Abstract
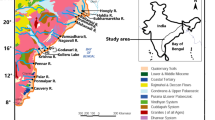
Fine-grained floodplain sediments of the catastrophic 2002 flood deposited along the lower reaches of the Berounka and Vltava Rivers, Czech Republic, were not highly contaminated with heavy metals and other toxic elements. This is due to the dominantly mineral character of the sediments (Ctot in the range 3.97–5.01%, relatively low content of clay minerals), and due to the very high degree of contamination dilution by eroded pre-industrial non-contaminated floodplain sediments. Despite this high degree of dilution, the influence of the small Litavka River, draining the historical Pb–Zn–Ag Příbram ore region, is well visible. The Litavka River is one of important sources of Pb and Zn contamination in the whole Berounka–Vltava–Labe river system. The 2002 flood sediments deposited in the floodplain of the Berounka and Vltava Rivers show poor vertical chemical zoning, except for some components enriched in the uppermost layer by precipitation from evaporated pore-water contained in the mud, i.e. secondary carbonate. The content of Ccarb of the sediments (0.05–0.15%) is partly represented by this secondary carbonate, which is later leached by rainwater, and partly by fragments of river mollusk shells. A majority of the heavy metals contained in sediments can be readily leached by diluted acids, and to a much smaller degree by rainwater.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baborowski M, Büttner O, Morgenstern P, Kruger F, Lobe I, Rupp H, Tümpling Wv (2007) Spatial and temporal variability of sediment deposition on artificial-lawn traps in a floodplain of the River Elbe. Environ Pollut 148(3):770–778
Baborowski M, von Tümpling W Jr., Friese K (2004) Behaviour of suspended particulate matter (SPM) and selected trace metals during the 2002 summer flood in the River Elbe (Germany) at Magdeburg monitoring station. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 8(2):135–150
Becker A, Grunevald U (2003) Flood risk in Central Europe. Science 300(5622):1099
Brugmann L (1995) Metals in sediments and suspended matter of the river Elbe. Sci Total Environ 159(1):53–65
Czudek T (2005) Vývoj reliéfu krajiny České republiky v kvartéru (Quaternary development of the landscape relief in the Czech Republic). Moravské zemské muzeum, Brno (in Czech with English summary), p 238
Darnley AG, Björklund A, Bølviken B, Gustavsson N, Koval PV, Plant JA, Steenfelt A, Tauchid M, Xuejing X, Garrett RG & Hall GEM (1995) A global geochemical database for environmental and resource management. Recommendations for international geochemical mapping, Final Report of IGCP Project 259. UNESCO Publishing, p 122
Demetriades A, Pirc S, De Vos W, Ottesen RT, Reeder S, O’Connor PJ, Bidovec M, De Vivo B, Tarvainen T, Batista MJ, Lax K, Halamic J, Pasieczna A, Slaninka I, Birke M, Siewers U, Breward N, Lima A, Duris M, Locutura J, Bel-lan A, Salpeteur I, Klein P, Jordan G, Mazreku A, Petersell V (2006) Distribution of elements in floodplain sediment. In: Salminen R (ed) Geochemical atlas of Europe. Espoo: Geological Survey of Finland, pp 41–44
Ettler V, Mihaljevič M, Šebek O, Molek M, Grygar T, Zeman J (2005) Geochemical and Pb isotopic evidence for sources and dispersal of metal contamination in stream sediments from the mining and smelting district of Příbram, Czech Republic. Environ Pollut 142(3):409–417
Holoubek I (project manager), Adamec V, Bartoš M, Černá M, Čupr P, Bláha K, Demnerová K, Drápal J, Hajšlová J, Holoubková I, Jech L, Klánová J, Kocourek V, Kohoutek J, Kužílek V, Machálek P, Matějů V, Matoušek J, Matoušek M, Mejstřík V, Novák J, Ocelka T, Pekárek V, Petira K, Provazník O, Punčochář M, Rieder M, Ruprich J, Sáňka M, Tomaniová M, Vácha R, Volka K, Zbíral J (2003) Úvodní národní inventura persistentních organických polutantů v České republice (Initial national inventory of persistent organic pollutants in the Czech Republic). Project GF/CEH/01/003: Enabling activities to facilitate early action on the implementation of the stockholm convention On Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in the Czech Republic. Tocoen, s.r.o., Brno on behalf of consortium Recetox—Tocoen & Associates, Tocoen report No. 249, Brno (in Czech)
Lehmann J, Puff T, Damke H, Eidam J, Henning KH, Julich WD, Rossberg H (1999) The Odra river load of heavy metals at Hohenwutzen during the flood in 1997. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 27(5):321–324
Martin CW (1997) Heavy metal concentrations in floodplain surface soils, Lahn River, Germany. Environ Geol 30:119–125
Martin CW (2000) Heavy metal trends in floodplain sediments and valley fill, River Lahn, Germany (2000) Catena, 39 (1):53–68. Cited 12 times. doi:10.1016/s0341-8162(99)00080-6
Mikuláš R (2007) Ichnofabric of the Holocene and modern floodplain deposits, Czech Republic. Paper presented at 9th International Ichnofabric Workshop, Calgary, August 2007, Abstracts
sine (2003a) Výsledná zpráva o projektu Vyhodnocení katastrofální povodně v srpnu 2002 a návrhu úpravy systému prevence před povodněmi (Final report of the project Evaluation of catastrophic flood of August 2002 and of proposal of the Flood preventive system). Unpublished report, the final version accepted by the Government of Czech Republic on 21 January 2004. Ministry of the Environment of the Czech Republic. Praha (in Czech)
sine (2003b) Souhrnná zpráva o povodni v srpnu 2002 za Povodí Vltavy, státní podnik. (Summary report on the major flood in August 2002 in the river Moldau catchment). Povodí Vltavy, s.p., Praha (in Czech), p 95
Sixta V (1977) Coulometric determination of carbonates in rock samples. Fresenius’ Zeitschrift für Analytische Chemie 285(5):369–372
Swartjes FA (1999) Risk-based assessment of soil and groundwater quality in the Netherlands: standards and remediation urgency. Risk Anal 19(6):1235–1249
Taylor MP (1996) The variability of heavy metals in floodplain sediments: a case study from mid Wales. Catena 28:71–87
Walling DE, Owens PN, Cartera J, Leeks GJL, Lewis S, Meharg AA, Wright J (2003) Storage of sediment-associated nutrients and contaminants in river channel and floodplain systems. Appl Geochem 18:195–220
Žák K, Táborský Z, Lachmanová M, Pudilová M (2001) Heavy mineral assemblages in allochthonous clastic cave sediments of the Bohemian Karst: a pilot study. Český Kras 27:5–14. Beroun (in Czech with English abstract)
Žák K, Vysoká H, Bruthans J, Hlaváč J (2004) Hydrogeology of karst system of Spring Domášov—Tetín resurgence: new observation and data. Český Kras 30:45–50. Beroun (in Czech with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
This research was financed through the project IAA300130505 of the Grant Agency of the Czech Academy of Sciences and project No.AV0Z30130516 of the Institute of Geology, ASCR. Radek Mikuláš collected the sediment samples from floodplain of Vltava River. Lenka Lisá and Sergio Sánchez de la Nieta Morote participated in sample sieving and homogenization. J. Hlaváč determined the shells of mollusks. P. Skřivan did the pilot leaching experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navrátil, T., Rohovec, J. & Žák, K. Floodplain sediments of the 2002 catastrophic flood at the Vltava (Moldau) River and its tributaries: mineralogy, chemical composition, and post-sedimentary evolution. Environ Geol 56, 399–412 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1178-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1178-8