Abstract.
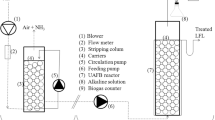
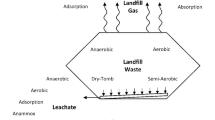
Air extraction and injection were evaluated for extracting hazardous landfill gas and enhancing degradation of organic materials in a landfill in Korea. From the pilot and full-scale tests, the following results were obtained. The pressure radii of influence varies with direction (anisotropy). A smaller oxygen radius of influence compared with the pressure radius of influence was observed in the landfill where the oxygen consumption rate was relatively high. This was in contrast to a petroleum-contaminated site, where the oxygen radius of influence was estimated to be larger than the pressure radius of influence. The increase in the pressure radius of influence was relatively small compared with the increase in air injection rate. When air was injected at a flow rate of 1 pore volume, the air temperature inside the landfill material increased by up to 20 °C because of a calorific reaction. It was also observed that the air-extraction system recovered landfill gas (LFG), and also enhanced aerobic degradation of landfill materials. Methane oxidation occurred during the continuous air injection, which was supported by a decrease in the CH4/CO2 ratio. Oxygen consumption rate for the air injection was larger than that for the LFG extraction. Furthermore, the intermittent air injection appeared less effective in landfill stabilization than the continuous injection when they are applied to an active younger landfill with larger oxygen consumption rates, whereas the reverse is the case when applied to an aged landfill.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, .J., Lee, .C. & Lee, .K. Evaluation of air injection and extraction tests in a landfill site in Korea: implications for landfill management. Env Geol 42, 945–954 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0599-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0599-7