Abstract
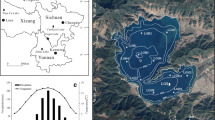
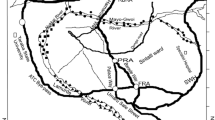
Rock-magnetic techniques have become a useful tool in environmental issues; in particular, magnetic studies constitute an alternative way to study pollution in different media. The present contribution focuses on magnetic parameters as pollution indicators, especially from their relationship with contents of heavy metals. The work was carried out in two Indian rivers located in Tamil Nadu, southern India. Several sediment samples were collected and studied in the laboratory using magnetic techniques, magnetic susceptibility, anhysteric remanent magnetization, isothermal remanent magnetization, and chemical techniques to determine contents of heavy metals. Magnetic mineralogy indicates the predominance of ferrimagnetic minerals; although magnetite-like minerals are the main magnetic carriers, antiferromagnetic minerals can be present as subordinate carriers. Concentration-dependent magnetic parameters revealed noticeable differences between both rivers, e.g. magnetic susceptibility is four times higher in Cauvery than in Palaru River. Moreover, such increase can be interpreted as “magnetic enhancement” and therefore related to the pollution status. This magnetic enhancement indicated a different pollutant contribution in both rivers, and also, a different spatial distribution along these rivers, where critical (or more polluted) sites were identified. On the other hand, univariate and multivariate statistical analyses—e.g. PCoordA, Multifactorial Analysis of distance, PCA and RDA—were examined, revealing a link between magnetic and chemical variables. Among magnetic parameters, the concentration-dependent magnetic parameters (e.g. magnetic susceptibility) seem to be the most relevant for this study.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson TW (1958) An introduction to multivariate statistical analysis. Wiley, New York
Angulo E (1996) The Tomlinson pollution load index applied to heavy metal “Mussel-Watch” data: a useful index to assess coastal pollution. Sci Tot Environ 187:19–56
APHA, AWWA, WEF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn
Bartington Instruments Ltd. (1994) Operation manual. Environmental magnetic susceptibility—using the Bartington MS2 system. Chi Publishing, UK, 54 pp
Beckwith P, Ellis J, Revitt D, Oldfield F (1986) Heavy metal and magnetic relationships for urban source sediments. Phys Earth Planet Int 42:67–75
Bityukova L, Scholger R, Birke M (1999) Magnetic susceptibility as indicator of environmental pollution of soils in Tallin. Phys Chem Earth A 24(9):829–835
Boyko T, Scholger R, Stanjek H, MAGPROX TEAM (2004) Topsoil magnetic susceptibility mapping as a tool for pollution monitoring: repeatability of in-situ measurements. J Appl Geophys 55(3–4):249–259
Chan LS, Ng SL, Davis AM, Yim WWS, Yeung CH (2001) Magnetic properties and heavy-metal contents of contaminated seabed sediments of Penny’s bay, Hong Kong. Mar Pollut Bull 42(7):569–583
Chaparro MAE, Bidegain JC, Sinito AM, Gogorza CS, Jurado S (2003) Preliminary results of magnetic measurements on stream-sediments from Buenos Aires province, Argentina. Stud Geophys Geod 47(1):121–145
Chaparro MAE, Bidegain JC, Sinito AM, Jurado S, Gogorza CS (2004) Relevant magnetic parameters and heavy metals from relatively polluted stream sediments—vertical and longitudinal distribution along a cross-city stream in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Stud Geophys Geod 48(3):613–634
Chaparro MAE, Lirio JM, Nunez H, Gogorza CSG, Sinito AM (2005) Preliminary magnetic studies of lagoon and stream sediments from Chascom´us area (Argentina)—magnetic parameters as pollution indicators and some results of using an experimental method to separate magnetic phases. Environ Geol 49(1):30–43
Chaparro MAE, Gogorza CSG, Chaparro MAE, Irurzun MA, Sinito AM (2006) Review of magnetism and pollution studies of various environments in Argentina. Earth Planets Space 58(10):1411–1422
Chaparro MAE, Nuñez H, Lirio JM, Gogorza CSG, Sinito AM (2007a) Magnetic screening and heavy metal pollution studies in soils from Marambio Station, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 19(3):379–393
Chaparro MAE, Chaparro MAE, Marinelli C, Sinito AM (2007b) Multivariate techniques as alternative statistical tools applied to magnetic proxies for pollution: cases of study from Argentina and Antarctica. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0823-6 (Online First™)
Cuadras CM (1981) Métodos de analisis multivariante. Eunibar, Barcelona
Dearing J, Dann R, Hay K, Lees J, Loveland P, Maher B, O’Grady K (1996) Frequency-dependent susceptibility measurements of environmental materials. Geophys J Int 124:228–240
