Abstract
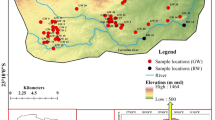
The lower Vamsadhara river basin, spreading over an area of 817 sq.km in northern Andhra Pradesh, represents a typical rural setting. The occurrence of phosphorus-bearing minerals reported in literature, and the increasing application of phosphatic fertilizers in the area have prompted these studies. Water samples from 113 wells were analysed for Ca, Mg, Na, K, Cl, SO4, HCO3, F, NO3 and PO4. The results indicate the presence of phosphate in the groundwater ranged from 0.72 to 7.07 mg/l, which is beyond the limits recommended for domestic and water treatment purposes. Samples of soils and weathered rocks were analyzed for their water-soluble phosphate and other chemical parameters. The water-soluble phosphate in the widely used fertilizers of the area was determined. The spatial variation of phosphate in the aquifer and the soil leachate characteristics supplemented by the chemical equilibrium calculations clearly indicate the dominance of geological sources over the fertilizer sources in contributing PO4 to the groundwaters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 March 1996 / Accepted: 29 July 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, N., Prasad, P. Phosphate pollution in the groundwater of lower Vamsadhara river basin, India. Environmental Geology 31, 117–122 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050170
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050170