Abstract
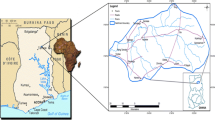
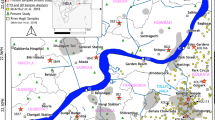
This study was based on the analysis of isotopic compositions of hydrogen and oxygen in samples from precipitation, groundwater and stream water. In addition, parts of groundwater samples were dated by carbon-14 and tritium. These data are integrated to provide other views of the hydrologic cycle in the Hsinchu-Miaoli groundwater district. The groundwater district is principally composed of Pleistocene and Holocene aquifers. The Pleistocene aquifers are highly deformed by folding and faults into small sub-districts with areas of only tens of square kilometers. These aquifers are exclusively recharged by local precipitation. The Holocene aquifers cover narrow creek valleys, only tens of meters in thickness. The local meteoric water line (LMWL), constructed from rainfall samples in the Hsinchu Science Park, is described by the equation δD=8.02δ18O+10.16, which agrees with the global meteoric water line. In addition, the precipitation isotopic compositions can be categorized into two distinct end members: typhoon type and monsoon type. The groundwater isotopic compositions are perfectly located on an LMWL and can be considered a mixture of precipitations. Based on the mass balance of isotopic compositions of oxygen and hydrogen, infiltration is more active in the rainy season with depleted isotopic compositions. The amount of infiltration during May–September is roughly estimated to comprise at least 55% of the whole year’s recharge. The isotopic compositions of stream water are expressed by a regression equation: δD=7.61δ18O+9.62, which is similar to the LMWL. Although precipitation isotopic compositions are depleted during summer time, the isotopic compositions contrarily show an enriched trend in the upstream area. This is explained by the opposite altitude effect on isotopic compositions for typhoon-related precipitations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chou JT (1977) Sedimentology and Paleogeography of the Pleistocene Toukoshan Formation in Western Taiwan. Pet Geol Taiwan 14:25–36
Coleman ML, Shepherd TJ, Durham JJ, Rouse JE, Moore GR (1982) Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis. Anal Chem 54(6):993–995
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Craig H, Gordon L, Horibe Y (1963) Isotopic exchange effects in the evaporation of water: Low-temperature experimental results. J Geophys Res 68:5079–5087
Darling WG, Bath AH (1988) A stable isotope study of recharge processes in the English chalk. J Hydrol 101:31–46
Epstein S, Mayeda T (1953) Variation of O-18 content of waters from natural sources. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 4:213–224
Fontes JC (1980) Environmental isotopes in groundwater hydrology. In: Fritz P, Fontes JC (eds) Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 75–140
Friedman I, Redfield AC, Schoen B, Harris J (1964) The variation of the deuterium content of natural waters in the hydrologic cycle. Rev Geophys 2:303–317
Fritz P, Drimmie RJ, Frape SK, O’Shea K (1987) The isotopic composition of precipitation and groundwater in Canada. IAEA-SM-299/17:539–550
Gat JR (1980) The isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in precipitation. In: Fritz P, Fontes JC (eds) Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 21–47
