Abstract
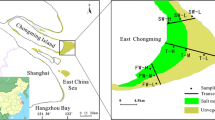
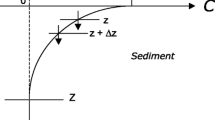
The influences of exposure to the atmosphere on ammonium cycle in the intertidal surface sediments were in situ studied with a geochemical approach at a typical station in the Yangtze Estuary during three tidal cycles in September 2003. During an about 8-h emersion period of each diurnal tide, six high-resolution vertical profiles of adsorbed and dissolved ammonium were measured. It was observed that both adsorbed and dissolved ammonium generally had an increasing trend in sediment cores during the exposure. The rate of ammonium regeneration in sediments was estimated using the accumulation amount of ammonium including adsorbed and soluble fractions during the daytime emersion. The calculation result showed that there was relatively high ammonification rate (˜500 nmol N cm−3 day−1), which reflected that organic nitrogen in sediments was quickly decomposed with a residence time of ˜52.7 days. Due to the dramatic temperature difference observed in sediment profiles, free convection was considered an important mechanism of regulating the efflux of produced ammonium into overlying waters. The total estimated amount of regenerated ammonium was ˜1.35×105 t N year−1 in the intertidal flat of the Yangtze Estuary, which occupied 7.6% of the total inorganic nitrogen annually transported to the estuarine ecosystem.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller RC, Yingst JY (1980) Relationships between microbial distribution and the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter in surface sediment of Long Island Sound. Mar Biol 56:29–42
Anderson FE, Howell BG (1984) Dewatering of an unvegetated muddy tidal flat during exposure—dessication or drainage? Estuaries 6:225–232
Andersen FO, Jensen HS (1992) Regeneration of inorganic phosphorus and nitrogen from decomposition of seston in a freshwater sediment. Hydrobiologia 228:71–81
Bartoli M, Cattadori M, Giordani G, Viaroli P (1996) Benthic oxygen respiration ammonium and phosphorus regeneration in surfacial sediments of the Sacca di Goro Northern Italy and two French coastal lagoons, a comparative study. Hydrobiologia 329:143–159
Berner RA (1980) Early diagenesis—a theoretical approach. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Blackburn TH (1979) Method for measuring rates of NH +4 turnover in anoxic marine sediments using 15N- NH +4 dilution technique. Appl Environ Microbiol 37(4):760–765
Blackburn TH, Henriksen K (1983) Nitrogen cycling in different types of sediments from Danish waters. Limnol Oceanogr 28:477–493
Blackburn TH, Nedwell DB, Biebe WJ (1994) Active mineral cycling in a Jamaican seagrass sediment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 110:233–239
Boatman CD, Murray JW (1982) Modelling exchangeable ammonium adsorption in marine sediments: process and controls of adsorption. Limnol Oceanogr 27:99–110
Bowden WB (1984) A nitrogen-15 isotope dilution study of ammonium production and consumption in a marsh sediment. Limnol Oceanogr 29:1004–1015
Chen JY (1988) The integrated investigation of Shanghai coastal and tidal resources. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai, China
Chen X, Zhong Y (1998) Coastal erosion along the Changjiang deltaic shoreline, China: history and prospective. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:733–742
De Jonge VN, Van Beusekom JEE (1995) Wind tide-induced resuspension of sediment and microphytobenthos from tidal flats of the Ems estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 40:766–778
Emerson S, Jahnke R, Heggie D (1984) Sediment–water exchange in shallow water estuarine sediments. J Mar Res 42:709–730
Han WY (1986) The investigation manual on chemical elements in seawater. China Ocean Press, Beijing
Hansen LS, Blackburn TH (1992) Effect of algal bloom deposition on sediment respiration rates and fluxes. Mar Biol 112:147–152
Herbert RA (1999) Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 23:563–590
Hou LJ, Liu M, Jiang HY, Xu SY, Ou DN, Liu QM, Zhang BL (2003) Ammonium adsorption by tidal sediments from the Yangtze Estuary. Environ Geol 45:72–78
Hou LJ, Liu M, Jiang HY, Xu SY, Ou DN, Lu JJ, Yu J, Cheng SB, Yang Y (2005) The effects of semi-lunar spring and neap tidal changes on nutrients cycling in the intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Environ Geol 48:255–264
Howes BL, Goehringer DD (1994) Pore water drainage and dissolved organic carbon and nutrient losses through the intertidal creekbanks of a New England Salt marsh. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 114:289–301
Howle L, Behringer RP, Georgiadis J (1993) Visualization of convective fluid flow in a porous medium. Nature 362:230–232
Huettel M, Gust G (1992) Solute release mechanisms from confined sediment cores in stirred benthic chambers and flume flows. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 82:187–197
