Abstract.
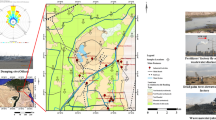
This study attempts to determine the impact of industries such as paper mills and ferro-alloy units and mining of Mn ore deposits on soil and river geochemistry in a monsoon-dominated area on the southwest coast of India. Soils, suspended particulate matter (SPM), andbottom sediments from the Kali River are all enriched with Al, Fe, Ni and Co, but strongly depleted in Na, Ca, K, Mg, Rb and Sr due to intense chemical weathering. However, even in river water the concentrations of dissolved alkaline and alkaline earth elements are low. Manganese, in particular, is anomalously high in bottom sediments and suspended particles by factors of 2.3 to 20.76 in relation to average shale and world river SPM. This enrichment is attributable to mining of Mn ore deposits in the riverdrainage area. The concentration of dissolved Pb, Co and Cd in Kali River water is much higher (by factors of 2 to 13) in comparison to the world's major rivers, implying anthropogenic inputs of these metals through localized discharge of sewage and industrial effluents. Assessment of heavy metal pollution determined by the element enrichment factor (EF) and the index of geo-accumulation (Igeo) suggests that most of the hazardous heavy metals studied are within the background level. However, Al, Fe, Co andNi are enriched due to their immobility during chemical weathering and their adsorption subsequently by Al and Fe oxides. These studies show that, although there are major industries in the study area, their impact is not yet visible due to the large input of pristine sediments from the catchment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjunatha, .B., Balakrishna, .K., Shankar, .R. et al. Geochemistry and assessment of metal pollution in soils and river components of a monsoon-dominated environment near Karwar, southwest coast of India. Env Geol 40, 1462–1470 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540100342
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540100342