Abstract
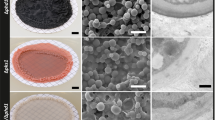
Microbial biofilms are ubiquitous in aquatic and terrestric ecosystems as well as on man-made material. They are initial colonizers on all surfaces and take part in biogenic weathering on natural rocks as well as on building stone. The structure and function of the biofilm matrix, mainly extracellular polysaccharides (EP), is documented for biofilms on stone surfaces: the hydrated gel acts as glue between the organisms and the material surface. Besides EP, living cells, cell debris and mineral particles are embedded in the matrix. These particles appear to be deposited on the surfaces of cell walls and interfaces in the biofilm matrix. As an important function of the matrix, EP stabilizes the biological activity against periodic desiccation. It was demonstrated that in several polymers (alginate, dextran, levan and others) a typical extracellular enzyme, the alpha-amylase, develops enhanced resistance against desiccation stress. Consequences of EP production and biofilm development on surfaces are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albeck S, Weiner S, Addadi L (1996) Polysaccharides of intracrystalline glycoproteins modulate calcite crystal growth in vitro. Chem Eur J 2:278–284
Beveridge TJ, Makin SA, Kadurugamuwa JL, Li Z (1997) Interactions between biofilms and the environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev 20:291–303
Booth G (1997) Gecko: a continuous 2-D world for ecological modeling. Artificial Life J 3:147–163
Brandes D (1992) Flora und Vegetation von Stadtmauern. Tuexenia 12:315–339
Delieu T, Walker DA (1972) Improved cathode for measurement of photosynthetic oxygen evolution by isolated chloroplasts. New Phytol 71:201–225
Douglas S, Beveridge TJ (1998) Mineral formation by bacteria in natural microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26:79–88
Gillooly JF, Brown JH, West GB, Savage VM, Charnov EL (2001) Effects of size and temperature on metabolic rate. Science 293:2248–2251
Gross M, Rudolph K (1987) Studies on the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) produced in vitro by Pseudomonas phaseolicola. 1. Indications for a polysaccharide resembling alginic acid in 7 Pseudomonas syringae pathovars. J Phytopathol 118:276–287
Hoppert M (2003) Microscopic techniques in biotechnology, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Hoppert M, Holzenburg A (1998) Electron microscopy in microbiology. RMS Handbook Series No. 43, Bios Scientific, Oxford
Hoppert M, Berker R, Flies C, Kämper M, Pohl W, Schneider J, Ströbel S (2002) Biofilms and their extracellular environment on geomaterials: methods for investigation down to nanometre scale. Geol Soc of London, Spec Publ 205, pp 207–215
Kreft J-U, Booth G, Wimpenny JWT (1998) BacSim, a simulator for individual-based modelling of bacterial colony growth. Microbiology 144:3275–3287
Kreft J-U, Piciorenau C, Wimpenny JWT, van Losdrecht MCM (2001) Individual-based modelling of biofilms. Microbiology 147:2897–2912
Labuza TP (1975) Interpretation of sorption data in relation to the state of constituent water. In: Duckworth R (ed) Water relations of foods. Academic Press, New York, pp 155–172
Mansch R, Bock E (1998) Biodeterioration of natural stone with special reference to nitrifying bacteria. Biodegradation 9:47–52
Raha M, Kawagishi I, Müller V, Kihara M, Macnab RM (1992) Escherichia coli produces a cytoplasmic alpha-amylase, Amy A. J Bacteriol 174:6644–6652
Schulze-Lam S, Fortin, D, Davis BS, Beveridge TJ (1996) Mineralization of bacterial surfaces. Chem Geol 132:171–181
Warscheid T (1996a) Biogene Schäden an Werkstoffen—Erkennung und Analyse im REM und in der Lichtmikroskopie. In: Vetters H. (ed) DVM-Manuskript zur 17. Tagung des Arbeitskreises Rastermikroskopie in der Materialprüfung. Berlin, pp 229–236
Warscheid T (1996b) Impacts of microbial biofilms in the deterioration of inorganic building materials and their relevance for conservation practice. Int Zeitschr Bauinstandsetzung 2:493–504
Warscheid T, Braams J (2000) Biodeterioration of stones—a review. Int Biodeterioration Biodegradation 46:343–368
Wingender J, Strathmann M, Rode A, Leis A, Flemming HC (2001) Isolation and biochemical characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Meth Enzymol 336:302–314
Acknowledgements
This work has been partially supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 471).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue: Stone decay hazards
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kemmling, A., Kämper, M., Flies, C. et al. Biofilms and extracellular matrices on geomaterials. Env Geol 46, 429–435 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1044-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1044-x