Abstract
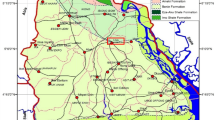
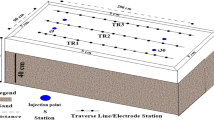
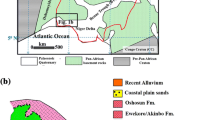
Electrical imaging (resistivity tomography) is increasingly used as a geophysical exploration technique in contaminated land research. The present work demonstrates the efficiency of electrical imaging in monitoring pollution plume evolution under both in-situ and model conditions. The in-situ campaign was done at an unlined landfill site situated in the city of Patras, Hellas. A partially saturated zone of alluvial fan deposits underlies the site, which retards leachate percolation to the underlying water table. Electrical imaging provided details of the internal structure of the waste tip, and confirmed the presence of a leachate plume beneath the base of the landfill. This field data component provided the constraints for the design of a generic model of contaminant infiltration into partially saturated sand. The aim was to study leachate plume evolution in a laboratory environment. For this purpose, a miniaturised resistivity tomography technique, developed at Cardiff University, was used to image the resistivity distribution before during and after contaminant infiltration. Comparison of resulting two-dimensional tomography with observed plume geometry at the end of the test showed the miniaturised electrical imaging technique to be highly effective. Experiment showed that contaminant evolution taking place in the model was gravity-driven, with capillary water in the vadose zone being displaced by the denser contaminant solution.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker RD (1997) Electrical imaging and its application in engineering investigations. Modern Geophysics in Engineering Geology. Geological Society Engineering Geology. Published by the British Geogolical Society, Special Publication N.12:37–43
Depountis N, Harris C, Koukis G (1998a) Assessment of leachate plume dispersal at an old unlined landfill site: a case study. In: Proceedings of the 8th IAEG congress, Vancouver, Canada, September 1998. Balkema Rotterdam, ISBN 90 5410 990 4, pp 2329–2334
Depountis N, Harris C, Koukis G (1998b) Engineering geological conditions and hydrogeological setting at Riganokmapos landfill site, Achaia county, Greece. In: Proceedings of the 8th international congress, Patras, Greece, May 1998. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece, vol XXXII/4, pp 159–166
Depountis N, Harris C, Davies MCR (1999) The application of miniaturised electrical imaging in scaled centrifuge modelling of pollution plume migration. In: Proceedings of the 2nd BGS international geoenvironemental engineering conference, London, UK, September 1999. Thomas Telford, ISBN 0 7227 2840 7, pp 214–221
Griffiths DH, Barker RD (1993) Two-dimensional resistivity imaging and modelling in areas of complex geology. J Appl Geophys 29:211–226
Koukis G, Depountis N (1995) Geotechnical and hydrogeological research at the old waste tip of the city of Patras in Riganokampos area. Special report, Municipality of Patras, Hellas
Loke MH, Barker RD (1995) Least-squares deconvolution of apparent resistivity pseudosections. Geophysics 60:1682–1690
Loke MH, Barker RD (1996) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys Prospect 44:131–152
Rozos DE (1991) Engineering geological conditions in Achaia province. Geomechanical characteristics of the Plio-Pleistocene sediments. PhD Thesis, University of Patras, Hellas
Acknowledgements
This research was sponsored by NECER (Network of European Centrifuges for Environmental Research). This support is gratefully acknowledged. Dr. Depountis also acknowledges the continuous support of the Greek State Scholarships Foundation (SSF), which provided the funds for his training.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Depountis, N., Harris, C., Davies, M.C.R. et al. Application of electrical imaging to leachate plume evolution studies under in-situ and model conditions. Environ Geol 47, 907–914 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1219-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1219-5