Abstract
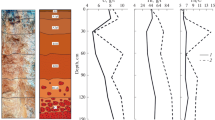
Iodine contents of soils developed over the major rock formations of the northern zone of the Eastern Pontide Tectonic Belt (Northeastern Turkey) have been investigated with respect to soil-parent rock relationship, effect of topography, elevation, and climate to construe its effect on the health of the local population. Samples were collected from the A and B horizons of the soils developed over the major stratigraphic units constituting the eastern Pontides, including the Lower Basic Complex of Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous age, the Berdiga limestone (Jurassic-lower Cretaceous), the Dagbasi granitoid (Upper Cretaceous), volcano-sedimentary sequence of Upper Cretaceous age, ore-bearing and barren dacites of Upper Cretaceous age, and Neogene alkaline basalts. Chemical analyses of soil samples indicate significantly lower iodine abundances for all the soils studied (5–28 ppm) in comparison to the average abundance of iodine in analogous soils of other parts of the world (22–93 ppm). The concentration of iodine in soils developed over the same geologic formation decrease with increasing elevation. In certain cases, this decrease may reach up to 70%. Goiter is highly common throughout this region in Turkey. The results of this study suggest that the iodine deficiency of region’s soils may be a principal underlying cause for this area of Turkey being an endemic goiter region.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arslan M, Aslan Z (2006) Mineralogy, petrography and whole-rock geochemistry of the tertiary granitic intrusions in the Eastern Pontides, Turkey. J Asian Earth Sci 27:177–193
Arslan M, Tüysüz N, Korkmaz N, Kurt H (1997) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Eastern Pontide Volcanic rocks, Northeastern Turkey. Chem Erde 57:157–187
Aslan Z (2005) Petrography and petrology of the calc-alkaline sarihan granitoid (NE Turkey): an example of magma mingling and mixing” Turkish. J Earth Sci 14:185–2007
Aslaner M, Van A, Yalçınalp B (1995) General features of the Pontide metallogenic belt. In: Erler A, Ercan T, Bingöl E, Örçen S (eds) Geology of the Black Sea Region. General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration and Chamber of Geological Engineers, Ankara, pp 209–213
Aston SR, Brazier PH (1979) Endemic goiter, the factors controlling iodine deficiency in soils. Sci Total Environ 11(1):99–104
Aydın F, Karslı O, Sadıklar MB, Şen C, Altherr R (2003) The youngest K-Ar ages and new petrographical data of the eastern Pontide alkaline volcanics, NE-Turkey. Symposium on the Geology and Mining Potential of Eastern Black Sea Region (Trabzon, NE Turkey), Trabzon
Chilean Iodine Educational Bureau (CIEB) (1952) Iodine contents of foods. Shenval Press, London
Ciftci E (2000) Mineralogy, paragenetic sequence, geochemistry and genesis of the gold and silver bearing Upper Cretaceous mineral deposits, Northeastern Turkey. PhD Thesis, University of Missouri-Rolla, Missouri
Çiftçi E, Kolaylı H, Tokel S (2005) Lead-arsenic soil geochemical study as an exploration guide over the killik volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, Northeastern Turkey. J Geochem Explor 86:49–59
Davidson S, Passmore R, Brock JF, Truswell AS (1975) Human nutrition and dietetics, 6th edn (chapter 10). Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Dubravcic M (1955) Determination of iodine in natural waters. Analyst 80:295–300
Fuge R, Johnson CC (1986) The geochemistry of iodine—a review. Environ Geochem Health 8(2):31–54
Fuge R, Johnson CC, Phillips WC (1978) An automated method for the determination of iodine in geochemical samples. Chem Geol 23:255–265
Gedikoğlu A (1978) Harşit Granit Karmaşığı ve Çevre Kayaçları. Associate Professorship Thesis. KTU, Trabzon
Goldschmidt VM (1954) Geochemistry. Oxford University Press, London
Johnson CC (1980) The geochemistry of iodine and a preliminary investigation into its potential use as a pathfinder element in geochemical exploration, PhD Thesis. College of Wales, Australia
Köhrle J (1999) The trace element selenium and the thyroid gland. Biochimie 81(5):527–533
Kologlu S, Kologlu B (1966) endemic goiter in turkey- daily iodine content of waters and foods taken by human body. Ankara Univ Med J XIX:572
Kologlu S, Kologlu B (1967) An investigation on endemic goiter etiology in Black Sea Region. TUBA Report No 67
Köprübaşı N (1993) Petrology and geochemistry of the Jurassic-Cretaceous magmatic rocks between Tirebolu-Harsit (Giresun). TJK Bull 36:139–50
Korkmaz S, Tüysüz N, Er M, Musaoğlu A, Keskin İ (1992) Geology of the Black Sea Region. Proceedings of the international symposium on the geology of the Black Sea Region. Ankara
Lâg J, Steinnes E (1976) Regional distribution of halogens in Norwegian Forest Soils. Geoderma 16(4):317–325
Mocan MZ, Mocan H, Tokel S (1989) Possible effects in the etiology of endemic goiter in the northeast of Turkey. Trace Elem Med 6(1):4–8
Moore WJ, McKee EH, Akıncı Ö (1980) Chemistry and chronology of plutonic rocks in the Pontide Mountains, Northern Turkey. European Copper Deposits, Belgrade, pp 209–216
Pelin S(1977) “Alucra (Giresun) GD Yöresinin Petrol Olanakları Bakımından Jeolojik İncelemesi” KTÜ Yayın No: 87, Trabzon
Reimann C, de Caritat P (1998) Chemical elements in the environments. Springer, Heidelberg
Taşhan E (1993) Trabzon civari topraklardaki iyot derişimi, MS Thesis. KTÜ, Trabzon
Tokel S, Mocan MZ (1984) Doğu Karadeniz Bölgesinde Görülen Endemik Guvatrın Bölge Jeokimyası ve Diğer Etiyolojik Faktörlerle İlişkisinin İncelenmesi. TÜBİTAK PROJECT TAG-498, Ankara
Tokel S, Mocan MZ (1985) Reasons of endemic goiter prevalence in the Black Sea Region: geochemical environment. TJK Bull 17–21
Topuz G, Çapkınoğlu Ş (2003) Preliassic basement rocks of the eastern pontides. symposium on the geology and mining potential of Eastern Black Sea Region (Trabzon, NE Turkey), Trabzon
Van A (1990) Pontid Kuşağında Artvin Bölgesinin Jeokimyasi, Petrojenezi ve Masif Sülfit Mineralizasyonlari. PhD Thesis, KTÜ, Trabzon
Yalçınalp B (1992) Güzelyayla (Maçka-Trabzon) Porfiri Cu-Mo Cevherleşmesinin Jeolojik Yerleşimi ve Jeokimyasi. PhD Thesis, KTÜ, Trabzon
Yalçınalp B (1994) Sürmene (Trabzon) Yöresi Bazaltlarının Jeolojik Yerleşimi ve Jeokimyasi. TJK Bull 37(2):65–71
Acknowledgment
Author is indebted to Dr. John P. Hogan (University of Missouri-Rolla) and the anonymous reviewers for their contributions and constructive criticisms that significantly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çiftçi, E., (Taşhan) Şevketbeyoğlu, E. & Tokel, S. Iodine concentrations of soils near Trabzon, Turkey: a region of endemic goiter. Environ Geol 53, 457–465 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0661-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0661-6