Abstract
Objective
To prospectively evaluate the precision and reproducibility of T2*-derived measurements of the peripheral nerves.
Materials and methods
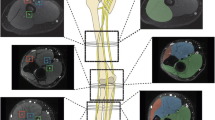
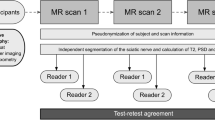
The study was approved by the local ethics committee and written informed consent was obtained. Bilateral upper and lower limb MRI examination was performed in 40 healthy subjects on a 3.0-T scanner. MRI protocol included T1-turbo spin-echo, T2-turbo spin-echo with fat suppression, and multiecho gradient recalled echo. Measurements of T2* times on T2* maps at different anatomical levels were performed. Three authors measured independently and in different sessions at baseline and after 4 weeks. Non-parametric tests and Bland–Altman statistics were used.
Results
Minimum and maximum percentage variability were 10 % and 19 % for T2* (84–91 % of reproducibility). Maximum values of minimum detectable differences between limbs was 16 % (with 95 % CI: 2–37). Intra- and inter-observer agreement of the three radiologists for T2* was considered good. Evaluating the combined influence of the observer and of the repeated measurements the reproducibility was 87–98 %.
Conclusions
T2* measurement of the peripheral nerves is precise and reproducible. The healthy contralateral side can be used as an internal control. Variations in T2* values up to 16 % have to be considered.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kermarrec E, Demondion X, Khalil C, Le Thuc V, Boutry N, Cotten A. Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of the peripheral nerves: current techniques, promising directions, and open issues. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2010;14(5):463–72.
Gambarota G. T2 relaxometry of human median nerve. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2009;13(1):24–8.
Bendszus M, Stoll G. Technology insight: visualizing peripheral nerve injury using MRI. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2005;1(1):45–53.
Bäumer P, Pham M, Ruetters M, et al. Peripheral neuropathy: detection with diffusion-tensor imaging. Radiology. 2014;273(1):185–93.
Juras V, Apprich S, Szomolanyi P, Bieri O, Deligianni X, Trattnig S. Bi-exponential T2 analysis of healthy and diseased Achilles tendons: an in vivo preliminary magnetic resonance study and correlation with clinical score. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(10):2814–22.
Andreisek G, Weiger M. T2* mapping of articular cartilage: current status of research and first clinical applications. Invest Radiol. 2014;49(1):57–62.
Du J, Carl M, Bydder M, Takahashi A, Chung CB, Bydder GM. Qualitative and quantitative ultrashort echo time (UTE) imaging of cortical bone. J Magn Reson. 2010;207(2):304–11.
Juras V, Zbyn S, Pressl C, et al. Regional variations of T-2* in healthy and pathologic achilles tendon in vivo at 7 Tesla: preliminary results. Magn Reson Med. 2012;68(5):1607–13.
Hwang D, Kim DH, Du YP. In vivo multi-slice mapping of myelin water content using T2* decay. Neuroimage. 2010;52(1):198–204.
Zhang X, Zhang F, Lu L, Li H, Wen X, Shen J. MR imaging and T2 measurements in peripheral nerve repair with activation of Toll-like receptor 4 of neurotmesis. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(5):1145–52.
Stoll G, Bendszus M. Imaging of inflammation in the peripheral and central nervous system by magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroscience. 2009;158(3):1151–60.
Bitar R, Leung G, Perng R, et al. MR pulse sequences: what every radiologist wants to know but is afraid to ask. Radiographics. 2006;26:513–37.
Tagliafico A, Martinoli C. Reliability of side-to-side sonographic cross-sectional area measurements of upper extremity nerves in healthy volunteers. J Ultrasound Med. 2013;32(3):457–62.
Tagliafico A, Cadoni A, Fisci E, Bignotti B, Padua L, Martinoli C. Reliability of side-to-side ultrasound cross-sectional area measurements of lower extremity nerves in healthy subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2012;46(5):717–22.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159–74.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Measurement error proportional to the mean. BMJ. 1996;313(7049):106.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Measurement error. BMJ. 1996;313(7059):744.
Padhani AR, Hayes C, Landau S, Leach MO. Reproducibility of quantitative dynamic MRI of normal human tissues. NMR Biomed. 2002;15(2):143–53.
Tagliafico A, Calabrese M, Puntoni M, et al. Brachial plexus MR imaging: accuracy and reproducibility of DTI-derived measurements and fibre tractography at 3.0-T. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(8):1764–71.
Di Leo G, Di Terlizzi F, Flor N, Morganti A, Sardanelli F. Measurement of renal volume using respiratory-gated MRI in subjects without known kidney disease: intraobserver, interobserver, and interstudy reproducibility. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80(3):e212–6.
Farrell JA, Landman BA, Jones CK, et al. Effects of signal-to-noise ratio on the accuracy and reproducibility of diffusion tensor imaging-derived fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, and principal eigenvector measurements at 1.5 T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;26(3):756–67.
Bradley Jr WG. MR appearance of hemorrhage in the brain. Radiology. 1993;189(1):15–26.
Lotan CS, Miller SK, Cranney GB, Pohost GM, Elgavish GA. The effect of postinfarction intramyocardial hemorrhage on transverse relaxation time. Magn Reson Med. 1992;23(2):346–55.
Mamisch TC, Hughes T, Mosher TJ, et al. T2 star relaxation times for assessment of articular cartilage at 3 T: a feasibility study. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(3):287–92.
Kali A, Tang RL, Kumar A, Min JK, Dharmakumar R. Detection of acute reperfusion myocardial hemorrhage with cardiac MR imaging: T2 versus T2*. Radiology. 2013;269(2):387–95.
Haacke E, Brown R, Thompson M, Venkatesan R. Magnetic resonance imaging: physical principles and sequence design. 1st ed. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1999.
Du J, Pak BC, Znamirowski R, et al. Magic angle effect in magnetic resonance imaging of the Achilles tendon and enthesis. Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;27(4):557–64.
Chappell KE, Robson MD, Stonebridge-Foster A, et al. Magic angle effects in MR neurography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(3):431–40.
Acknowledgement
The authors state that this work is supported by the Univerisity of Genova with a grant to Alberto Tagliafico (PRA 2014).
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Author contributions
Alberto Tagliafico, Bianca Bignotti, Giulio Tagliafico, Carlo Martinoli contributed equally to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tagliafico, A., Bignotti, B., Tagliafico, G. et al. Peripheral nerve MRI: precision and reproducibility of T2*-derived measurements at 3.0-T. Skeletal Radiol 44, 679–686 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2106-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2106-8