Abstract
Objective
To compare joint space width (JSW) measurements obtained from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with a semi-automated computer algorithm to the Kellgren and Lawrence grading of osteoarthritis (OA).
Materials and methods
Three hundred and six patients (234 female, 72 male) with a mean age of 56.7 years (range 31–81 years) underwent MRI of their knees with a fast oblique spiral spoiled gradient (SPGR) sequence. A board-certified musculoskeletal radiologist graded the OA of all the patients in accordance with the Kellgren and Lawrence OA scale. A previously validated computer algorithm was used to determine the minimum JSW for both the tibiofemoral joint and the patellofemoral joint. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Student–Newman–Kuels post-hoc test was used to determine if there were differences in JSW as a function of OA grade.
Results
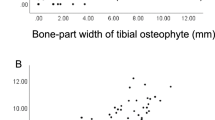
The radiologic grade of OA was inversely associated with the JSW. In the medial compartment the JSW did not change significantly between grade 1 and grade 2, but there was a significant decrease in JSW between grade 0 (normal) and grade 1 and for each OA grade above grade 2. In the lateral compartment no statistical differences were found till grade 2, while grade 3 was found to be statistically different from the previous one. The number of patients with a grade 4 patellofemoral OA was too low for the statistical significance to be assessed. In the patellofemoral joint the JSW did not change significantly until grade 2, while a statistically significant reduction was found for both grade 3 and grade 4.
Conclusion
This study showed that an inverse non-linear relationship exists between radiologic grade and JSW. The relationship differs for the tibiofemoral and the patellofemoral joint.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kellgren J, Lawrence J. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957; 16: 494–502.
Outerbridge RE. The etiology of chondromalacia patellae. 1961. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001; 389: 5–8.
Gunther KP, Sun T. Reliability of radiographic assessment in hip and knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1999; 7: 239–246.
Agnesi F, Amrami KK, Frigo C, Kaufman KR. Semiautomated digital analysis of knee joint space width using MRI images. Skeletal Radiol 2007; 36: 437–344.
Buckland-Wright JC, MacFarlane DG, Williams SA, Ward RJ. Accuracy and precision of joint space width measurements in standard and macro-radiographs of osteoarthritic knees. Ann Rheum Dis 1995; 54: 872–880.
Setton LA, Mow VC, Muller FJ, Pita JC, Howell DS. Mechanical properties of canine articular cartilage are significantly altered following transection of the anterior cruciate ligament. J Orthop Res 1994; 12: 451–463.
Baysal O, Baysal T, Alkan A, Altay Z, Yologlu S. Comparison of MRI graded cartilage and MRI based volume measurement in knee osteoarthritis. Swiss Med Wkly 2004; 134: 283–288.
Cicuttini FM, Wluka AE, Forbes A, Wolfe R. Comparison of tibial cartilage volume and radiologic grade of the tibiofemoral joint. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 682–688.
Dashtu M, Wulka AE, Geso M, Davis SR, Stuckley S, Cicuttini FM. Relationship between the area of the cartilage shown on the magnetic resonance imaging middle-slice image of the medial and lateral tibial cartilage volume and grade of osteoarthritis over time. Scand J Rheumatol 2004; 33: 87–93.
Schipplein OD, Andriacchi T. Interaction between active and passive knee stabilizers during level walking. J Orthop Res 1991; 9: 113–119.
Uri DS, Dalinka MK. Imaging of arthropathies. Crystal disease. Radiol Clin North Am 1996; 34: 359–374.
Preidler KW, Resnick D. Imaging of osteoarthritis. Radiol Clin North Am 1996; 34: 259–271.
Uebelhart D, Thonar EJ, Delmas PD, Chantraine A, Vignon E. Effects of oral chondroitin sulfate on the progression of knee osteoarthritis: a pilot study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1998; 6 [Suppl A]: 39–46.
Hunter DH, Lo GH, Gale D, Grainger AJ, Guermazi A, Conaghan PG. The development and reliability of a new scoring system for knee osteoarthritis MRI: BLOKS (Boston Leeds Osteoarthritis Knee Score). Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67: 206–211
Peterfy CG, Guermazi A, Zaim S et al. Whole-organ magnetic resonance imaging score (WORMS) of the knee in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2004; 12: 177–190.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Kathie Bernhardt and Christine Hughes for their work on this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by National Institutes Of Health (NIH) grant R01 AR48768.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agnesi, F., Amrami, K.K., Frigo, C.A. et al. Comparison of cartilage thickness with radiologic grade of knee osteoarthritis. Skeletal Radiol 37, 639–643 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-008-0483-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-008-0483-y