Abstract
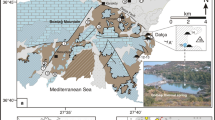
Pamukkale thermal waters (35 °C), exhibiting calcium-bicarbonate-sulfate composition and high carbon dioxide concentration, are of a predominantly meteoric origin. The meteoric fluid, circulating through faults and fractures, is heated by magmatic intrusions at great depth, and ascends from deep reservoirs to the surface. Mixing with relatively cold groundwater in the near surface zone promotes different saturation conditions with respect to calcium carbonate that later precipitates at depth and/or the surface. Dissolution-deposition processes of calcium carbonate both at surface and depth environments may help to reconstruct past climate direction in the field. During wet climate conditions a high-rate of calcium carbonate accumulation would be expected to occur at the surface because thermal fluid would be under-saturated with respect to calcium carbonate at depth because of a relatively higher mixing ratio with cold groundwater. During dry climate conditions the thermal fluid would be super-saturated at depth because of the highly acidic environment. Hydrometeorological studies reveal that the annual precipitation at the Pamukkale hydrothermal field tends to decrease with time. This climatic change in the area was also detected from geological records. While humid climate conditions prevailed during the late Quaternary, the area has recently been affected by arid/semi-arid climate conditions, followed by some episodic transitions. This study has shown how the system has possibly reacted to different climate conditions since antiquity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altunel E (1994) Active tectonics and the evolution of Quaternary travertines at Pamukkale, Western Turkey. PhD Thesis, Department of Geology, University of Bristol, UK (unpublished)
Altunel E, Hancock PL (1993) Morphology and structural setting of Quaternary travertines at Pamukkale, Turkey. Geol J 28:335–346
Altunel E, Hancock PL (1996) Structural attributes of travertine-filled extensional fissures in the Pamukkale plateau, western Turkey. Int Geol Rev 38:768–777
Appelo CAJ (1988) Groundwater chemistry. IHE Lecture notes, Delft
Bjornsson A, Axelsson G, Flovenz OG (1990) The nature of hot springs in Iceland. Natturufraedingurinn 60:15–38 (with English abstract)
Bolognesi L (2000) Earthquake-induced variations in the composition of the water in the geothermal reservoir at Vulcano Island, Italy. J Volcanol Geoth Res 99:139–150
Capasso G, Inguaggiato S (1998) A simple method for the determination of dissolved gases in natural waters: An application to thermal waters from Vulcano Island. Appl Geochem 13(5):631–642
Cohen HA, Dart CJ, Akyuz HS, Barka, AA (1995) Syn-rift sedimentation and structural development of Gediz and Buyuk Menderes grabens, western Turkey. J Geol Soc London 152:629–638
COHMAP Members (1988) Climatic changes of the last 18,000 years: observations and model simulations. Science 241:1043–1052
Denizli Governorship, Ministry of Culture, UNESCO (1992) Pamukkale (Hierapolis) preservation and development plan, and the international workshop on Pamukkale. June 30–July 3 1991, Pamukkale, Denizli
Dramis F, Materazzi M, Cilla G (1999) Influence of climatic changes on freshwater travertine deposition: a new hypothesis. Phys Chem Earth (A) 24(10):893–897
Drever JI (1997) The geochemistry of natural waters, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Dreybrodt W (1988) Processes in karst systems: physics, chemistry and geology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Engin B, Guven O (1997) Thermoluminescence dating of Denizli travertines from the southwestern part of Turkey. Appl Radiat Isotopes 48(9):1257–1264
Engin B, Guven O, Koksal F (1999) Electron spin resonance age determination of a travertine sample from the southwestern part of Turkey. Appl Radiat Isotopes 51:689–69
Engin K, Guclu U, Uz Z (1967) A catalog of earthquakes for Turkey and surrounding areas (11 ad to 1964 ad). Istanbul Tech Univ, Faculty of Mining Eng, Istanbul
Favara R, Grassa F, Inguaggiato S, Valenza M (2001) Hydrogeochemistry and stable isotopes of thermal springs: earthquake-related chemical changes along Belice Fault (western Sicily). Appl Geochem 16:1–17
Fournier RO (1989) Geochemistry and dynamics of the Yellowstone national park hydrothermal system. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 17:13–53
