Abstract
Background
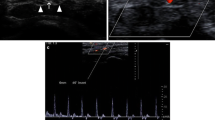
Patients with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) have a variety of vasomotor symptoms. Here, we aimed to study the vasomotor activity of the radialis indicis (RI) artery (median nerve territory) and the radial palmar digital (RPD) artery of the little finger (ulnar nerve territory) before and after sympathetic stimulation in CTS patients using color Doppler ultrasound.
Methods
We performed a cross-sectional study of 46 consecutive CTS patients plus 36 healthy controls. All patients underwent electromyography studies and were classified into mild and moderate/severe groups according to electrodiagnostic findings. Color Doppler examination of the RI artery and the RPD artery of the little finger were performed with the participants in a relaxed sitting position and after a deep breath followed by a cough (sympathetic stimulation). The pulsatility index (PI) was recorded at the point of maximal change in waveform, before and after this stimulus.
Results
The PI of RI artery was significantly lower (p < 0.01) in CTS patients than healthy controls, both before and after stimulation. The changes in PI of RI artery after stimulation were significantly lower in CTS patients than healthy controls (1.18 ± 0.37 vs. 5.41 ± 0.87; p < 0.001). The same pattern was seen for PI of RI artery when comparing patients with mild vs. moderate/severe CTS. No difference was found in PI of RPD artery of the 5th finger between patients vs. controls and between patients with mild vs. moderate/severe CTS, both before and after stimulation.
Conclusions
We showed that color Doppler ultrasound can readily determine impaired vasomotor activity in CTS patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atroshi I, Gummesson C, Johnsson R, Ornstein E, Ranstam J, Rosen I. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population. JAMA. 1999;282:153–8.
Carlson H, Colbert A, Frydl J, Arnall E, Elliot M, Carlson N. Current options for nonsurgical management of carpal tunnel syndrome. Int J Clin Rheumtol 5:129–42.
Kwon BC, Jung KI, Baek GH. Comparison of sonography and electrodiagnostic testing in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:65–71.
Werner RA, Andary M. Carpal tunnel syndrome: pathophysiology and clinical neurophysiology. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002;113:1373–81.
de Krom MC, Knipschild PG, Kester AD, Thijs CT, Boekkooi PF, Spaans F. Carpal tunnel syndrome: prevalence in the general population. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45:373–6.
Biafora SJ, Gonzalez MH. Sensory communication of the median and ulnar nerves in the palm. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2007;16:192–5.
Wall JT, Nepomuceno V, Rasey SK. Nerve innervation of the hand and associated nerve dominance aggregates in the somatosensory cortex of a primate (squirrel monkey). J Comp Neurol. 1993;337:191–207.
Campero M, Verdugo RJ, Ochoa JL. Vasomotor innervation of the skin of the hand: a contribution to the study of human anatomy. J Anat. 1993;182:361–8.
Kuwabara S, Tamura N, Yamanaka Y, et al. Sympathetic sweat responses and skin vasomotor reflexes in carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008;110:691–5. Epub 2008 May 16.
Chung MS, Gong HS, Baek GH. Raynaud’s phenomenon in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: postoperative alteration in its prevalence. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82:818–9.
Zyluk A, Kosowiec L. Regional sympathetic disturbances in carpal tunnel syndrome–a review. Chir Narzadów Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2008;73:30–6.
Gautherie M, Jesel M, Daemgen F, Meyer S. Vasomotor disorders of the hand and carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Chir Main Memb Supér. 1995;14:85–95.
Wilder-Smith EP, Fook-Chong S, Chew SE, Chow A, Guo Y. Vasomotor dysfunction in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2003;28:582–6.
Galea LA, Mercieca A, Sciberras C, Gatt R, Schembri M. Evaluation of sympathetic vasomotor fibres in carpal tunnel syndrome using continuous wave Doppler ultrasonography. J Hand Surg Br. 2006;31:306–10. Epub 2006 Feb 17.
Gassner EM, Schocke M, Peer S, Schwabegger A, Jaschke W, Bodner G. Persistent median artery in the carpal tunnel: color Doppler ultrasonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med. 2002;21:455–61.
Mallouhi A, Pulzl P, Trieb T, Piza H, Bodner G. Predictors of carpal tunnel syndrome: accuracy of gray-scale and color Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186:1240–5.
Klauser AS, Halpern EJ, De Zordo T, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome assessment with US: value of additional cross-sectional area measurements of the median nerve in patients versus healthy volunteers. Radiology. 2009;250:171–7.
Visser LH, Smidt MH, Lee ML. High-resolution sonography versus EMG in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:63–7.
Padua L, Padua R, Aprile I, Pasqualetti P, Tonali P. Multiperspective follow-up of untreated carpal tunnel syndrome: a multicenter study. Neurology. 2001;56:1459–66.
Beekman R, Visser LH. Sonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: a critical review of the literature. Muscle Nerve. 2003;27:26–33.
Johnson EW. Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. The gold standard. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;72:1.
Wong SM, Griffith JF, Hui AC, Lo SK, Fu M, Wong KS. Carpal tunnel syndrome: diagnostic usefulness of sonography. Radiology. 2004;232:93–9.
Hug C, Huber H, Terrier F, et al. Detection of flexor tenosynovitis by magnetic resonance imaging: its relationship to diurnal variation of symptoms. J Rheumatol. 1991;18:1055–9.
Nakamichi K, Tachibana S. The use of ultrasonography in detection of synovitis in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Br. 1993;18:176–9.
Ghasemi Esfe AR, Khalilzadeh O, Mazloumi M, et al. Combination of high-resolution and color Doppler ultrasound in diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Acta Radiol. 2011;52:191–7.
Boutte C, Gaudin P, Grange L, Georgescu D, Besson G, Lagrange E. Sonography versus electrodiagnosis for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome in routine practice. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2009;165:460–5.
Wenderhold W, Kunkel M, Eicke BM, Reimers CD. Continuous wave Doppler ultrasound for evaluation of vasomotor tone of the radial artery. Eur J Ultrasound. 1999;10:11–20.
Aminoff MJ. Involvement of peripheral vasomotor fibres in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979;42:649–55.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi-Esfe, A.R., Morteza, A., Khalilzadeh, O. et al. Color Doppler ultrasound for evaluation of vasomotor activity in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Skeletal Radiol 41, 281–286 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-011-1149-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-011-1149-8