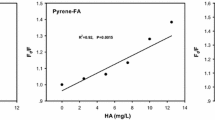
Abstract
The effect of organic matter on the sorption of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on lake sediments is critical to understanding the fate and transport of contaminants at the sediment–water interface in lake ecosystems. Results indicate that DOM sorption on sediment is largely due to ligand exchange between the DOM and hydroxyl groups, and the amount of DOC sorbed is a linear function of added DOC. With increasing organic matter content the sediment has lower binding strength, higher releasing ability for DOM, and the higher amount of DOM sorbed by sediment naturally. There was no clear difference before and after the sediment was treated with H2O2, but the constant b implied that after the sediments were treated DOC release was promoted. Organic matter in the sediment tends to impede the sorption of DOC and results in a remarkable decrease in DOC sorption rates.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus JB, Kevin CJ (1996) The effects of particle size, organic matter, crop residues and dissolved organic matter on the sorption kinetic of atrazine and isoproturon by clay soil. Chemosphere 32:2345–2358
Benner R, Pakulskl JD, McCarthy M, Hedges JL, Hatcher PG (1992) Bulk chemical characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the ocean. Science 255:1561–1564
Berggren D, Bergkvist B, Falkengren-Grerup U, Folkeson L, Tyler G (1990) Metal solubility and pathways in acidified forest ecosystem of South Sweden. Sci Total Environ 96:103–114
Cai QM, Gao XY, Chen YW et al (1995) Dynamic variations of water quality in Taihu Lake and multivariate analysis of its influential factors (in Chinese). J Lake Sci 7(2):97–106
Chiou CT, Porter PE, Sehmedding DW (1983) Partition equilibrium of nonionic organic compounds between soil organic matter and water. Environ Sci Technol 17:295–297
Cole JJ, Pace ML, Carpenter SR, Kitchell JF (2000) Persistence of net heterotrophy in lakes during nutrient addition and food web manipulation. Limnol Oceanog 45:1718–1730
David IK, Graham G, William N, Gary WVL, Horton JH (2003) Competitive adsorption of phosphate and carboxylate with natural organic matter on hydrous iron oxides as investigated by chemical force microscopy. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 212:249–264
David JB (2001) Dissolved organic matter in Chesapeake Bay sediment pore waters. Org Geochem 32:487–505
Donald RG, Anderson DW, Steward JWB (1993) Potential role of dissolved organic carbon in phosphorus transport in forest soils. Soil Sci Am J 57:1611–1618
Guggenberger G, Zech W (1992) Retention of dissolved organic carbon and sulfate in aggregated acid forest soils. J Environ Qual 21:643–654
Hedges JI, Cowie GL, Richey JE, Quay PD, Benner R, Strom M, Forsberg BR (1994) Origins and processing of organic matter in the Amazon River as indicated by carbohydrates and amino acids. Limnol Oceanogr 39:743–761
Hedges JI, Keil RG (1995) Sedimentary organic matter preservation: an assessment and speculative synthesis. Mar Chem 49:81–115
ISSCAS (Institute of soil science Chinese academy of sciences) (1978) Soil physics and chemistry analyze. Shanghai science and technology publishing company, Shanghai, pp 35–64
Klaus K, Georg G (2000) The role of DOM sorption to mineral surfaces in the preservation of organic matter in soils. Org Geochem 31:711–725
Klaus K, Georg G, Wolfgang Z (1996) Sorption of DOM and DOM fractions to forest soils. Geoderma 74:281–303
Kukkonen J, McCarthy JF, Oikari A (1990) Effects of XAD-8 fractions of dissolved organic carbon on the sorption and bioavailabitity of organic micropollutants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:551–557
Liu HL, Jin XC, Jing YF (1999) Environmental dredging technology of lake sediment (in Chinese). Chinese Eng Sci 1(1):81–84
Lopez P, Lluch X, Vidal M, Morguí JA (1996) Adsorption of phosphorus on sediments of the Balearic Islands (Spain) related to their composition. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 42:185–196
McDowell WH, Wood T (1984) Podzolization: soil processes control dissolved carbon concentrations in stream water. Soil Sci 137:23–32
Michael LP, Jonathan JC (2002) Synchronous variation of dissolved organic carbon and color in lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 47(2):333–342
Muhammad TS, Robinson JS (2004) Difference in phosphorus retention and release in soils amended with animal manures and sewage sludge. Soil Sci soc Am J 68:1421–1428
Nelson PN, Baldock J., Oades JM (1993) Concentration and composition of dissolved organic carbon in streams in relation to catchment properties. Biogeochemistry 19:27–50
Qin BQ (2002) Approaches to mechanisms and control of eutrophication of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River (in Chinese). J Lake Sci 14:193–202
Qualls R G(2000) Comparison of the behavior of soluble organic and inorganic nutrients in forest soils. For Ecol Manage 138:29–50
Qulla R, Haines BL (1991) Geochemistry of dissolved organic nutrient in water percolating through a forest ecosystem. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:1112–1123
Ruban VJF, Lopez SP, Pardo G, Rauret H, Muntau PH (2001) Quevauviller Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments—a synthesis of recent works. Fresenius J Anal Chem 370:224–228
Shaw PJ, Jones RI, Haan HD (2000) The influence of humic substances on the molecular weight distributions of phosphate and iron in epilimnetic lake waters. Freshw Biol 45:383–393
Shen YH (1999) Sorption of natural dissolved organic mater on soil. Chemosphere 38(7):1505–1515
Stumm W (1992) Chemistry of the solid–water interface: process at the mineral–water and particle–water interface in natural systems. Wiley, New York, p 30
Swift RS (1980) The effect of adsorbed organic materials on the cation exchange of clay minerals. In: Banin A, Kafkafi U (eds) Agrochemicals in soils, pp 123–129
Vanve GF, David MB (1992) Dissolved organic carbon and sulfate sorption by spodosol mineral horizons. Soil Sci 154:136–144
Wang SR, Jin XC, Pang Y et al (2005a) The study on the effect of pH on phosphate sorption by different trophic lake sediments. J Colloid Interface Sci 285:448–457
Wang SR, Jin XC, Zhao HC et al (2005b) Phosphate adsorption characteristics onto the sediments from shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze Rive. Environ Sci 26(3):38–43
Zech W, Guggenberger G, Schulten HH (1994) Budgets and chemistry of dissolved organic carbon in forest soils. Effects of anthropogenic soil acidification. Sci. Total Environ 152:49–62
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for financial support from China’s national basic research program: “Studies on the Process of Eutrophication of Lakes and the Mechanism of the Blooming of Blue Green Alga” (2002CB412304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, X., Wang, S., Zhao, H. et al. Effect of organic matter on DOM sorption on lake sediments. Environ Geol 56, 391–398 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1177-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1177-9