Abstract
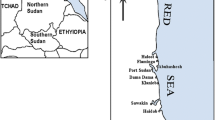
The purpose of this study was to investigate the concentration levels of heavy metals in different species of the main three marine algal divisions from the Gulf of Aden coastal waters, Yemen. The divisions included Chlorophyta—green plants (Halimeda tuna, Rhizoclonium kochiamum, Caldophora koiei, Enteromorpha compressa, and Caulerpa racemosa species), Phaeophyta—brown seaweeds (Padina boryana, Turbinaria elatensis, Sargassum binderi, Cystoseira myrica, and Sargassum boveanum species), and Rhodophyta—red seaweeds (Hypnea cornuta, Champia parvula, Galaxaura marginate, Laurencia paniculata, Gracilaria foliifere, and species). The heavy metals, which included cadmium (Cd), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), Iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), and vanadium (V) were measured by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAs). The concentrations of heavy metals in all algal species are in the order of Fe >> Cu > Mn > Cr > Zn > Ni > Pb > Cd > V > Co. The results also showed that the uptake of heavy metals by different marine algal divisions was in the order of Chlorophyta > Phaeophyta > Rhodophyta. These heavy metals were several order of magnitude higher than the concentrations of the same metals in seawater. This indicates that marine alga progressively uptake heavy metals from seawater.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Shwafi N (2003) Distribution of trace metals in sediment of red sea coat of Yemen. J Fac Educ, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt 28:117–126
Al-Shiwafi N, Rushdi AI, Ba-Issa A (2005) Trace metals in surface seawaters and sediments from various habitats of the Red Sea coast of Yemen. Environ Geol 48:590–598
Bawazir G, Abu Al-Fatooh A (2001) A preliminary study on the present state of the coastal zone in the Aden Governorate. Report submitted to Regional Organization for the Conservation of the Environment of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden (PERSGA), Integrated Coastal Zone Management Component, C2001/004
Burkill PH, Mantoura RFC, Owens NJP (1993) Biogeochemical cycling in the Northwestern Indian Ocean; a brief overview. Deep Sea Res 40:643–649
Clark RB (1998) Marine pollution, 4th edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Crystal D (1990) (ed) The Cambridge encyclopedia. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1334pp
Cushing DH (1971) Upwelling and fish production. Adv Mar Biol 9:255–334
Cushing DH (1973) Production in the Indian Ocean and the transfer from the primary to secondary level. In: Zeitschel B (ed) The biology of the Indian Ocean. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 475–486
DouAbul AA-Z, Al-Shiwafi HA (1998) Dissolved/dispersed hydrocarbons in Arabian region. Mar Pollut Bull 36:844–850
DouAbul AA-Z, Hebba HMA, Fareed KH (1997) Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) in fish from the Red Sea coast of Yemen. Hydrobiologia 352:251–262
Donat J, Dryden C (2001) Transition metals and heavy metal speciation. In: Steele J, Thorpe S, Turekian K (eds) Encyclopedia of ocean sciences. Academic, Elsevier Science, New York, pp 3027–3035
EPC (Environmental Protection Council) (1996) Beach pollution study Gulf of Aden/Arabian sea ‘‘chemical analysis’’. EPA-Sana’a University, Yemen, p 48
FAO (1967) The present status of fisheries and assessment of potential resources of the Indian Ocean and adjacent seas. Rome, FAO, COFI: I/1/67/9/1st draft 41pp
Gerlach SA (1976) Marine pollution. Diagnosis and therapy. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, p 218
Guraishee GS (1984) Circulation in the north Arabian Sea at Murry Ridge during S.W. monsoon. Deep Sea Res 31:651–664
Haskoning (1991) Proposal for developing a coastal management plan in the Republic of Yemen. Report by Haskoning (Royal Dutch consulting Engineering and Archeticts). Support to Secretariate of the Environmental Protection Council, Yemen, Royal Haskoning, Netherlands, p 53
Ho YB (1987) Metals in 19 international Macro-algae in Hong Kong waters. Mar Pollut 18:564–566
