Abstract
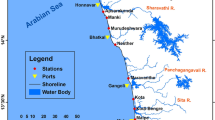
The subtidal sediments of four coastal environments (beach, berm, surf zone and nearshore sea floor) of Kuala Terengganu have been studied in terms of their textural characteristics and depositional process. Sampling and statistical analyses of the grain size distributions of beach, surf zone and shallow sea-floor sediments at various locations along the coastline show that they varied in their mean grain size as well as values of sorting and skewness. The statistical parameters of grain size distributions thus allowed recognition of distinct sub-environments. The size distribution of such sediments suggests that the various processes that are responsible for their transportation and deposition are wave, current and wind action. The different energy conditions and the morphology of each coastal environment seem to be reflected in the characteristics of the sediments in each environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dale WL (1956) Wind and drift currents in the South China Sea. Malaya J Trop Geogr 8:1–31
Engstron WN (1978) The physical stability of the Lake Tahoe shoreline. Shore Beach 46:9–13
Folk RL, Ward WC (1957) Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameter. Sediment Petrol J 27:3–26
Friedman GM (1962) On sorting, sorting coefficients and the lognormality of the grain-size distribution of sandstones. J Geol 70:737–756
Liong PC (1974) hydrographic conditions off the East Coast of the Peninsular Malaysia during August 72. Malay Agri J 19:124–128
Mason CC, Folk RL (1958) Differentiation of beach, dune and eolian flat environments by size analysis, Mustang Island, Texas. J Sediment Petrol 28(2):211–226
McBride EF (1971) Mathematical treatment of size distribution data. In: Carver RE (ed) Procedures in sedimentary petrology. Wiley Interscience, New York, pp 109–207
Mohd-Lokman H, Rosnan Y, Ejria S, Kassim KKY (1998) Deducing sediment transport direction and the relative importance of rivers on a tropical microtidal beach using the “McLaren Model”. Environ Geol 34(2/3)
Pethick J (1984) An introduction to coastal geomorphology. Edward Arnold (Publisher) Ltd. pp 260
Phillips RP (1985) Long shore transport of sediment during August and September on the Terengganu coast. Pertanika J 8(2):273–279
Raj JK (1982) Net directions and rates of present day beach sediment transport by littoral drift along the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Bull Geol Soc Malaysia 15:57–70
Rosnan Y, Saadon MN (1989) Grain size distribution and shore drift direction along the coastal areas of Terengganu. In: 12th annual seminar, Malaysian Society, 18 November 1989
Self RP (1977) Long shore variation in beach sands, Nautia Area, Verecruz, Mexico. J Sediment Petrol 47:37–43
Shiozawa T (1984) Report for the study on siltation problems in Chendering Fishing Port. Colombo Plan Report to Jabatan Kerja Raya, pp 73
Stanley Consultants, Inc. (1986) National coastal erosion study. Phase ii. Feasibility studies-unit perancang Ekonomi, Jabatan Perdana Menteri, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, vol 1
Sunamura T, Horikawa K (1972) Improved for infering the direction of littoral drift from grain-size properties of beach sands. In: Annual report of the engineering Research Institute, Faculty of Engineering, Tokyo vol 31, pp 61–68
Taggart BE, Schwart MC (1988) Net shore-drift direction determination: a systematic approach. J Shoreline Manage 3:285–309
Acknowledgements
This research was conducted, using the funding from the Malaysia Ministry of Science under the Intensified Research for Priority Areas (IRPA) project number 55005. The authors wish to express their gratitude to the lab assistants of the KUSTEM Oceanography laboratory teams for their assistance throughout the sampling period. The authors wish to express their gratitude to Professor Dr. John K. Raj for his invaluable discussions and comments. The authors are also thankful to the staff of the Geology Department, University Malaya for their assistance in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaacob, R., Hussain, M.L. The relationship of sediment texture with coastal environments along the Kuala Terengganu Coast, Malaysia. Environ Geol 48, 639–645 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-1321-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-1321-3