Gat JR (1981) Isotopic fractionation. In: Stable isotope Hydrology, Deuterium and oxygen-18 in the Water Cycle. IAEA Technical Reports Series 210:21–34
Gat JR (1996) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 24:225–262
Ingraham NL, Taylor BE (1991) Light stable isotope systematics of large-scale hydrologic regimes in California and Nevada. Water Resour Res 27(1):77–90
Kuo CH, Wang CH (2001). Implication of seawater intrusion on the delineation of the hydrogeologic framework of the shallow Pingtung Plain aquifer. West Pac Earth Sci 1(4):459–471
Liu TK (2001) Radiometric dating and vertical quality variation of groundwater from wells in Taiwan: Hsinchu-Miaoli area (in Chinese). Water Resources Agency, Taipei, Taiwan, pp 18–34
Patra KC (2001) Hydrology and water resources engineering. Alfa Science International Ltd., Pangbourne, pp 402–406
Peng TR (1995) Environmental Isotopic Study (δ13C, δD, δ18O, 14C, T) on Meteoric Water and Groundwaters in I-Lan Area. Ph.D. Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan (in Chinese)
Peng TR, Wang CH, Huang CC, Chen WC, Fei LY, Lai TC (2002) Groundwater recharge and salinization in south Chianan Plain: hydrogen and oxygen isotope evidences. J Chinese Soil Water Conserv 33(2):87–100
Rozanski K, Johnsen SJ, Schotterer U, Thompson LG (1997) Reconstruction of past climates from stable isotope records of palaeo-precipitation preserved in continental archives. Hydrol Sci J 42:725–745
Shieh YN, Cherng FP, Hoering TC (1983) Oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies of meteoric and thermal waters in Taiwan. Geol Soc China Mem 5:127–140
Viessman W, Lewis GL, Knapp JW (1989) Introduction to hydrology. 3rd edn. Harper & Row, New York, pp 79–80
Wang CH, Kuo CH, Peng TR, Chen WF, Liu TK, Chiang CJ, Liu WC, Hung JJ, (2001) Isotope Characteristics of Taiwan Groundwaters. West Pac Earth Sci 1(4):415–428
Wang CH, Peng TR (2001) Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of Taipei precipitation: 1990–1998. West Pac Earth Sci 1(4):429–442
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Chao-Chung Lin and Li-Yuan Fei for their support throughout the project. We also thank the journal reviewers for their detailed and helpful comments. This study was funded by the Central Geological Survey, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
Stable isotopic compositions of precipitations collected from the Hsinchu Science Park in HMGD
Sample number | Sampling date | δD (‰) | δ18O (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 2003/1/9 | −16.9 | −3.7 |
2 | 2003/1/22 | −7.1 | −2.2 |
3 | 2003/2/4 | −18.8 | −4.0 |
4 | 2003/2/10 | 3.0 | −1.2 |
5 | 2003/2/15 | −6.1 | −2.1 |
6 | 2003/3/3 | −5.9 | −2.2 |
7 | 2003/3/6 | −13.1 | −3.2 |
8 | 2003/3/9 | −14.2 | −3.4 |
9 | 2003/3/10 | −5.9 | −2.2 |
10 | 2003/3/19 | −8.0 | −2.6 |
11 | 2003/3/20 | −16.8 | −3.6 |
12 | 2003/3/23 | −5.1 | −0.9 |
13 | 2003/3/24 | −6.2 | −2.3 |
14 | 2003/3/29 | −12.8 | −2.9 |
15 | 2003/4/3 | −26.7 | −4.9 |
16 | 2003/4/4 | −22.2 | −4.2 |
17 | 2003/4/7 | 3.0 | −1.0 |
18 | 2003/4/8 | 13.0 | 0.3 |
19 | 2003/4/9 | −11.9 | −3.0 |
20 | 2003/4/11 | 3.1 | −0.8 |
21 | 2003/4/14 | −2.0 | −1.6 |
22 | 2003/4/15 | 0.9 | −1.4 |
23 | 2003/4/25 | 1.1 | −1.1 |
24 | 2003/5/1 | 11.0 | −0.1 |
25 | 2003/5/4 | −2.9 | −1.2 |
26 | 2003/5/8 | −25.1 | −3.8 |
27 | 2003/5/15 | −29.8 | −4.6 |
28 | 2003/5/16 | −45.3 | −6.6 |
29 | 2003/5/17 | −15.1 | −3.0 |
30 | 2003/5/18 | −25.9 | −4.4 |
31 | 2003/6/8 | −69.2 | −9.8 |
