Abstract
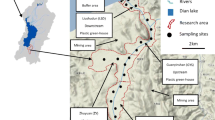
To understand Phosphorus (P) sources and transport processes in the subsurface in Bwaise III Parish, Kampala, P attenuation and adsorption capacities of soils were studied in situ and from laboratory measurements. Relationships between sorption parameters and soil matrix properties, rates and mechanism of the adsorption process and soil P fractions were also investigated. P was generally higher in the wet than the dry season, but for both seasons, the maximum was 5 mgP/l. P transport mechanisms appeared to be a combination of adsorption, precipitation, leaching from the soil media and by colloids with the latter two playing an important role in the wet season. The sorption process comprised two phases with the first stage rate constants being about fourfold those of the second stage. The Langmuir isotherm described the sorption data well (R 2 ≥ 0.95) with the second soil layer exhibiting the highest sorption maximum (C max) (average value 0.6 ± 0.17 mgP/gDW). The best prediction of C max had organic carbon, Ca, available P and soil pH. Residual P consisting mostly of organics was the main fraction in all the layers followed by inorganic HCl-P and NaOH-P in the top and middle layers, respectively. Loosely bound P (NH4Cl-P) was the least fraction (<0.4% of total P) in all layers indicating the high binding capacity of P by the soils. The study results suggest that P dynamics is related to Ca, Fe and organic carbon content of the soils.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA/AWWA/WEF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation Publication, Washington DC, USA
Adhityan A, Hong W (2000) Sorption isotherms and kinetics of sediment phosphorus in a tropical reservoir. J Environ Eng 126(11):993–998
Clement B, Merlin G (1995) The contribution of ammonia and alkalinity to landfill leachate toxicity to duckweed. Sci Total Environ 170(1–2):71–79
Ige DV, Akinremi OO, Flaten DN (2005) Environmental Index for estimating the risk of phosphorus loss in calcareous soils of Manitoba. J Environ Qual 34:1944–1951
Baldwin DS, Mitchell AM (2000) The effects of drying and re-flooding on the sediment and soil nutrient dynamics of lowland river-floodplain systems: a synthesis. Regul Rivers Res Manage 16:457–467
Biryabarema M (2001) Groundwater contamination and the role of geologic strata in retaining pollutants around waste disposal sites in Greater Kampala. PhD, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Börling K, Ottabong E, Barberis E (2001) Phosphorus sorption in relation to soil properties in some cultivated swedish soils. Nutr Cycle Agroecosys 59:39–46
BS (1975, 1990) Methods of test for soils for civil engineering purposes, parts 2 & 5. British Standard Institution, London
Djodjic F, Börling K, Bergström L (2004) Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content. J Environ Qual 33:678–684
Furumai H, Ohgaki S (1982) Fractional composition of phosphorus in sediments related to release. Wat Sci Tech 14:215–226
Geohring LD, McHugh OV, Walter M, Todd ST, Akhtar MS, Walter M (2001) Phosphorus transport into subsurface drains by macropores after manure applications: implications for best manure management practices. Soil Sci 166(12):896–909
HACH (1997) DR/2010 Spectrophotometer Handbook (Model 49300–22). Hach Company, USA
Heidmann I, Christl I, Leu C, Kretzchmar R (2005) Competitive sorption of protons and metal cations onto kaolinite: experiments and modelling. J Colloid Interface Sci 282(2):270–282
Heathwaite AL, Dils RM (2000) Characterising phosphorus loss in surface and subsurface hydrological pathways. Sci Tot Environ 251/252:523–538
Holtan H, Kamp-Nielsen L, Stuanes AO (1988) Phosphorus in soil, water and sediment: an overview. Hydrobiologia 170:19–34
Houba VJG, Van der lee JJ, Novozamsky I (1995) Soil analysis procedures (soil and plant analysis, part 5B), a series of syllabi, 6th edn. Department of Science and Plant Nutrition, Wageningen Agricultural University, The Netherlands
Howard G, Pedley S, Barrett M, Nalubega M, Johal K (2003) Risk factors contributing to microbiological contamination of shallow groundwater in Kampala, Uganda. Water Res 37(14):3421–3429
Jensen MB, Olsen TB, Hansen HCB, Magid J (2000) Dissolved and particulate phosphorus in leachate from structured soil amended with fresh cattle faeces. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 56:253–261
Kansiime F, Nalubega M (1999) Wastewater treatment by a Natural Wetland: the Nakivubo Swamp, Uganda, processes and implications. PhD, Wageningen University/International Institute for Infrastructural, Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, Delft, The Netherlands
Kilroy G, Coxon C (2005) Temporal variability of phosphorus fractions in Irish karst springs. Environ Geol 47:421–430
Kisand A (2005) Distribution of sediment phosphorus fractions in hypertrophic strongly stratified Lake Verevi. Hydrobiologia 547:33–39
