Abstract
Objective
Our objective was to evaluate the similarities and differences in bone mass and structure between pairs of monozygotic twins as measured by means of the quantitative ultrasound (QUS) technique.
Design
A cohort of monozygotic twins was measured by QUS of the hand phalanges using the DBM sonic bone profiler (IGEA, Carpi, Italy). The parameters studied were amplitude-dependent speed of sound (AD-SoS), ultrasound bone profile index (UBPI), signal dynamics (SDy) and bone transmission time (BTT). Linear correlation coefficients, multivariate linear analysis and the ANOVA test were used to assess intrapair associations between variables and to determine which factors influence the intrapair differences in QUS variables.
Patients
One hundred and six pairs of monozygotic twins were enrolled in the study, 68 females and 38 males in the age range 5 to 71 years.
Results
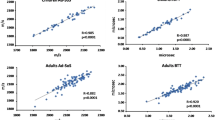
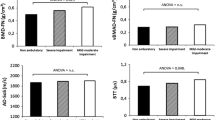
Significant intrapair correlations were obtained in the whole population and separately for males and females, regarding height ( r =0.98–0.99, p <0.0001), weight ( r =0.95–0.96, p <0.0001), AD-SoS ( r =0.90–0.92, p <0.0001), BTT ( r =0.94–0.95, p <0.0001) and other QUS parameters ( r >0.74, p <0.0001). Multivariate analysis revealed that intrapair differences between AD-SoS, SDy, UBPI and BTT are significantly influenced by age in the whole population and in the female population. Furthermore, the ANOVA test showed, for the female group, a significant increase in the intrapair differences in SDy and UBPI above 40 years.
Conclusions
A relative contribution of genetic factors to skeletal status could be observed by phalangeal QUS measurement in monozygotic twins. A significant increase in the intrapair difference in QUS parameters with increasing age and onset of menopause also suggests the importance of environmental factors in the female twin population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ralston SH. The genetics of osteoporosis. Q J Med 1997; 90:247–251.
Jouanny P, Guillemin F, Kuntz C, Jeandel C, Pourel J. Environmental and genetic factors affecting bone mass. Arthritis Rheum 1995; 38:61–67.
Slemenda CW, Christian JC, Reed T, Reister TK, Williams CJ, Johnston CC. Long-term bone loss in men: effects of genetic and environmental factors. Ann Intern Med 1992; 117:286–291.
Andrew T, Mak YT, Reed P, MacGregor AJ, Spector TD. Linkage and association for bone mineral density and heel ultrasound measurements with a simple tandem repeat polymorphism near the osteocalcin gene in female dizygotic twins. Osteoporos Int 2002; 13:745–754.
Brown MA, Haughton MA, Grant SF, Gunnell AS, Henderson NK, Eisman JA. Genetic control of bone density and turnover: role of the collagen 1alpha1, estrogen receptor, and vitamin D receptor genes. J Bone Miner Res 2001; 16:758–764.
Kannus P, Palvanen M, Kaprio J, Parkkari J, Koskenvuo M. Genetic factors and osteoporotic fractures in elderly people: prospective 25 year follow up of a nationwide cohort of elderly Finnish twins. BMJ 1999; 319:1334–1337.
Kleerekoper M, Nelson DA, Flynn MJ, Pawluszka AS, Jacobsen G, Peterson EL. Comparison of radiologic absorptiometry with dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and quantitative computed tomography in normal older white and black women. J Bone Miner Res 1994; 9:1745–1750.
Ferrari S, Rizzoli R, Bonjour JP. Genetic aspects of osteoporosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1999; 11:294–300.
Guglielmi G, Grimston SK, Fischer KC, Pacifici R. Osteoporosis: diagnosis with lateral and posteroanterior dual X-ray absorptiometry compared with quantitative CT. Radiology 1994; 192:845–850.
Pacifici R, Rupich RC, Griffin MG, Chines A, Susman N, Avioli LV. Dual energy radiography versus quantitative computed tomography for the diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1990; 70:705–710.