Desenfant F, Petrovský E, Rochette P (2004) Magnetic signature of industrial pollution of stream sediments and correlation with heavy metals: case study from South France. Water Air Soil Pollut 152:297–312
Dunlop J, Özdemir Ö (1997) Rock magnetism. Fundamentals and frontiers. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 573 pp
Durza O (1999) Heavy contamination and magnetic susceptibility in soils around metallurgical plant. Phys Chem Earth A 24(6):541–543
Environmental Protection Agency, EPA SW-846 (1986) Method 3050 Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soils. Chapter 3: metallic analysis, volume one, section A, part 1 of test methods for evaluating solid waste, Washington DC
Georgeaud VM, Rochette P, Ambrosi JP, Vandamme D, Williamson D (1997) Relationship between heavy metals and magnetic properties in a large polluted catchment: The Etang de Berre (South of France). Phys Chem Earth A 22(1–2):211–214
Gower JC (1966) Some distance properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis. Biometrika 53:325–338
Gower JC (1987) Introduction to ordination techniques. In: Legendre P, Legendre L (eds) Development in numerical ecology. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–64
Gower JC, Krzanowski WJ (1999) Analysis of distance for structured multivariate data and extensions to multivariate analysis of variance. Appl Stat 48(4):505–519
Hanesch M, Scholger R (2002) Mapping of heavy metal loadings in soils by means of magnetic susceptibility measurements. Environ Geol 42:857–870
Heller F, Strzyszcz Z, Magiera T (1998) Magnetic record of industrial pollution in soils of Upper Silesia, Poland. J Geophys Res 103(B8):17767–17774
Hoffmann V, Knab M, Appel E (1999) Magnetic susceptibility mapping of roadside pollution. J Geochem Int 66(1–2):313–326
Hu S, Wang Y, Appel E, Zhu Y, Hoffmann V, Shi C, Yu Y (2003). Magnetic responses to acidification in Lake Yangzonghai, SW China. Phys Chem Earth 28:711–717
Hunt A, Jones J, Oldfield F (1984) Magnetic measurements and heavy metals in atmospheric particulates of anthropogenic origin. Sci Total Environ 33:129–139
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (1992) Applied multivariate statistical analysis, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 642 pp
Jongman RHG, Ter Braak CJF, Van Tongeren OFR (1987) Data analysis in community and landscape ecology. Pudoc. Wageningen. 299 pp
Jordanova D, Veneva L, Hoffmann V (2003) Magnetic susceptibility screening of anthropogenic impact on the Danube River sediments in Northwestern Bulgaria—preliminary results. Stud Geophys Geod 47:403–418
Jordanova DV, Hoffmann V, Thomas Fehr K (2004) Mineral magnetic characterization of anthropogenic magnetic phases in the Danube river sediments (Bulgarian part). Earth Planet Sci Lett 221:71–89
Kapicka A, Petrovský E, Ustjak S, Machácková K (1999) Proxy mapping of fly-ash pollution of soils around a coal-burning power plant: a case study in Czech Republic. J Geochem Explor 66:291–297
King J, Banerjee SK, Marvin J, Özdemir Ö (1982) A comparison of different magnetic methods for determining the relative grain size of magnetite in natural materials: some results from lake sediments. Earth Planet Sci Lett 59:404–419
Knab M, Appel E, Hoffmann V (2001) Separation of the anthropogenic portion of heavy metal contents along a highway by means of magnetic susceptibility and fuzzy c-means cluster analysis. Eur J Environ Eng Geophys 6:125–140
Knab M, Hoffmann V, Petrovský E, Kapicka A, Jordanova N, Appel E (2006) Surveying the anthropogenic impact of the Moldau river sediments and nearby soils using magnetic susceptibility. Environ Geol 49:527–535
Kruiver PP, Passier HF (2001) Coercivity analysis of magnetic phases in sapropel S1 related to variations in redox conditions, including an investigation of the S ratio. Geochem Geophys Geosyst Paper number 2001GC000181
Kruiver PP, Dekkers MJ, Heslop D (2001) Quantification of magnetic coercivity components by the analysis of acquisition curves of isothermal remanent magnetisation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 189:269–276
Kukier U, Fauziah Ishak C, Summer ME, Miller WP (2003) Composition and element solubility of magnetic and non-magnetic fly ash fractions. Environ Pollut 123:255–266
Lecoanet H, Leveque F, Ambrosi J-P (2003) Combination of magnetic parameters: an efficient way to discriminate soil-contamination sources (south France). Environ Pollut 122:229–234
Magiera T, Strzyszcz Z (1999) Ferrimagnetic minerals of anthropogenic origin in soils of some Polish national parks. Water Air Soil Pollut 124:37–48
Magiera T, Strzyszcz Z, Kapicka A, Petrovsky E, MAGPROX TEAM (2006) Discrimination of lithogenic and anthropogenic influences on topsoil magnetic susceptibility in Central Europe. Geoderma 130:299–311
