen RP. Gigantiform cementoma affecting a Caucasian family. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991;29:194–7.
Thorawat A, Kalkur C, Naikmasur VG, Tarakji B. Familial florid Cemento-osseous dysplasia—case report and review of literature. Clin Case Rep. 2015;3(12):1034–7.
Srivastava A, Agarwal R, Soni R, Sachan A, Shivakumar GC, Chaturvedi TP. Familial florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: a rare manifestation in an Indian family. Case Rep Dent. 2012;2012:574125.
Lopes MA, Kim HS, Mariano FV, Correa MB, Rabelo NT, Vargas PA. Clinico-pathologic conference: case 1. High-grade osteosarcoma (OS) and florid cemento-osseous dysplasia (FCOD). Head Neck Pathol. 2010;4:329–33.
Schneider L, Dolinsky H, Grodjesk J, Mesa M, Doyle J. Malignant spindle cell tumor arising in the mandible of a patient with florid osseous dysolasia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999;88:69–73.
Lee L. Inflammatory lesions of the jaws. In: White SC, Pharoah MJ, editors. Oral radiology. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 2000. p. 338–54.
Suei Y, Tanimoto K, Miyauchi M, Ishikawa T. Partial resection of the mandible for the treatment of diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis: report of four cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;55:410–4.
Payne M, Anderson JA, Cook J. Gardner’s syndrome—a case report. Br Dent J. 2002;193(7):383–4.
Lew D, DeWitt A, Hicks RJ, Cavalcanti MG. Osteomas of the condyle associated with Gardner’s syndrome causing limited mandibular movement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;57(8):1004–9.
Costa AG, Costa RO, Oliveira LR, Grossmann SM. Multiple oral radiopaque masses leading to Gardner’s syndrome diagnosis. Gen Dent. 2013;614:e12–4.
Kubo K, Miyatani H, Takenoshita Y, Abe K, Oka M, Iida M, et al. Widespread radiopacity of jaw bones in familial adenomatosis coli. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1989;17(8):350–3.
Wolf J, Heitamen J, Sane J. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia (gigantiform cementoma) in a Caucasian woman. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989;27:46–52.
Loh FC, Yeo JF. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia in Orientals. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989;68:748–53.
Jacobsson S. Diffuse sclerosing ostemyelitis of the mandible. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1979;360:61–3.
Johannsen A. Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis of the mandible. Radiographic differential diagnosis from fibrous dysplasia. Acta Radiol Diagn. 1977;18:360–8.
Schneider LC, Mesa ML. Differences between florid osseous dysplasia and chronic diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1990;70:308–12.
Rabe WC, Angelillo JC, Leipert DW. Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis: treatment considerations in an atypical case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1980;49:117–21.
Groot RH, van Merkesteyn JP, Bras J. Diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis and florid osseous dysplasia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996;81:333–42.
Orpe EC, Lee L, Pharoah MJ. A radiological analysis of chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis of the mandible. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1996;25:125–9.
Eversole LR, Leider AS, Corwin JO, Karian BK. Proliferative periostitis of Garre: its differentiation from other neoperiostoses. J Oral Surg. 1979;37:725–31.
Kawai T, Murakami S, Sakuda M, Fuchihata H. Radiographic investigation of mandibular periostitis ossificans in 55 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996;82:704–12.
Kawai T, Hiranuma H, Kishino M, Murakami S, Sakuda M, Fuchihata H. Gross periostitis ossificans in mandibular osteomyelitis. Review of the English literature and radiographic variation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;86:376–81.
Nortje CJ, Wood RE, Grotepass F. Periostitis ossificans versus Garre’s osteomyelitis. Part II: radiologic analysis of 93 cases in the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988;66:249–60.
Larheim TA, Aspestrand F, Trebo S. Periostitis ossificans of the mandible. The value of computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1993;22:93–6.
Jacobson HL, Baumgartner JC, Marshall JG, Beeler WJ. Proliferative periostitis of Garre: report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94:111–4.
Belli E, Matteini C, Andreano T. Sclerosing osteomyelitis of Garre periostitis ossificans. J Craniofac Surg. 2002;13:765–8.
Jacobsson S, Hollender L, Lindberg S, Larsson A. Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis of the mandible. Scintigraphic and radiographic findings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1978;45:167–74.
El-Mofty S. Chronic diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973;36:898–904.
Keen EG, Sammartino CA, Johnson ES. Chronic sclerosing osteomyelifis of the mandible. J Am Dent Assoc. 1968;76:597–9.
Shafer WG. Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis. J Oral Surg. 1957;15:138–42.
Towns TL. Chronic diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis of the maxilla and the mandible. J Oral Surg. 1972;30:903–5.
MacDonald-Jankowski D. Fibrous dysplasia: a systematic review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2009;38(4):196–215.
Petrikowski CG et al. Radiographic differentiation of osteogenic sarcoma, osteomyelitis, and fibrous dysplasia of the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995;80(6):744–50.
Eversole LR, Sabes WR, Rovin S. Fibrous dysplasia: a nosologic problem in the diagnosis of fibro-osseous lesions of the jaws. J Oral Pathol. 1972;1:189–220.
Hirshberg A, Shnaiderman-Shapiro A, Kaplan I, Berger R. Metastatic tumours to the oral cavity—pathogenesis and analysis of 673 cases. Oral Oncol. 2008;44(8):743–52.
Nawale KK, Vyas M, Kane S, Patil A. Metastatic tumors in the jaw bones: a retrospective clinicopathological study of 12 cases at tertiary cancer center. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2016;20(2):252–5.
D’Silva NJ, Summerlin DJ, Cordell KG, Abdelsayed RA, Tomich CE, Hanks CT, et al. Metastatic tumors in the jaws: a retrospective study of 114 cases. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006;137(12):1667–72.
van der Waal RI, Buter J, van der Waal I. Oral metastases: report of 24 cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;41:3–6.
Nishimura Y, Yakata H, Kawasaki TT, Nakajima T. Metastatic tumors of the mouth and jaws. A review of the Japanese literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1982;10:253–8.
Zachariades N. Neoplasms metastatic to the mouth, jaws and surrounding tissues. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg. 1989;17:283–90.
Hirshberg A, Leibovich P, Buchner A. Metastatic tumors to the jawbones: analysis of 390 cases. J Oral Pathol Med. 1994;23(8):337–41.
Hirshberg A, Buchner A. Metastatic tumours to the oral region. An overview. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1995;31B(6):355–60.
Kumar G, Manjunatha B. Metastatic tumors to the jaws and oral cavity. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2013;17(1):71–5.
Meyer I, Shklar G. Malignant tumors metastatic to the mouth and jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1965;20:350–62.
Muttagi SS, Chaturvedi P, D’Cruz A, Kane S, Chaukar D, Pai P, et al. Metastatic tumors to the jaw bones: retrospective analysis from an Indian tertiary referral center. Indian J Cancer. 2011;48(2):234–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fenerty, S., Shaw, W., Verma, R. et al. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: review of an uncommon fibro-osseous lesion of the jaw with important clinical implications. Skeletal Radiol 46, 581–590 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2590-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2590-0