Abstract
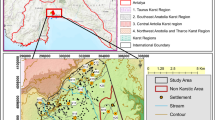
Hydrogeochemical investigations are carried out in the different blocks of Burdwan district, West Bengal, India in order to assess its suitability for drinking as well as irrigation water purpose. Altogether 49 representative groundwater samples are collected from bore wells and the water chemistry of various ions viz. Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, CO 2−3 , HCO −3 , Cl−, SO 2−4 and NO −3 are carried out. The chemical relationships in Piper and Gibbs diagram suggest that the groundwater mainly belongs to alkali type and Cl− group and are controlled by rock dominance. A comparison of groundwater quality in relation to drinking water quality standards proves that most of the water samples are suitable for drinking water purpose whereas groundwater in some areas of the district has high salinity and high sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), indicating unsuitability for irrigation water and needs adequate drainage.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal V, Jagetia M (1997) Hydrogeochemical assessment of ground water quality in Udaipur city, Rajasthan, India. In: Proceedings of national conference on “Dimensions of Environmental Stress in India”, Department on Geology, M S University, Baroda, India, pp 151–154
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Appelo CA, Postma D (1993) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Balkema, Rotterdam
BIS (1975) Indian standard drinking water specification. Bureau of Indian standard, New Delhi
Balusu KR, Pande SP (1990) Nitrate—a serious threat to groundwater pollution. Bhu-Jal News 5:39–43
Chatterjee A, Mondal B, Roy Chowdhury T (1995) Arsenic in groundwater in six districts of West Bengal, India. The biggest Arsenic Calamity in the world Part I. Arsenic species in drinking water and urine of the affected people. Analyst 120:643–650
Chow VT (1964) Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Das D, Chatterjee A, Samanta G, Mondal B, Roy Chowdhury T (1994) Arsenic contamination in groundwater in six districts of West Bengal. Analyst 119:168–170
Dasgupta AM, Purohit KM (2001) Status of surface and groundwater quality of Mandiakadar-Part II: agricultural utilities. Pollut Res 20(2):219–225
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1990) Physical and chemical hydrology. Wiley, New York
Drever JI (1988) The geochemistry of natural waters. 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, New York
Durvey VS, Sharma LL, Saini VP, Sharma BK (1997) Handbook on the methodology of water quality assessment. Rajasthan Agriculture University, India
Fetter CW (1990) Applied hydrogeology. CBS, New Delhi
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 17:1088–1090
Handa BK (1979) Groundwater pollution in India. In: Proceedings of national symposium on hydrology. IAHS, Publ Univ Roorkee, India, pp 34–49
Hem JD (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters, Book 2254, 3rd edn. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur
Holden WS (1971) Water treatment and examination. Churchill, London
Hussain I, Hussain J, Dhinsa SS (2005) Groundwater quality variation in Bhilwara district, Rajasthan. Pollut Res 24(3):723–725
ISI (1983) Indian standard specification for drinking water. IS: 10500, Indian Standard Institute, India
Johnson CC (1979) Land application of water—an accident waiting to happen. Groundwater 17(1):69–72
Karanth KR (1997) Groundwater assessment, development and management. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Khurshid SH, Hasan N, Zaheeruddin (2002) Water quality Status and environmental hazards in parts of Yamuna–Karwan sub-basin of Aligarh–Mathura district, UttarPredesh, India. J Appl Hydrol 14(4):30–37
Majumdar D, Gupta N (2000) Nitrate pollution of ground water and associated human health disorders. India J Environ Health 42(1):28–39
Niranjan Babu P, Subba Rao N, Chandra Rao P, Prakesa Rao J (1997) Ground water quality and its importance in the land developmental programmes. India J Geol 69(4):305–312
Piper AM (1953) A graphic procedure in the chemical interpretation of water analysis. US Geological Survey Groundwater Note 12
Pulle JS, Khan AM, Ambore NE, Kadam DD, Pawar Sk (2005) Assessment of ground water quality of Nanded City. Pollut Res 24(3):657–660
Rahman MM, Sengupta M, Ahamed S, Chaudhury U, Hassain A (2005) The magnitude of arsenic contamination in groundwater and its health effects to the inhabitants of the Jalangia, West Bengal, India. Sci Total Environ 338(3):189–200
Sastri JCV (1994) Groundwater chemical quality in river basins. Hydrogeochemical modeling lecture notes. Refresher Course School of Earth Science, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirapalli, Tamilnadu
Sawyer CN, McCarthy PL (1967) Chemistry for sanitary engineers, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development. UNESCO, pp 54–83
Schoeller H (1967) Geochemistry of groundwater. An international guide for research and practice. UNESCO, chap 15, pp 1–18
Spalding RF, Exner ME (1993) Occurrence of nitrate in groundwater—a review. J Environ Qual 22:392–402
Sreedevi PD (2004) Groundwater quality of Pageru river basin, Cuddepah district, Andhra Pradesh. J Goel Soc India 64(5):619–636
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1981) Aquatic chemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Subba Rao N (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 49:413–429
Subba Rao N, Srinivasa Rao G, Venkateswara Rao S, Madhusudhana Reddy P, John Devadas D (1999) Environmental control of groundwater quality in a tribal region of Andhra Pradesh, India J Goel 71(4):299–304
Sujatha D, Reddy RB (2003) Quality characterization of groundwater in the south-eastern part of the Ranja Reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 44(5):579–586
Sunitha V, Sudarsha V, Rajeswara Reddy B (2005) Hytdrogeochemistry of groundwater, Gooty area, Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Pollut Res 24(1):217–224
Thorne DW, Peterson HB (1954) Irrigated soils. Constable and Company, London
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley, New York
US Salinity Laboratory Staff (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. US Department of Agricultural soils. US Department of Agricultural Hand Book 60, Washington
Walton WC (1970) Groundwater resources evaluation. McGraw-Hill, New York
WHO (1984) Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wilcox LV (1948) The quality of water for irrigation use. US Department of Agricultural Technical Bulletin 1962, Washington
Zaporozec A (1972) Graphical interpretation of water quality data. Groundwater 10(2):32–43
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. A. R. Ghosh, Reader, Department of Environmental Science, Burdwan University, for his critical evaluation and suggestions, which greatly helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Mahato, A., Roy, P. et al. Geochemistry of groundwater, Burdwan District, West Bengal, India. Environ Geol 53, 1271–1282 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0725-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0725-7