Abstract
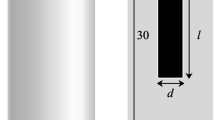
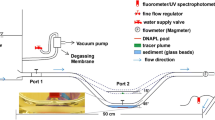
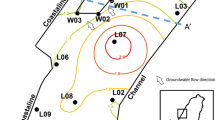
A three-dimensional numerical flow and contaminant transport model is developed to investigate the effect of variable hydraulic conductivity on average mass transfer coefficients associated with the dissolution of dense nonaqueous phase liquid (DNAPL) pools in heterogeneous, water-saturated subsurface formations. Randomly generated, three-dimensional hydraulic conductivity fields are used to represent a heterogeneous confined aquifer. Model simulations indicate that the average mass transfer coefficient is inversely proportional to the variance of the log-transformed hydraulic conductivity. A power law correlation relating the Sherwood number to the variance of the log-transformed hydraulic conductivity and appropriate Peclet numbers is developed. A reasonable fit between predicted and numerically determined mass transfer coefficients is observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, .W., Vogler, .E. & Chrysikopoulos, .C. Nonaqueous liquid pool dissolution in three-dimensional heterogeneous subsurface formations. Env Geol 43, 968–977 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0721-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0721-x