Abstract
Jordan is part of the arid and semi-arid region of the Middle East, where water resources are known to be scarce. Thorough planning is inevitable and must be applied wisely, especially as it is known that drought conditions were evidenced for many years in Jordan.
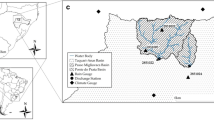
Surface water average accounts for 693 MCM/year out of which 359 MCM/year is base flow and 334 MCM/year flood flow. Therefore, management of surface water has been given great attention in Jordan because of the overexploitation of groundwater resources. Hydrological simulation models interfaced with Geographical Information Systems (GIS) were examined in this study. GIS interfaced hydrological models were considered as a major tool for surface water management at a watershed scale because they are capable of presenting the relationship between the spatial and hydrological features of the watershed in an efficient way. This study aimed at exploring the advantages of using GIS-based hydrological models as a water management tool to study the largest river basin in Jordan namely, the Zarqa River basin.
In this study, the Spatial Water Budget Model (SWBM) and HEC-HMS / HEC-GeoHMS extension model were used. The models were calibrated and validated based on King Talal Reservoir inflow for a period of eight years. The calibration was performed for the most sensitive parameters. The calibration for the two models was performed for the years 1979, 1980, 1981 and 1982. Satisfactory results were obtained for both models with an R2 of 0.90 and 0.85 for the HEC-HMS and SWBM model, respectively. Validation for the models was performed using the years 1993, 1994, 1995 and 1996, and the results were satisfactory with an R2 of 0.75 and 0.80 for the SWBM and HEC-HMS model, respectively. Models after their calibration and verification can then be used to test scenarios related to climate change and/or land-use change at the watershed scale.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad AA (1989) Jordan environmental profile status and abatement. Deposited No. 424/7/1989 1- Environmental – Amman, Jordan
Beven KJ (2001) Rainfall-runoff Modelling: The primer. Wiley, New York, 360 pp
Bosch DD, Bingner RL, Theurer FD, Felton G (1998) Evaluation of the AnnAGNPS water quality model. ASAE, MI. No. 98–2195
Harza Engineering Company and Arabtech Consulting Engineers (1989) Storage facilities in the Jordan Valley, Amman, Jordan, pp 306
Hydrocomp Inc (1996) Hydrologic Journal. http://www.hydrocomp.com
Loague K, Corwin DL (2000) Regional-scale assessment of non-point source groundwater contamination. In: Gurnell AM, DR Montgomery (eds) Hydrological applications of GIS. Wiley, New York, 176 pp
Luijten JC (1999) A tool for community based water resources management in hillside watersheds. University of Florida, 176 pp
MMRAE (Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs and Environment) (1991) National environment strategy of Jordan. Resources book of information and guidelines for action, pp 305–324
MWI (1989) The North Jordan Water Resources investigation project staff (Amman Zarqa Basin): water resources study, 234 pp
MWI (2002) Ministry of Water and Irrigation, Annual Report, Amman, Jordan
UND Agrar-GMBH Hydrotechnik (Consulting Engineers, Essen Germany) (1983) Zarqa River Basin project: feasibility study (lower Zarqa River catchments area), pp 154–162
World Bank (1997) The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, Water Sector Review, 23 pp
Acknowledgements
The research on which this paper was based was part of the MSc thesis of the third author. This research was also funded by the Higher Council for Science and Technology, Jordan. The authors want to thank the anonymous reviewers for their reading of this manuscript, and for their suggestions and valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Abed, N., Abdulla, F. & Abu Khyarah, A. GIS-hydrological models for managing water resources in the Zarqa River basin. Env Geol 47, 405–411 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1165-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1165-2