32 | 2003/6/9 | −78.2 | −11.0 |
33 | 2003/6/12 | −17.1 | −3.0 |
34 | 2003/6/13 | −6.0 | −1.5 |
35 | 2003/6/18 | −20.9 | −3.4 |
Appendix 2
Stable isotopic compositions of groundwaters from HMGD
Sample number | Screen depth (m) | δD (‰) | δ18O (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 36 | −36.6 | −5.8 |
2 | 100 | −32.7 | −5.7 |
3 | 176 | −39.1 | −6.2 |
4 | 234 | −42.1 | −6.4 |
5 | 76 | −39.3 | −6.5 |
6 | 114 | −43.2 | −6.6 |
7 | 150 | −43.0 | −6.5 |
8 | 63 | −39.2 | −6.8 |
9 | 108 | −41.1 | −7.0 |
10 | 64 | −32.7 | −6.0 |
11 | 36 | −45.8 | −6.9 |
12 | 85 | −43.8 | −6.9 |
13 | 134 | −43.3 | −6.8 |
14 | 163 | −44.3 | −6.8 |
15 | 21 | −33.7 | −5.9 |
16 | 99 | −36.0 | −6.1 |
17 | 132 | −42.4 | −6.4 |
18 | 18 | −36.6 | −6.2 |
19 | 107 | −38.5 | −6.2 |
20 | 53 | −37.6 | −6.6 |
21 | 99 | −36.9 | −6.5 |
22 | 26 | −37.5 | −5.8 |
23 | 20 | −42.0 | −6.6 |
24 | 66 | −44.5 | −6.8 |
25 | 24 | −44.7 | −6.8 |
26 | 51 | −41.6 | −6.4 |
27 | 85 | −47.1 | −7.1 |
28 | 48 | −43.0 | −7.1 |
29 | 106 | −46.1 | −7.6 |
30 | 22 | −45.0 | −6.7 |
31 | 146 | −40.2 | −6.2 |
32 | 58 | −41.0 | −6.2 |
33 | 107 | −42.1 | −6.8 |
Appendix 3
Stable isotopic compositions of stream waters from HMGD
Sample number | Sample altitude (m) | 2001/2 | 2001/7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
δD (‰) | δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | δ18O (‰) | ||
1 | 10 | −24.6 | −4.42 | −34.2 | −5.8 |
2 | 90 | −38.1 | −6.32 | −35.4 | −6.1 |
3 | 10 | −32.4 | −5.06 | −36.4 | −6.1 |
4 | 50 | −36.4 | −5.9 | −38.5 | −6.5 |
5 | 140 | −39.2 | −6.55 | −43.1 | −7.1 |
6 | 220 | −52.3 | −7.74 | −46.3 | −7.5 |
7 | 160 | −41.3 | −6.85 | −41.7 | −6.8 |
8 | 10 | −47.3 | −7.48 | −53 | −8.2 |
9 | 70 | −51.6 | −8.05 | −54.6 | −8.5 |
10 | 90 | −55.7 | −8.34 | −53 | −8.3 |
11 | 150 | −56.1 | −8.4 | −56.8 | −8.8 |
12 | 210 | −59.1 | −9.07 | −58.5 | −9.0 |
13 | 310 | −62.4 | −9.38 | −63.4 | −9.3 |
14 | 810 | −64.1 | −9.57 | −64.4 | −9.5 |
15 | 130 | −54.8 | −8.38 | −52.2 | −8.3 |
16 | 270 | −55.8 | −8.54 | −53.7 | −8.5 |
17 | 430 | −59.4 | −8.97 | −55.5 | −8.7 |
18 | 570 | −59.2 | −9.05 | −58.9 | −9.0 |
19 | 10 | −45.3 | −7.23 | −46.3 | −7.4 |
20 | 70 | −33.9 | −5.88 | −35.1 | −5.9 |
21 | 150 | −54.3 | −8.42 | −48.4 | −7.8 |
22 | 10 | −37.4 | −6.38 | −49.5 | −7.5 |
23 | 40 | −46.4 | −7.18 | −47.5 | −7.6 |
24 | 150 | −52.6 | −8.2 | −55.8 | −8.2 |
25 | 570 | −53.5 | −8.41 | −53.6 | −8.5 |
26 | 650 | −62.8 | −9.47 | −58.9 | −9.1 |
27 | 10 | −40.9 | −6.2 | −47.7 | −7.2 |
28 | 10 | −44.2 | −7.02 | −46.2 | −7.5 |
29 | 70 | −45.5 | −7.21 | −50.1 | −7.7 |
30 | 330 | −57.1 | −8.62 | −53.8 | −8.5 |
31 | 250 | −51.9 | −7.89 | −55.1 | −8.1 |
32 | 370 | −45.1 | −7.35 | −52.3 | −8.0 |
33 | 450 | −58.7 | −8.57 | −55.3 | −8.6 |
34 | 450 | −62.4 | −8.98 | −56.7 | −8.8 |
35 | 10 | −25.1 | −4.2 | −32.2 | −5.5 |
36 | 50 | −33.8 | −5.46 | −35.2 | −6.0 |
37 | 120 | −42.8 | −6.54 | −38.1 | −6.3 |
38 | 210 | −44.3 | −6.88 | −46.1 | −7.2 |
39 | 340 | −46.8 | −7.52 | −51.5 | −7.7 |
40 | 10 | −54.5 | −7.88 | −53.6 | −8.4 |
41 | 70 | −59.7 | −8.5 | −51.7 | −8.0 |
42 | 70 | – | – | −34.1 | −5.8 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, HY., Peng, TR., Liu, TK. et al. Study of stable isotopes for highly deformed aquifers in the Hsinchu-Miaoli area, Taiwan. Environ Geol 50, 885–898 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0260-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0260-y