De Terlizzi F, Battista S, Cavani F, Canè V, Cadossi R. Influence of bone tissue density and elasticity on ultrasound propagation: an in vitro study. J Bone Min Res 2000; 15:2458–2466.
Barkmann R, Lüsse S, Stampa B, Sakata S, Heller M, Glüer C-C. Assessment of the geometry of human finger phalanges using quantitative ultrasound in vivo. Osteoporos Int 2000; 11:745–755.
Hans D, Wu C, Njeh CF et al. Ultrasound velocity of trabecular cubes reflects mainly bone density and elasticity. Calcif Tissue Int 1999; 64:18–23.
Gluer CC, Wu CY, Jergas M, Goldstein SA, Genant HK. Three quantitative ultrasound parameters reflect bone structure. Calcif Tissue Int 1994; 55:46–52.
Wuster C, Albanese C, De Aloysio D et al. Phalangeal osteosonogrammetry study: age-related changes, diagnostic sensitivity, and discrimination power. J Bone Miner Res 2000; 15:1603–1614.
Hartl F, Tyndall A, Kraenzlin M et al. Discriminatory ability of quantitative ultrasound parameters and bone mineral density in a population-based sample of postmenopausal women with vertebral fractures: result of the Basel Osteoporosis Study. J Bone Miner Res 2002; 17:321–330.
Grampp S, Henck C, Lu Y et al. Quantitative US of the calcaneus cutoff levels for the distinction of healthy and osteoporotic individuals. Radiology 2001; 220:400–405.
Ventura V, Mauloni M, Mura M, Paltrinieri F, de Aloysio D. Ultrasound velocity changes at the proximal phalanxes of the hand in pre-, peri- and postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 1996; 6:368–375.
Guglielmi G, Cammisa M, De Serio A et al. Phalangeal US velocity discriminates between normal and vertebrally fractured subjects. Eur Radiol 1999; 9:1632–1637.
Guglielmi G, Njeh CF, de Terlizzi F et al. Phalangeal quantitative ultrasound, phalangeal morphometric variables, and vertebral fracture discrimination. Calcif Tissue Int 2003; 72:469–477.
Von Wurmb-Schwark N, Schwark T, Christiansen L, Lorenz D, Oehmichen M. The use of different multiplex PCRs for twin zygosity determination and its application in forensic trace analysis. Leg Med (Tokyo) 2004; 6:125–130.
Mele R, Masci G, Ventura V, de Aloysio D, Bicocchi M, Cadossi R. Three-Year longitudinal study with quantitative ultrasound at the hand phalanx in a female population. Osteoporosis Int 1997; 7:550–557.
Montagnani A, Gonnelli S, Cepollaro C et al. Quantitative ultrasound at the phalanges in healthy Italian men. Osteoporos Int 2000; 11:499–504.
Montagnani A, Gonnelli S, Cepollaro C et al. Usefulness of bone quantitative ultrasound in management of osteoporosis in men. J Clin Densitom 2001; 4:231–237.
Drozdzowska B, Pluskiewicz W, de Terlizzi F. Quantitative ultrasound at the hand phalanges in monozygotic twins: a preliminary report. Ultrasound Med Biol 2002; 28:1153–1156.
Howard GM, Nguyen TV, Harris M, Kelly PJ, Eisman JA. Genetic and environmental contribution to the association between quantitative ultrasound and bone mineral density measurements: a twin study. J Bone Miner Res 1998; 13:1318–1327.
Hunter DJ, de Lange M, Andrew T, Snieder H, MacGregor AJ, Spector TD. Genetic variation in bone mineral density and calcaneal ultrasound: a study of the influence of menopause using female twins. Ostoporos Int 2001; 12:406–411.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guglielmi, G., de Terlizzi, F., Torrente, I. et al. Quantitative ultrasound of the hand phalanges in a cohort of monozygotic twins: influence of genetic and environmental factors. Skeletal Radiol 34, 727–735 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-005-0933-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-005-0933-8