Abstract
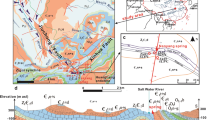
The Songshan hot spring occurs in granite in Yanqing County in northwestern Beijing, China. TDS of the hot water ranges from 459 to 475 mg/L and pH varies between 8.6 and 9.13. The water is of Na–SO4 type. Isotopic analyses indicate that the hot spring is meteoric in origin and receives recharge from precipitation in the northern and northwestern granite mountain with elevation of about 1,600–1,800 m. The depth of circulation of the thermal groundwater is estimated to be 2,240 m below the spring’s threshold and the temperature of the geothermal reservoir, 76°C. The residence time of the thermal groundwater is estimated to be about 52 years. A flowing well near the spring has chemical compositions and formation conditions similar to the spring. The discharge of the flowing well is approximately eighteen times larger than that of the spring and the residence time of the former (about 15.4 years) is about three times smaller than that of the latter. Although the well and spring are close to each other, the well’s larger flow rates, indicated residence time and high hydraulic head suggest that the well taps a separate, but genetically similar flow system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beijing Institute of Geology (1999) Explanation of the geological map of the Yanqing area through a regional geological investigation with the scale of 1:50000 (K50E022008)
Bureau of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology of the Ministry of Geology of China (1956) Investigation report of mineral springs in the western mountain area of Beijing
Center of Geothermal Development and Research of the Beijing Institute of Geological Engineering Investigation (1995) Report on drilling of well Yanren-3 in the Songshan Forest Park in Yanqing County
Cherdyntsev VV (1971) Uranium-234, Keter Press, Jerusalem
Cook PG, Herczeg AL (2000) Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science l33:1702–1703
Fournier RO (1977) Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems. Geothermics 5(1–4):41–50
Giggenbach WF (1988) Geothermal solute equilibrium, derivation of Na–K–Mg–Ca geoindicators. Geochim et Cosmochim Acta 52(12):2749–2765
Huang S, Feng J, Zheng K, Xie C, Ma D (1989) Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of waters in Beijing geothermal field and vicinity. In: (eds) Institute of Geodynamics of China Academy of Geological Science, Geothermal Special Issue (2). Geological Publishing House, 155–162
Li X, Shi W, Sun Z, Zhang W (1993) Isotope hydrogeology of natural waters in the hot spring area of Chongren-Linchuan in the central Jiangxi. In: Proceedings of the second national symposium on isotopic hydrogeology: advances in isotopic hydrogeology in China. Press of Tianjin University, pp 47–56
Wang H (1991) Introduction to isotopes in hydrogeology. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Wang J, Xiong L, Pang Z (1993) Low-medium temperature geothermal system of convective type. Science Press, Beijing
Wang G, Zhang Z, Wang M, Wang J, Liu W, Yi L, Sun M (2003) Geochemistry of geothermal water and noble gases in Yanqing basin, China. Seism Geol 25(3):421–429
Wu L, Shi K (1996) Exploration of thermal groundwater in the Songshan area and a discussion of its genetic model. Geophys Geochem Explor 20(4):300–315
Zhang W (1993) Isotopic studies of the formation of the Linchuan hot spring water in Jiangxi. In: Proceedings of the second national symposium on isotopic hydrogeology: advances in isotopic hydrogeology in China. Press of Tianjin University, pp 57–62
Zhang W (2001a) Application of hydrogeochemical methods to analyses of the formation of geothermal water in the Hengjing area in southern Jiangxi. Hydrogeol Eng Geo (4):45–48
Zhang W (2001b) The application of SiO2 geothermometer to estimating temperature of the geothermal reservoir: exemplified by some thermal springs in the Henjing area, south Jiangxi. Acta Geosci Sin 22(2):185–188
Zhang C (2002) Research on thermal groundwater resources in the northern part of Yangqing County, Beijing. Coal Geol China 14(3):39–41
Zhou X, Li C (1993) Hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of subsurface bines in sedimentary basins and their application. In: Proceedings of the second national symposium on isotopic hydrogeology: advances in isotopic hydrogeology in China. Press of Tianjin University, pp 85–90
Zhou H, Zhou X, Fang B, Li J, Liu C (2006a) Hot springs in Beijing and its northwestern neighboring district. City Geology 1(1):9–15
Zhou X, Zhou H, Fang B, Fan Y, Li J, Wang X (2006b) Evolution of thermal groundwater resources under the conditions of exploitation: a preliminary analysis. Geol Bull China 25(4):482–486
Acknowledgments
This work was cooperatively supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (8042019), the Natural Science Foundation of China (40572147) and the Construction Plan for the Co-Construction Subjects from the Education Committee of Beijing (JD104910555).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xun, Z., Juan, L., Haiyan, Z. et al. Increase in thermal groundwater due to a flowing well near the Songshan hot spring in Beijing, China. Environ Geol 53, 1405–1411 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0749-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0749-z