Iizumi H, Hattori A, McRoy CP (1982) Ammonium regeneration and assimilation in eelgrass (Zostera marina) beds. Mar Biol 66:59–65
Kuwae T, Kibe E, Nakamura Y (2003) Effect of emersion and immersion on the porewater nutrient dynamics of an intertidal sandflat in Tokyo Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 57:929–940
Liu M, Hou LJ, Xu S, Ou DN, Zhang B (2001) Nitrogen and phosphorus diffusion fluxes across sediment–water interface in estuarine and coastal tidal flats. Mar Environ Sci 20:19–23
Liu M, Hou LJ, Xu S, Ou DN, Yang Y, Zhang B, Liu Q (2002) Adsorption of phosphate on tidal flat surface sediments from the Yangtze Estuary. Environ Geol 42:657–665
Lu JJ (1990) Wetlands in China. East China Normal University Press, Shanghai
Mackin JE, Aller RC (1984) Ammonium adsorption in marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 29:250–257
Milliman JD, Xie QC, Yang ZS (1984) Transport of particulate organic carbon and nitrogen from the Yangtze River to the ocean. Science 284:824–834
Milliman JD, Shen HT, Yang ZS, Meade RH (1985) Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent continental shelf. Cont Shelf Res 4:37–45
Musgrave DL, Reeburgh WS (1982) Density-driven interstitial water motion in sediments. Nature 299:331–334
Nielsen LP, Christensen PB, Revsbech NP, Soensen J (1990) Denitrification and oxygen respiration in biofilm studied with a microsensor for nitrous oxide and oxygen. Microb Ecol 19:63–72
Riedl RJ, Machan R (1972) Hydrodynamic patterns in intertidal sands and their bioclimatological implications. Mar Biol 13:179–209
Risgaard-Petersen NS, Rysgaard LP, Nielsen LP, Revsbech NP (1994) Diurnal variation of denitrification and nitrification in sediments colonized by benthic microphytes. Limnol Oceanogr 39:573–579
Rocha C (1998) Rhythmical ammonium regeneration and flushing in intertidal sediments of the Sado estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 43:823–831
Rocha C, Madureira MJ, Caetano M (1995) Role of microorganisms in mineralization processes in intertidal sediments subject to high temperature: an incubation experiment. Neth J Aquat Ecol 29(3–4):257–263
Rosenfeld JK (1979) Ammonium adsorption in nearshore anoxic sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 24:356–364
Rosenfeld JK (1981) Nitrogen diagenesis in Long Island Sound sediments. Science 281:436–462
Seitzinger SP (1988) Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystem: ecological and geochemical significance. Limnol Oceanogr 33:702–724
Shen ZL (2001a) The main factors controlling inorganic nitrogen in the Yangtze Estuary. Oceanol Limnol Sin 32:465–473
Shen ZL (2001b) The biogeochemical study on nitrogen in the Yangtze Estuary—the main sources for inorganic nitrogen. Mar Sci 25:56
Sumi T, Koike I (1990) Estimation of ammonification and ammonium assimilation in surficial coastal and estuarine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 35:270–286
Sundbäck K, Miles A, Hulth S, Pihl L, Engström P, Selander E, Svenson A (2003) Importance of benthic nutrient regeneration during initiation of macroalgal blooms in shallows bays. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 246:115–126
Van Der Loeff R (1981) Wave effects on sediment water exchange in a submerged sand bed. Neth J Sea Res 15:100–112
Vouvé F, Guiraud G, Mariol C, Girard M, Richard P, Laima MJC (2000) NH +4 turnover in intertidal sediment of Marennes-Oléron bay (France): effect of sediment temperature. Oceanol Acta 23:575–584
Walsh JJ (1991). Importance of continental margins in the marine biogeochemical cycling of carbon and nitrogen. Nature 350:53–55
Webster IT, Norquay SJ, Ross FC, Wooding RA (1996) Solute exchange by convection within estuarine sediments. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 42:171–183
Yu XZ, Lu JJ (2001) Influence of diking on the benthic macro-invertebrate community structure and diversity in the south bank of the Changjiang Estuary. Acta Ecol Sin 21:1642–1647
Zhang J, Yu ZG, Liu SM, Xu H, Wen QB, Shao B, Chen JF (1997) Dominance of terrigenous particulate organic carbon in the high-turbidity Shuangtaizihe Estuary. Chem Geol 138:211–219
Acknowledgements
This research is part of the project of the biogeochemical cycling of multi-materials in the Yangtze estuarine and coastal complex ecosystem supported by the National Natural Science Key Foundation of China (Nos. 40131020 and 49801018), Tidal Flat Project by Science & Technology Committee of Shanghai (No. 04DZ12049), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2005037135) and Shanghai Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 04R214122). The anonymous reviewers are thanked for their constructive comments on a preliminary draft of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, L., Liu, M., Lu, J. et al. Ammonium regeneration in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze estuary during air-exposure. Environ Geol 49, 937–945 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-0125-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-0125-9