Giggenbach WF (1988) Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2749–2765
Grasby SE, Hutcheon I, Krouse HR (2000) The influence of water-rock interaction on the chemistry of thermal springs in western Canada. Appl Geochem 15:439–454
Grun R (1989) Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dating. Quat Int 1:65–109
Gulec N, Hilton DR, Mutlu H (2002) Helium isotope variations in Turkey: relationship to tectonics, volcanism and recent seismic activities. Chem Geol 187:129–142
Gunay G, Simsek S, Ekmekci M, Elhatip H, Yesertener C, Dilsiz C, Cetiner Z (1997) Karst hydrogeology and environmental impacts of Pamukkale thermal springs. In: Gunay G, Johnson AI (eds) Karst waters and environmental impacts, Balkemia, Rotterdam, pp 29–35
Hem JD (1970) Study and interpretation of chemical characteristics of natural waters, 2nd edn. Geological Survey Water, United States Department of the Interior
Kehew AE (2001) Applied chemical hydrogeology. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Leng M, Eastwood W, Roberts N (2001) Environmental change in the Mediterranean. NERC News, Spring Issue, pp 10–11
Mercado A, Billings GU (1975) The kinetics of mineral dissolution in carbonate aquifers as a tool for hydrological investigations, I: Concentration-time relationships. J Hydrol 24:303–331
Ozler HM (2000) Hydrogeology and hydrochemistry in the Curuksu (Denizli) hydrothermal field, western Turkey. Environ Geol 39(10):1169–1180
Ozpinar Y (1994) Tectonism of Denizli geothermal field. In: Ozpinar Y (ed) Geothermal Applications Symposium’94, Pamukkale University, Denizli, pp 114–129
Panichi C, Tongiorgi E (1975) Carbon isotopic composition of CO2 from springs, fumaroles, moffetes and travertines of Central—Southern Italy: a preliminary prospection method of geothermal area. Proc Second United Nations Symp on the Development and Use of Geothermal Resources, San Francisco, pp 815–825
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (VERSION 2) – A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. USGS, Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259
Pentecost A (1995) The Quaternary travertine deposits of Europe and Asia minor. Quat Sci Rev 14:1005–1028
Seyitoglu G, Scott BC (1992) The age of Buyuk Menderes graben (west Turkey) and its tectonic implications. Geol Mag 129:239–242
Seyitoglu G, Scott BC, Rundle CC (1992) Timing of Cenozoic extensional tectonics in west Turkey. J Geol Soc London 149:533–553
Smart PL (1991) Uranium series dating. In: Smart PL, Frances PD (eds) Quaternary dating methods, a user’s guide. Quaternary Research Association, Technical guide 4, pp 45–83
Soysal H, Sipahioglu S, Kocak D, Altinok Y (1981) Historical earthquake catalog of Turkey and its environment (2100 bc to 1900 ad). The Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey, Ankara
Trudgill S (1985) Limestone geomorphology. Longman, Harlow
UKAM (1994) Report on conservation and development of Pamukkale travertines, Phase I Final Report. Hacettepe University, Ankara
UKAM (1995) Report on conservation and development of Pamukkale travertines, Phase II Final Report. Hacettepe University, Ankara
UKAM (1996) Report on conservation and development of Pamukkale travertines, Phase III Final Report. Hacettepe University, Ankara
Yilmaz Y, Genc SC, Gurer F, Bozcu M, Yilmaz K, Karacik Z, Altunkaynak S, Elmas A (2000) When did the eastern Anatolian grabens begin to develop? In: Bozkurt E, Winchester JA, Piper JDA (eds) Tectonics and magmatism in Turkey and the surrounding area. Geol Soc London, Spec Publ 173:383–384
Westaway R (1993) Neogene evolution of the Denizli region of western Turkey. J Struct Geol 15(1):37–53
Vengosh A, Helvaci C, Karamanderesi IH (2002) Geochemical constraints for the origin of thermal waters from western Turkey. Appl Geochem 17:163–183
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to give special thanks to Prof. Dr. Nilgun Gulec (Middle East Technical University, Geological Department, Ankara-TR) for her helpful comments on regional tectonism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dilsiz, C., Marques, J.M. & Carreira, P.M.M. The impact of hydrological changes on travertine deposits related to thermal springs in the Pamukkale area (SW Turkey). Env Geol 45, 808–817 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0941-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0941-8