Kulabako R (2005) Analysis of the impact of anthropogenic pollution on shallow groundwater in peri-urban Kampala. Licentiate thesis, Land and Water Resources Engineering Department, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden
Kulabako NR, Nalubega M, Thunvik R (2007) Study of the impact of land use and hydrogeological settings on the shallow groundwater quality in a peri-urban area of Kampala, Uganda. Sci Total Environ. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.03.035
Kulabako R, Nalubega M, Thunvik R (2004) Characterization of peri-urban anthropogenic pollution in Kampala, Uganda. In: Godfrey S (ed) People-centred approaches to water and environmental sanitation, proceedings of the 30th WEDC international conference, Vientiane, Lao PDR, pp 474–482
KUSP (2004) Surveillance of spring water sources in Kampala District. First Interim report by Chemiphar (U) Ltd for Kampala Urban Sanitation Project (KUSP), Kampala City Council
Liu M, Hou L, Xu S, Ou D, Yang Y, Zhang B, Liu Q (2002) Adsorption of phosphate on tidal flat surface sediments from the Yangtze Estuary. Environ Geol 42:657–665
McGechan MB, Lewis DR (2002) Sorption of phosphorus by soil, part 1: principles, equations and models, a review paper. Biosyst Eng 82(1):1–24
McGechan MB (2002) Sorption of phosphorus by soil, part 2: measurement methods, results and model parameter values, a review paper. Biosyst Eng 82(2):115–130
Muhammad TS, Robinson JS (2003) Phosphorus sorption and availability in soils amended with animal manures and sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 32:1114–1121
Okalebo JR, Gathua KW, Wooner PL (2002) Laboratory methods of soil and plant analysis: a working manual, 2nd edn. Tropical soil biology and fertility programme. Sacred Africa Publishers, Nairobi, Kenya, p 88
Özacar M (2003) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of adsorption of phosphorus on calcined alunite. Adsorption 9:125–132
Portielje R, Lijklema L (1993) Sorption of phosphate by sediments as result of enhanced external loading. Hydrobiologia 253:249–261
Shenker M, Seitelbach S, Brand S, Haim A, Litaor MI (2005) Redox reactions and phosphorus release in re-flooded soils of an altered wetland. Eur J Soil Sci 56(4):515–525
Siddique MT, Robinson JS (2003) Phosphorus sorption and availability in soils amended with animal manures and sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 32:1114–1121
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Tamatamah RA (2004) Phosphorus sorption characteristics of sediment in the Simiyu and Kagera River basins: implications for phosphorus loading into L.Victoria. Afr J Aquat Sci 29(2):243–248
Taylor RG, Howard KWF (2000) A tectonic geomorphic model of the hydrogeology of deeply weathered crystalline rock: evidence from Uganda. J Hydrogeol 8:279–294
Torrent J, Delgado A (2000) Using phosphorus concentration in the soil solution to predict phosphorus desorption to water. J Environ Qual 30:1829–1835
UBOS (2002) Uganda population and housing census-main report. Uganda Bureau of Statistics, Kampala
USEPA (1992) Batch-type procedures for estimating soil adsorption of chemicals. Technical resource document, EPA/530/SW-87/006-F, United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), Washington
USEPA (1995) Technical guidance manual for hydrogeological investigations and groundwater monitoring (TGM). In: Monitoring well design and installation, Chap. 7. Environment Protection Agency, Ohio, 28 p
http://www.epa.state.oh.us/ddagw/Documents/chapter07DES.PDF
Van Beers WFJ (1983) The Auger hole method: a field measurement of the hydraulic conductivity of soil below the water table. International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Bulletin, vol 1. Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp 4–23
WHO, UNICEF (2000) Global water supply and sanitation assessment 2000 report. United Nations, New York
Zhang Y, Lin X, Werner W (2003) The effect of soil flooding on the transformation of Fe oxides and the adsorption/desorption behaviour of phosphate. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166:68–75
Zimmo OR, van der Steen NP, Gijzen HJ (2003) Comparison of ammonia volatilisation rates in algae and duckweed-based waste stabilisation ponds treating domestic wastewater. Water Res 37(19):4587–4594
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Swedish Sida/SAREC-Makerere University Research Collaborative Programme in the Lake Victoria Region. The authors wish to thank all the staff of Makerere University laboratories who assisted with the field measurements and analyses. Appreciation is expressed to the anonymous reviewers whose comments and suggestions resulted in substantial improvement to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulabako, N.R., Nalubega, M. & Thunvik, R. Phosphorus transport in shallow groundwater in peri-urban Kampala, Uganda: results from field and laboratory measurements. Environ Geol 53, 1535–1551 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0764-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0764-0