Abstract
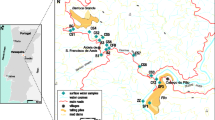
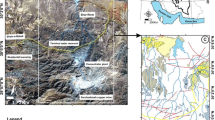
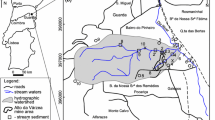
This study was conducted to determine the effects of the waste-rock dump (WRD) of the underground polymetallic Balya Mine on the Kocacay River and eventually on Lake Manyas in Turkey. Data presented in this paper include geochemical characteristics of various kinds of water (mine, surface and groundwater) and of suspended-particle samples in the vicinity of Balya. The more polluted mine waters have low pH and high conductivity, while high concentrations of Zn, Cd, Mn tend to be found in the dry and wet seasons. High concentrations of Pb, As, Cr, Cu and S appear only in the wet season. The sources of the heavy metal concentration within the Kocacay River are leached waste, surface run off, and overflow from the spillway of the WRD. To minimize the formation of acids and dissolved metal, and for the remediation of the harmful effects of extreme contamination conditions, it is recommended that lime or alkali materials and organic carbon be added to simulate the action of sulfate-reducing bacteria.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agdemir N, Kirikoglu S, Lehmann B, Tietze J (1994) Petrology and alteration geochemistry of the epithermal Balya Pb-Zn-Ag deposits, NW Turkey. Miner Deposita 29:366–371
Arizona Department of Environmental Quality (ADEQ) (1992) Human health-based guidance levels for the ingestion of contaminants in drinking water and soil. ADEQ, Phoenix, Arizona
Arizona Department of Environmental Quality (ADEQ) (1995) Arizona Administrative Code (AAC)—water quality boundaries and standards. ADEQ, Phoenix, Arizona, Title 18, Chapter 11, pp 1–39
Akyol Z (1982) Geology, mineralogy and ore potential of the Balikesir-Balya region (in Turkish). Earth Sci Rev 3(1–2):168–169
Aygen T (1956) Geology of Balya region (in Turkish). Bull Miner Res Expl Inst Turkey D/11
Aykol A, Orgun Y, Budakoglu M, Turhan M, Gultekin AH, Yavuz F, Esenli V, Kumral M (2002) Heavy metal pollution in Kocadere River Balya Balikesir, Turkey (in Turkish). 55th Geological Congress of Turkey, pp 30–31
Banks D, Younger PL, Arnesen RT, Iversen ER, Banks SB (1997) Mine water chemistry: the good, the bad and the ugly. Environ Geol 32:157–173
Benvenuti M, Mascaro I, Corsini F, Lattanzi P, Parrini P, Tanelli G (1995) Mine waste dumps and heavy metal pollution in abandoned mining district of Boccheggiano southern Tuscany, Italy. Environ Geol 30:238–243
Boulet MP, Larocque ACL (1998) A comparative mineralogical and geochemical study of sulfide mine tailings at two sites in New Mexico, USA. Environ Geol 33:130–142
Campos V (2002) The effect of carbon steel wool in removal of arsenic from drinking water. Environ Geol 42:81–82
Castro JM, Moore JN (2000) Pit lakes: their characteristics and the potential for their remediation. Environ Geol 39:1254–1260
Gjelsvik T (1958) Notes on the geology of Balya Mine. Bull Miner Res Expl Inst Turkey 51:19–25
Hart BT, Hines T (1995) Trace elements in rivers. In: Salbu B, Steinnes E (eds) Trace elements in natural waters. CRC, Boca Raton
Kovenko V (1940) Balya lead mines (Turkey). Bull Miner Res Expl Inst Turkey 4/21:587–594
Kwong YTJ, Roots CF, Roach P, Kettley W (1997) Post-mine metal transport and attenuation in the Keno Hill mining district, central Yukon, Canada. Environ Geol 30:98–107
Lee CH, Lee HK, Lee JC (2000) Hydrogeochemistry of mine, surface and groundwaters from the Sanggok Mine creek in upper Chungju Lake, Republic of Korea. Environ Geol 40:482–494
Ledin M, Pedersen K (1996) The environmental impact of mine wastes—roles of microorganisms and their significance in treatment of mine wastes. Earth Sci Rev 41:67–108
Lottermoser BG, Ashley PM, Lawie DC (1999) Environmental geochemistry of the Gulf Creek copper mine area, northeastern New South Wales, Australia. Environ Geol 39:61–74
Marques MJ, Martinez-Conde E, Rovira JV (2001) Heavy metals pollution of aquatic ecosystems in the vicinity of a recently closed underground lead-zinc mine (Basque Country, Spain). Environ Geol 40:1125–1137
Merrington G, Alloway BJ (1994) The transfer and fate of Cd, Cu and Zn from two historic metalliferous mine sites in the UK. Appl Geochem 9:677–687
Matheron G (1982) Image analysis and mathematical morphology, vol 1. Academic Press, London
Nordstrom DK, Alpers CN (1997) Geochemistry of acid mine waters. In: Plumlee GS, Logsdon MJ (eds) The environmental geochemistry of mineral deposits, Part A. Processes, techniques, and health issues, vol 7A. Soc Econ Geol, Littleton, Colorado, pp 1–28
Parsons MB, Bird DK, Einaudi MT, Alpers CN (2001) Geochemical and mineralogical controls on trace element release from the Penn Mine base-metal slag dump, California. Appl Geochem 16:1567–1593
Routh J, Ikramuddin M (1996) Trace-element geochemistry of Onion Creek near Van Stone lead-zinc mine (Washington, USA). Chemical analysis and geochemical modeling. Chem Geol 133:221–224
Rösner U (1998) Effects of historical mining activities on surface water and groundwater—an example from northwest Arizona. Environ Geol 33:224–230
Schafer WM (1992) Acid-forming mine waste: prediction, control, and treatment. Randol Gold Forum 1992,Vancouver, BC Randol International, Golden, CO, pp 345–353
Tate RL III (1995) Soil microbiology. Wiley, New York
Tuttle JH, Randles CI, Dugan PR (1968) Activity of microorganisms in acid mine water. Influence of acid water on aerobic heterotrophs of a normal stream. J Bacteriol 95:1495–1503
US Environmental Protection Agency (1998) Water quality standards, code of federal regulations, Title 40, Part 131, Section 36 (b)(2)(7-1-98 edition)
WHO guidelines for drinking water quality (1996) vol 2, 2nd edn. Health criteria and other supporting information, pp 940–949
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aykol, A., Budakoglu, M., Kumral, M. et al. Heavy metal pollution and acid drainage from the abandoned Balya Pb-Zn sulfide Mine, NW Anatolia,Turkey. Env Geol 45, 198–208 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0866-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0866-2