Maher BA (1986) Characterisation of soils by mineral magnetic measurements. Phys Earth Planet Int 42:76–92
Maher BA, Thompson R, Hounslow MW (1999) Introduction. In: Maher BA, Thompson R (eds) Quaternary climates, environments and magnetism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–48
Manly BFJ (1997) Randomization, bootstrap and Monte Carlo methods in biology. 2da. edición. Chapman & Hall, London
Mardia K (1980) Multivariate analysis. Academic, New York
Matzka J, Maher BA (1999) Magnetic biomonitoring of roadside tree leaves: identification of spatial and temporal variations in vehicle derived particulates. Atmos Environ 33:4565–4569
Mullins CE (1977) Magnetic susceptibility of the soil and its significance in soil science: a review. J Soil Sci 28:223–246
Peters C, Dekkers MJ (2003) Selected room temperature magnetic parameters as a function of mineralogy, concentration and grain size. Phys Chem Earth 28:659–667
Petrovský E, Elwood B (1999) Magnetic monitoring of air, land and water pollution. In: Maher BA, Thompson R (Eds) Quaternary climates, environment and magnetism, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 279–322
Petrovský E, Kapicka A, Zapletal K, Sebestová E, Spanilá T, Dekkers MJ, Rochette P (1998) Correlation between magnetic properties and chemical composition of lake sediments from northern Bohemia. Preliminary study. Phys Chem Earth A 23(9–10):1123–1126
Petrovský E, Kapicka A, Jordanova N, Knab M, Hoffmann V (2000) Low field susceptibility: a proxy method of estimating increased pollution of different environmental systems. Environ Geol 39(3–4):312–318
Ramasamy V, Murugesan S, Mullainathan S, Chaparro MAE (2006) Magnetic characterization of recently excavated sediments of Cauvery river, Tamilnadu, India. Pollut Res 25(2):357–362
Schibler L, Boyko T, Ferdyn M, Gajda M, Höll S, Jordanova N, Rösler N The Magprox team (2002) Topsoil magnetic susceptibility mapping: data reproducibility and compatibility, measurement strategy. Stud Geophys Geod 46:43–57
Scholger R (1998) Heavy metal pollution monitoring by magnetic susceptibility measurements applied to sediments of the river Mur (Styria, Austria). Eur J Environ Eng Geophys 3:25–37
Spiteri C, Kalinski V, Rösler W, Hoffmann V, Appel E, MAGPROX team (2005) Magnetic screening of a pollution hotspot in the Lausitz area, Eastern Germany: correlation analysis between magnetic proxies and heavy metal contamination in soils. Environ Geol 49:1–9
Strzyszcz Z (1993) Magnetic susceptibility of soils in the areas influenced by industrial emission, in soil monitoring. Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, Monte Verita, pp 255–269
Strzyszcz Z, Magiera T, Heller F (1996) The influence of industrial emissions on the magnetic susceptibility of soils in Upper Silesia. Stud Geophys Geod 40:276–286
Tauxe L (1993) Sedimentary records of relative paleointensity of the geomagnetic field: theory and practice. Rev Geophys 31(3):319–354
Thompson R, Oldfield F (1986) Environmental magnetism. Allen & Unwin, London, 225 pp
Thompson R, Bloemendal J, Dearing J, Oldfield F, Rummery J, Stober J, Turner G (1980) Environmental applications of magnetic measurements. Science 4430(207):481–486
Tite M, Linington R (1975) Effect of climate on the magnetic susceptibility of soils. Nature 256:565–566
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol Meeresunters 33:566–575
Wang X-S, Qin Y (2005) Correlation between magnetic susceptibility and heavy metals in urban topsoil: a case study from the city of Xuzhou, China. Environ Geol 49(1):10–18
Wang X-S, Qin Y (2006) Magnetic properties of urban topsoils and correlation with heavy metals: a case study from the city of Xuzhou, China. Environ Geol 49:897–904
Yang T, Liu Q, Chan L, Liu Z (2007) Magnetic signature of heavy metal pollution of sediments: case study from the East Lake in Wuhan, China. Environ Geol 52:1639–1650
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Annamalai University, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos Aires (UNCPBA), Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM), LEMIT, CICPBA and CONICET for their financial support. We also would like to express our thanks to Dr. Sandra Jurado and Raúl Pérez for their support in chemical determinations. The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their useful suggestions as well.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaparro, M.A.E., Sinito, A.M., Ramasamy, V. et al. Magnetic measurements and pollutants of sediments from Cauvery and Palaru River, India. Environ Geol 56, 425–437 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1180-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1180-1