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Natural Resources) (1987a) Yemen Arab Republic: marine conservation survey, vol 1. Distribution of habitats and species along the YAR coastline. IUCN Red Sea and Gulf of Aden Environmental Program/TMRU York, UK, p 100
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Natural Resources) (1987b) Yemen Arab Republic: marine conservation survey, vol 2. Distribution of habitats and species along the YAR coastline. IUCN Red Sea and Gulf of Aden Environmental Program/TMRU York, UK, Gland Switzerland
Kishe MA, Machiwa JF (2003) Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of Mwanza Gulf of Lake Victoria, Tanzania. Environ Int 28:619–625
Laws E (2000) Aquatic pollution. An introductory text, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, p 369
Marin JH, Knuaer GA (1973) The elemental composition of plankton. Geochimica Cosmochimica Act 37:1639–1653
Millward GE, Turner A (2001) Metal pollution. In: Steele J, Thorpe S, Turekian K (eds) Encyclopedia of ocean sciences. Academic, Elsevier Science, New York, pp 1730–1737
Moody JR, Lindstrom PM (1977) Selection and cleaning of plastic containers for storage of trace element samples. Anal Chem 49:2264–2267
Morcos SM (1970) Physican and chemical oceanography of the Red Sea. In: Barnes H (ed) Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 8:73–202
Morcos SM, Varely D (1990) Physical and chemical oceanography of the Red Sea. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 8:73–202
Murty TS, El-Sabh MI (1984) Cyclones and storm surges in the Arabian Seas: a brief review. Deep Sea Res 31:665–671
NAP (National Action Plan) (2003) Yemen national programme of action for the protection of the marine environment from land-based activities. Republic of Yemen, Ministry of Water and Environment (MWE) and Environment Protection Authority (EPA)
PERSEGA (Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden Development Program) (1981) Draft of the final act on the Jeddah regional conference plenipotentiary on the conservation of the marine environment and coastal area of the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden, Jeddah
Pfannkuche O, Lochte K (2000) The biogeochemistry of the deep Arabian Sea: overview. Deep Sea Res 47:2615–2628
Pytkowciz RM (1983) Equilibria, nonequilibria and natural waters. Wiley, New York, p 353
Rushdi AI, Ba-Issa AA, Ba-Bagi A (1991) Preliminary investigations of oil pollution along the Red Sea coast of Yemen. In: Proceedings of the seminar on the status of the environment in the Republic of Yemen, Sana’a, 1–5 January 1991
Rushdi AI, Abubakr MM, Hebba HMA (1994) Marine habitats of the Red Sea at AlUrj-Alsalif and Dhubab-Yaktul areas: their ecology, environment and management recommendations preliminary investigations. UN-Faculty of Sciences, Sana’a University, Yemen, p 117
Smith SL (1984) Biological indications of active upwelling in the Northwestern Indian Ocean in 1964 and 1979 and a comparison with Peru and Northwest Africa. Deep Sea Res 31:951–968
Szefer P, Ali AA, Ba-Haroon AA, Rajeh AA, Geldon J, Nabrzyski M (1999) Distribution and relationships of selected trace metals in mollusks and associated sediments from the Gulf of Aden, Yemen. Environ Pollut 106:299–314
Turner DR, Dickson AG, Whitfield M (1980) Water–rock partition coefficients and the composition of natural water—a reassessment. Mar Chem 9:211–218
UNEP (United Nation Environment Program) (1997) Assessment of land-used sources and activities affecting marine sediment in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. UNEP Regional Seas Report Study. No 166
van Weering TCE, Helder W, Schalk P (1997) Netherlands Indian Ocean program 1992–1993. First results and introduction. Deep Sea Res 44:1177–1193
Whitfield M (1979) The mean oceanic residence time (MORT) concept—a rationalization. Mar Chem 8:101–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Shwafi, N.A., Rushdi, A.I. Heavy metal concentrations in marine green, brown, and red seaweeds from coastal waters of Yemen, the Gulf of Aden. Environ Geol 55, 653–660 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1015-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1015-0